
- Discussion Forum
- Why and How: Using the Case Study Method in the Law Classroom

Post by: Jackie Kim and Lisa Brem
Why should legal educators use case studies and other experiential teaching methods, such as role plays and simulations, in their classes? Hasn’t the Langdell method served legal education well these last 140 years? Certainly creating and using experiential materials requires a different set of skills from faculty, elicits a different response and level of engagement from students, and poses barriers to implementation. The ABA’s LEAPS Project [i] has a comprehensive list of objections to practical problem solving in the classroom: materials are time consuming and expensive to create and deploy; addition of a case study or simulation to a syllabus inherently displaces other material; and there are few incentives from law school leaders to introduce this type of teaching.
Yet, the argument promoting experiential materials and techniques is strong. The 2007 Carnegie Report [ii] recommended integrating lawyering skills practice into the curriculum alongside doctrinal courses, and the ABA added simulation courses to the list of practical experiences that can and should be offered by law schools in its 2015 Guidance Memo [iii] .
In a 2007 Vanderbilt Law Review article [iv] , HLS Dean Martha Minow and Professor Todd D. Rakoff argued that Langdell’s approach to teaching students using appellate cases does not do enough to prepare law students for real-world problems: “The fact is, Langdell’s case method is good for some things, but not good for others. We are not talking about fancy goals here; we are talking about teaching students ‘how to think like a lawyer.’”
But does the case study method result in a higher degree of student learning? While we have not yet seen a study on the efficacy of the case study method vs. the Langdell method in law schools, research [v] from political science professor Matthew Krain suggests that case studies and problem-based activities do enhance certain types of learning over other types of pedagogy. In his investigation, Krain compared the results of pre-and post-course surveys of students who participated in active learning with those who received a traditional lecture course. The case studies and problems that Krain used in his non-traditional classes included: case studies in the form of popular press articles, formal case studies, films, or problem-based case exercises that required students to produce a work product.
Krain found that:
Student-centered reflection, in which students have the opportunity to discuss their understanding of the case, allows both students and instructors to connect active learning experiences back to a larger theoretical context. Case learning is particularly useful for dramatizing abstract theoretical concepts, making seemingly distant events or issues seem more “authentic” or “real,” demonstrating the connection between theory and practice, and building critical-thinking and problem-solving skills (Inoue & Krain, 2014; Krain, 2010; Kuzma & Haney, 2001; Lamy, 2007; Swimelar, 2013).
This study suggests that case-based approaches have great utility in the classroom, and they should be used more often in instances where students’ understanding of conceptual complexity or knowledge of case details is critical. Moreover, case-based exercises can be derived from a variety of different types of materials and still have great utility. If deployed selectively in the context of a more traditional classroom setting as ways to achieve particular educational objectives, case-based approaches can be useful tools in our pedagogical toolbox.
For those who might be ready to try a case study, role play, or simulation, there are resources that can help. Harvard Law School produces case studies for use throughout the legal curriculum. The HLS Case Studies program publishes these teaching materials, and makes them available to educators, academic staff, students, and trainers. Outside of Harvard Law School, links to resources for educators implementing the case study method can be found on the Case Studies Program Resources page. Listed are case study affiliates at Harvard, legal teaching and learning tools, tips for case teaching, and free case materials. Examples include the Legal Education, ADR, and Practical Problem Solving (LEAPS) Project [vi] from the American Bar Association , which provides resources for various topics on legal education, and the Teaching Post , an educators’ forum offered by the Harvard Business School where professors can seek or provide advice on case study teaching.
“… [O]ur society is full of new problems demanding new solutions, and less so than in the past are lawyers inventing those solutions. We think we can, and ought to, do better.” – Dean Martha Minow & Professor Todd Rakoff. [vii]
[i] “Overcoming Barriers to Teaching ‘Practical Problem-Solving’.” Legal Education, ADR & Practical Problem-Solving (LEAPS) Project, American Bar Association, Section of Dispute Resolution. Accessed March 16, 2017, http://leaps.uoregon.edu/content/overcoming-barriers-teaching-%E2%80%9Cpractical-problem-solving%E2%80%9D. [ii] William M. Sullivan, Anne Colby, Judith Welch Wegner, Lloyd Bond, and Lee S. Shulman, “Educating Lawyers,” The Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching (2007). [iii] American Bar Association, “Managing Director’s Guidance Memo,” Section of Legal Education and Admissions to the Bar (2015). [iv] Martha Minow and Todd D. Rakoff, “A Case for Another Case Method,” Vanderbilt Law Review 60(2) (2007): 597-607. [v] Matthew Krain, “Putting the learning in case learning? The effects of case-based approaches on student knowledge, attitudes, and engagement,” Journal on Excellence in College Teaching 27(2) (2016): 131-153. [vi] “Overcoming Barriers to Teaching ‘Practical Problem-Solving’.” [vii] Minow and Rakoff.

Share this:
About Lisa Brem
- Search for:
Subscribe to Blog via Email
Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive weekly notifications of new posts by email.
Email Address
Follow HLS Case Studies
Subscribe to our newsletter
Subscribe to our RSS feed
- Et Seq., The Harvard Law School Library Blog
- Harvard Negotiation and Mediation Clinical Program
- HLS Berkman Center for Internet and Society
- HLS Forum on Corporate Governance and Financial Regulation
- HLS Program on the Legal Profession
- Program on Negotiation
Recent Posts
- Worker Centers & OUR Walmart: Case studies on the changing face of labor in the United States
- Robbing the Piggy Bank? Moving from mutual to stock form at Friendly Savings Bank
- The Argument for Active Learning
- Spotlight on: International and Comparative Law
- Fair Use Week: 5 Questions with Kyle Courtney
Top Posts & Pages
- Reforming Partner Compensation at Mattos Filho
- Too Many Cooks in the FDA Kitchen?
- Keys to Facilitating Successful Student Group Work
- Case Development Initiative Blog Posts
- Case Study Program Blog Posts
- Experiential Learning and the Case Study Method
- Harvard Negotiation and Mediation Clinical Program Blog Posts
- Legal News and Debate
- Problem Solving Workshop Blog Posts
- Program on International Law and Armed Conflict Blog Posts
- Uncategorized
Any opinions expressed herein do not necessarily reflect those of Harvard University.
Product names, logos, brands, and other trademarks featured or referred to within this manuscript are the property of their respective trademark holders. These trademark holders are not affiliated with the author or any of the author's representatives. They do not sponsor or endorse the contents and materials discussed in this blog.
Outside images are used under a Creative Commons license, and do not suggest the licensor's endorsement or affiliation.
Comments are encouraged. Blog administrators will use their discretion to remove any inappropriate, uncivil, slanderous, or spam comments.
Email the site administrator at [email protected]

Library electronic resources outage May 29th and 30th
Between 9:00 PM EST on Saturday, May 29th and 9:00 PM EST on Sunday, May 30th users will not be able to access resources through the Law Library’s Catalog, the Law Library’s Database List, the Law Library’s Frequently Used Databases List, or the Law Library’s Research Guides. Users can still access databases that require an individual user account (ex. Westlaw, LexisNexis, and Bloomberg Law), or databases listed on the Main Library’s A-Z Database List.
- Georgetown Law Library
- Research Process
Case Law Research Guide
Introduction.
- Print Case Reporters
- Online Resources for Cases
- Finding Cases: Digests, Headnotes, and Key Numbers
- Finding Cases: Terms & Connectors Searching
Key to Icons
- Georgetown only
- On Bloomberg
- More Info (hover)
- Preeminent Treatise
Every law student and practicing attorney must be able to find, read, analyze, and interpret case law. Under the common law principles of stare decisis, a court must follow the decisions in previous cases on the same legal topic. Therefore, finding cases is essential to finding out what the law is on a particular issue.
This guide will show you how to read a case citation and will set out the sources, both print and online, for finding cases. This guide also covers how to use digests, headnotes, and key numbers to find case law, as well as how to find cases through terms and connectors searching.
To find cases using secondary sources, such as legal encyclopedias or legal treatises, see our Secondary Sources Research Guide . For additional strategies to find cases, like using statutory annotations or citators, see our Case Law Research Tutorial . Our tutorial also covers how to update cases using citators (Lexis’ Shepard’s tool and Westlaw’s KeyCite).
Basic Case Citation
A case citation is a reference to where a case (also called a decision or an opinion ) is printed in a book. The citation can also be used to retrieve cases from Westlaw and Lexis . A case citation consists of a volume number, an abbreviation of the title of the book or other item, and a page number.
The precise format of a case citation depends on a number of factors, including the jurisdiction, court, and type of case. You should review the rest of this section on citing cases (and the relevant rules in The Bluebook ) before trying to format a case citation for the first time. See our Bluebook Guide for more information.
The basic format of a case citation is as follows:

Parallel Citations
When the same case is printed in different books, citations to more than one book may be given. These additional citations are known as parallel citations .
Example: 265 U.S. 274, 68 L. Ed. 1016, 44 S. Ct. 565.
This means that the case you would find at page 565 of volume 44 of the Supreme Court Reporter (published by West) will be the same case you find on page 1016 of volume 68 of Lawyers' Edition (published by Lexis), and both will be the same as the opinion you find in the official government version, United States Reports . Although the text of the opinion will be identical, the added editorial material will differ with each publisher.
Williams Library Reference

Reference Desk : Atrium, 2nd (Main) Floor (202) 662-9140 Request a Research Consultation
Case law research tutorial.

Update History
Revised 4/22 (CMC) Updated 10/22 (MK) Links 07/2023 (VL)
- Next: Print Case Reporters >>
- © Georgetown University Law Library. These guides may be used for educational purposes, as long as proper credit is given. These guides may not be sold. Any comments, suggestions, or requests to republish or adapt a guide should be submitted using the Research Guides Comments form . Proper credit includes the statement: Written by, or adapted from, Georgetown Law Library (current as of .....).
- Last Updated: Feb 29, 2024 1:03 PM
- URL: https://guides.ll.georgetown.edu/cases
Primary tabs
Case law is law that is based on judicial decisions rather than law based on constitutions , statutes , or regulations . Case law concerns unique disputes resolved by courts using the concrete facts of a case. By contrast, statutes and regulations are written abstractly.
Case law, also used interchangeably with common law , refers to the collection of precedents and authority set by previous judicial decisions on a particular issue or topic. In that sense, case law differs from one jurisdiction to another. For example, a case in New York would not be decided using case law from California. Instead, New York courts will analyze the issue relying on binding precedent . If no previous decisions on the issue exist, New York courts might look at precedents from a different jurisdiction, that would be persuasive authority rather than binding authority. Other factors such as how old the decision is and the closeness to the facts will affect the authority of a specific case in common law.
Federalism also plays a major role in determining the authority of case law in a particular court. Indeed, each circuit has its own set of binding case law. As a result, a judgment rendered in the Ninth Circuit will not be binding in the Second Circuit but will have persuasive authority. However, decisions rendered by the Supreme Court of the United States are binding on all federal courts, and on state courts regarding issues of the Constitution and federal law.
[Last updated in May of 2020 by the Wex Definitions Team ]
- ACADEMIC TOPICS
- legal history
- THE LEGAL PROCESS
- criminal procedure
- judicial administration
- legal practice/ethics
- statutory interpretation
- civil procedure
- legal theory
- wex definitions

leiden lawmethods portal
Case study research.
Last update: April 07, 2022
A legal scholar who uses the term ‘case’ will probably first think of a legal case. From a socio-legal perspective, the understanding of this concept is, however, slightly different. Case study research is a methodology that is useful to study ‘how’ or ‘why’ questions in real-life.
Over the last forty years, researchers from sociology, anthropology and various other disciplines have developed the case study research methodology dramatically. This can be confusing for legal researchers. Luckily, both Webley and Argyrou have written an article on case study research specifically for legal researchers. Webley writes, for example, that this methodology allows us to know ‘how laws are understood, and how and why they are applied and misapplied, subverted, complied with or rejected’. Both authors rely upon the realist tradition of case study research as theorised by Yin. Yin defines the scope of a case study as: “An empirical inquiry that investigates a contemporary phenomenon in depth and within its real-life context, when the boundaries between phenomenon and context are not clearly evident”.
Before you start collecting data for your case study, it is important to think about the theory and the concepts that you will want to use, as this will very much determine what your case will be about and will help you in the analysis of your data. You should then decide which methods of data collection and sources you will consult to generate a rich spectrum of data. Observations, legal guidelines, press articles… can be useful. Legal case study researchers usually also rely extensively on interviews. The meaning that interview participants give to their experiences with legal systems can uncover the influence of socio-economic factors on the law, legal processes and legal institutions.
Case studies strive for generalisable theories that go beyond the setting for the specific case that has been studied. The in-depth understanding that we gain from one case, might help to also say something about other cases in other contexts but with similar dynamics at stake. However, you need to be careful to not generalize your findings across populations or universes.
Argyrou, A. (2017) Making the Case for Case Studies in Empirical Legal Research. Utrecht Law Review, Vol.13 (3), pp.95-113
Flyvbjerg, B. (2006.) Five Misunderstandings about Case-Study Research, Qualitative Inquiry 12( 2), 219-245.
Gerring, J. (2004) What Is a Case Study and What Is It Good for? American Political Science Review 98( 2), 341-354.
Simons, H. (2014) Case Study Research: In-Depth Understanding in Context. In P. Leavy (Ed.), The Oxford Handbook of Qualitative Research, Oxford University Press.
Webley, L. (2016) Stumbling Blocks in Empirical Legal Research: Case Study Research. Law and Method, 10.
Yin, R. K. (2009). Case study research: Design and methods (4th Ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
- --> Login or Sign Up

About Harvard Law Case Studies
Case studies at harvard law school.
"[In 2004], Harvard Law School embarked on a major curricular review aimed at determining what changes might help us to prepare our students even more effectively for the complex global challenges of this new millennium."
--Supreme Court Justice and former HLS Dean Elena Kagan, 2007
One of the major initiatives that came out of this review was the Problem Solving Workshop, a required first-year program aimed at practical lawyering skills. View this short video about the Problem-Solving Workshop:
Harvard’s curricular review in 2004 challenged the accepted way of teaching law. In 2007, HLS Dean Martha Minow and Professor Todd Rakoff published these findings, "A Case for Another Case Method," in the Vanderbilt Law Review.
The Langdellian case method , which focused on "a retrospective view of facts," was falling short in teaching critical problem solving skills. What law school needed, according to Minow and Rakoff, was a new way to simulate “legal imagination.”
Minow and Rakoff wrote: "What [students] most crucially lack ... is the ability to generate the multiple characterizations, multiple versions, multiple pathways, and multiple solutions, to which they could apply their very well-honed analytic skills."
To that end, Harvard Law School instituted the Problem Solving Workshop, a required first-year course that teaches problem solving skills through the case study method . The Problem Solving Workshop encourages the use of case studies throughout the HLS curriculum.
Now, several faculty initiatives produce case studies at Harvard Law School.
The Case Development Initiative
The Case Development Initiative creates case studies for J.D. and Executive Education classes. HLS faculty use case studies to teach a variety of legal topics, including career dilemmas that lawyers face and management issues that law firms and professional service firms experience. These case studies expose participants to real-world problems that lawyers and firm leaders confront, and help them work through possible approaches and solutions. CDI was founded by Professor Ashish Nanda and is now directed by Dr. Lisa Rohrer.
Great for: discussion-based case studies, law and business, management , professional development
Sample Teaching Units: Professional Development for In-House Counsel , Professional Development for Law Firms , Leadership
Additional Information: The Case Development Initiative at Harvard Law School
Harvard Negotiation and Mediation Clinical Program
The Harvard Negotiation and Mediation Clinical Program , directed by Professor Robert Bordone , developed several role plays for an advanced negotiation workshop at HLS. The course, Multiparty Negotiation, Group Decision Making, and Teams , enables students to participate in and conduct complex, multiparty negotiations. "Lawyers and other professionals, irrespective of their specialty, find themselves party to negotiations with multiple (more than two) principals all the time," explains Bordone. "This course combines theory and practice to give students an opportunity to hone their skills in multiparty settings." Students work in teams to address complex, global, and professional issues. The advanced workshop integrates intellectual and experiential learning by combining readings, lectures, and discussions with frequent exercises, extensive review, live and filmed examples, individual and small group reviews, and analysis of the negotiation process and the process of learning from experience.
Great for: role plays, multiparty negotiation, DVDs , mediation
Sample Teaching Units: Critical Decisions in Negotiation
Program on Negotiation
Program on Negotiation materials use real events or fictionalized versions of events to teach negotiation and mediation theory, issues, and practice. These materials can take the form of a discussion exercise, a role playing game, a dilemma-based case study, or a factual account of a negotiation event. Events and historical contexts, such as the rise of organized labor in the United States, the conflict between Catholics and Protestants in Northern Ireland, and the history of Zionists and Arabs in the Middle East, catalyze discussion and debate on negotiation and dispute resolution.
Great for: role plays, historical case studies, negotiation, value-based conflict resolution, water rights and environmental management, examples of Great Negotiators
Sample Teaching Units: Mediating Value-Based Conflict
Problem Solving Workshop
Problem Solving Workshop materials immerse students in the type of real-world problems faced every day by practicing lawyers. The case studies present the problem at hand and provide readings on related theory, excerpts of relevant law, and other illustrative documents, such as contracts and leases. Students complete team assignments and exercises that include tasks such as drafting a press release as general counsel of a toy company in trouble; determining, as an associate at a law firm, the possible actions open to a client facing a harassment change from a tenant; or deciding, as a new Assistant U.S. Attorney in New York, whether—and how—to charge someone with Section 8 housing fraud. Professors Todd Rakoff and Joseph Singer lead the PSW teaching group, which develops new materials yearly.
Great for: workshop-based case studies , 1Ls, J.D. programs, lawyering, problem solving , free materials
Sample Teaching Units: Problem Solving Workshop , Advanced Problem Solving Workshop: Cyberlaw, Intellectual Property, and Internet & Society
Additional Information: Information Law and Policy: Advanced Problem Solving Workshop
Case Studies Program
The Case Studies Program supports additional HLS faculty in developing case studies.
Great for: discussion-based case studies
Sample Teaching Units: Decision Making and Leadership in the Public Sector
Next: The Case Study Teaching Method >>
Recently viewed courses
Recently viewed.
Find Your Dream School
This site uses various technologies, as described in our Privacy Policy, for personalization, measuring website use/performance, and targeted advertising, which may include storing and sharing information about your site visit with third parties. By continuing to use this website you consent to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use .
COVID-19 Update: To help students through this crisis, The Princeton Review will continue our "Enroll with Confidence" refund policies. For full details, please click here.
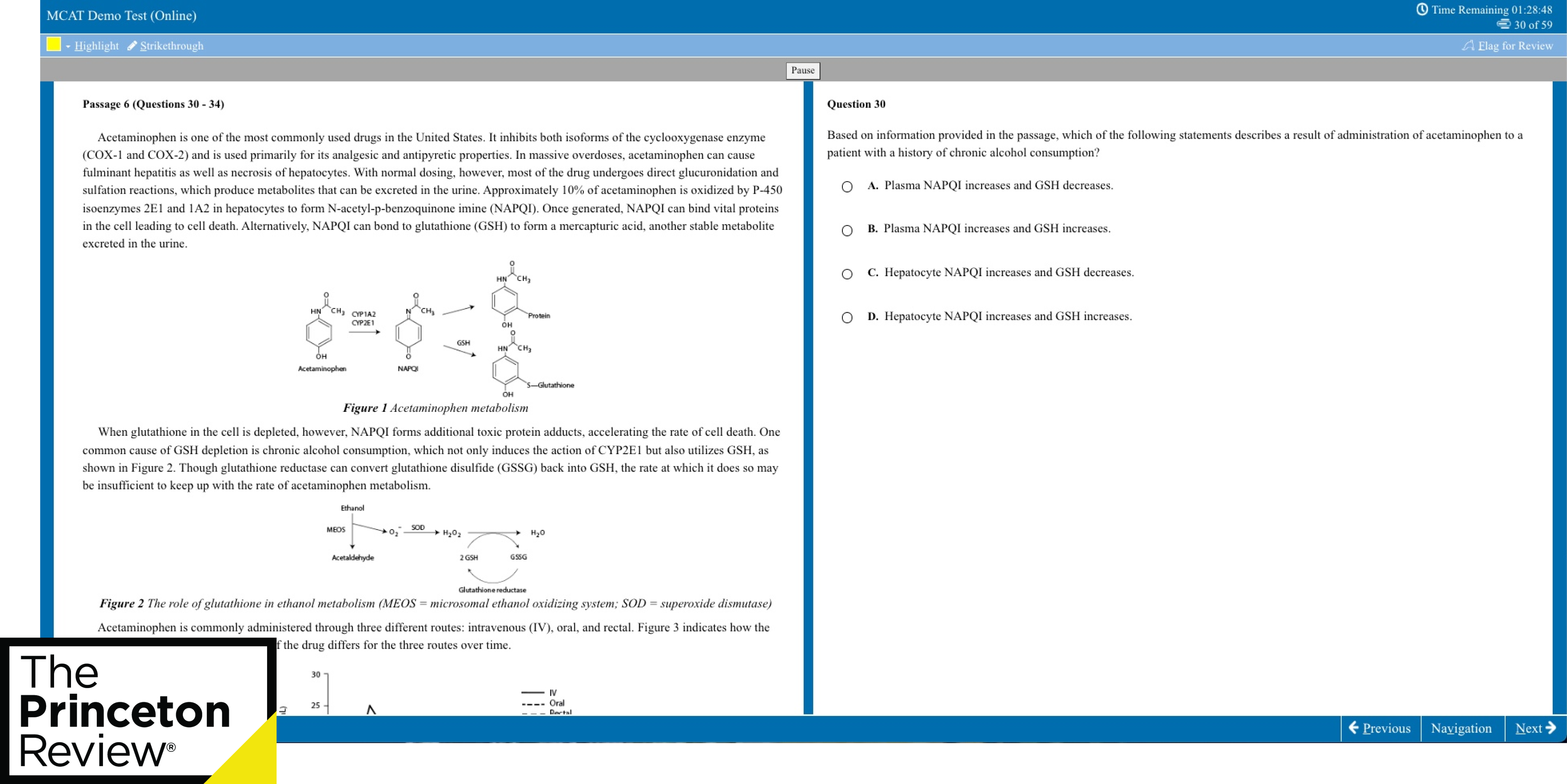
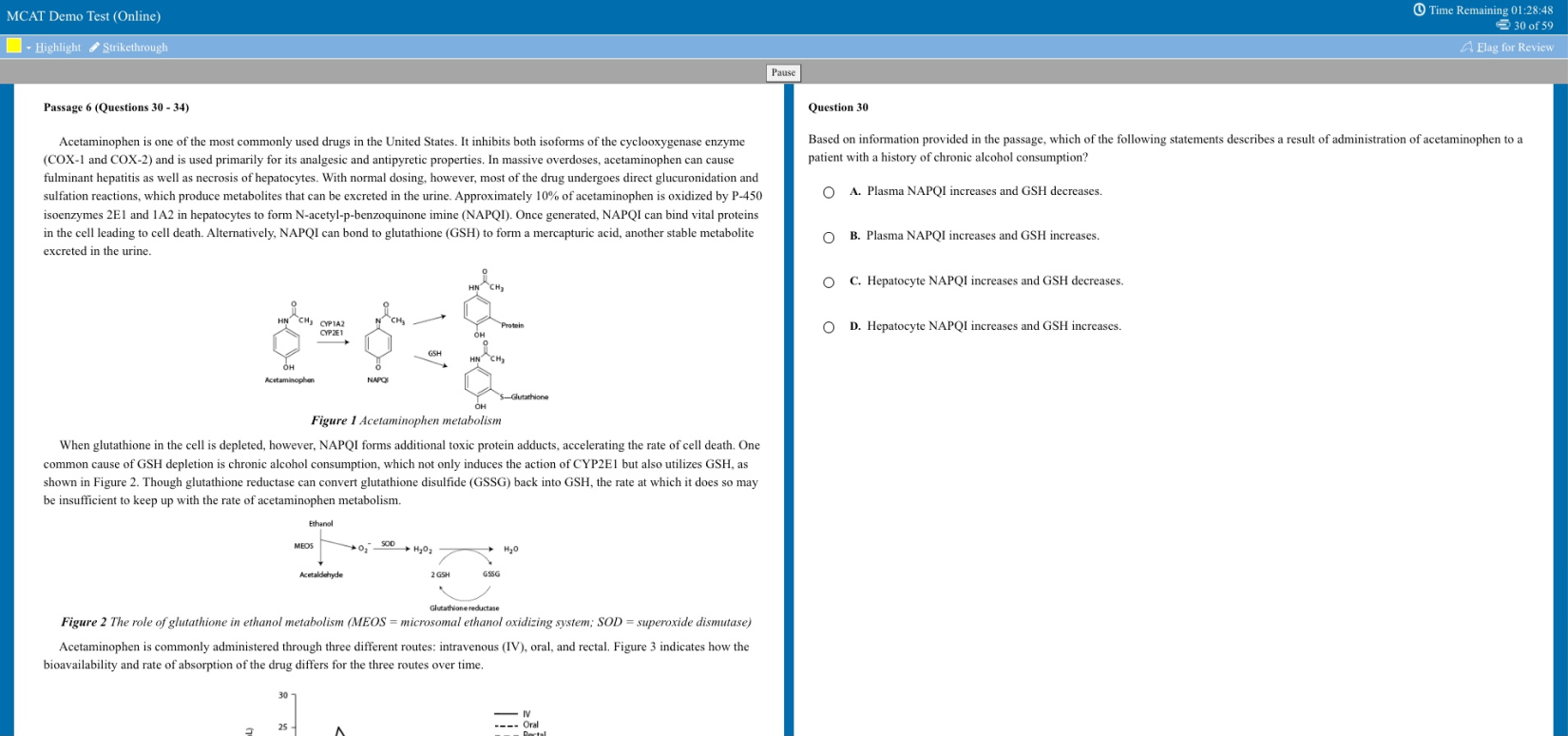
The Law School Case Method

In the majority of your law school courses, and probably in all of your first-year classes, your only texts will be casebooks—collections of written judicial decisions in actual court cases.
The case method eschews explanation and encourages exploration. In a course that relies entirely on the casebook, you will never come across a printed list of "laws."
Indeed, you will learn that in many areas of law there is no such thing as a static set of rules, but only a constantly evolving system of principles. You are expected to understand the law—in all of its ambiguity—through a critical examination of a series of cases that were decided according to such principles. You may feel lost, groping for answers to unarticulated questions. This is not merely normal, it is intended.
How the Case Method Works
In practical terms, the case method works like this: For every class meeting, you will be assigned a number of cases to read. The cases are the written judicial opinions rendered in court cases that were decided at the appellate level. (The reason for reading cases from courts of appeals or supreme courts is that such cases turn on issues of law, not of fact. If you are charged, tried, and convicted of murder and wish to appeal your case, you do not simply get a whole new trial at a higher level. You must argue that your conviction was improper, not that it was inaccurate.)
Your casebook will contain neither instructions nor explanations. Your assignments simply will be to read the cases and be in a position to answer questions based on them. There will be no written homework assignments, just cases, cases, and more cases.
You will write, for your own benefit, briefs of these cases. Briefs are your attempts to summarize the issues and laws around which a particular case revolves and to make sense of the court's findings in terms of similar cases. One way or another, your law school probably will tell you how to brief a case. If there's an optional seminar, you really ought to attend. In the event that you are left in the dark, it's utterly imperative that you find out how to brief a case. Google it. Ask a second year. Unless you are insanely brilliant, good briefing is really a key to getting good grades. Over the course of a semester, you will try to integrate the content of your case-briefs and your notes from in-class lectures, discussions, or dialogues into some kind of cohesive whole.
From Briefs to Outlines
Typically, you will take your copious briefs and class-notes and create an outline from which you will study for your final exams. Since almost all of your grade for a particular course will rest on your performance on the final, it is essential to establish a system that will allow you to recall the case appropriate for a given legal circumstance within an exam period.
This is especially true since most of your exams will be open book. Once you've see your case-books, you'll understand why having them on the day of the test will not be particularly helpful. Unless, of course, you have your outline handy. Outlines, whether you write your own, create them in a study group, or buy the commercial variety, will be an intrinsic part of this system. Don't neglect them. Your academic success rests on it.

Explore Graduate Programs for You
Explore our featured graduate schools & programs to find those that both match your interests and are looking for students like you.

Best Online JD Programs
Online JD programs offer flexibility, affordability, access to innovative technologies, students from a diversity of career backgrounds, and global opportunities.

Best Online MSL Programs
Master of Studies in Law (MSL) programs are for non-lawyers whose careers in their organizations will benefit from legal training even though they are not required to be practicing attorneys.

Find MBA Programs Matched to Your Interests
Explore our featured business schools to find those that are looking for students like you.
Free MCAT Practice Test
I already know my score.
MCAT Self-Paced 14-Day Free Trial
Enrollment Advisor
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 1
1-877-LEARN-30
Mon-Fri 9AM-10PM ET
Sat-Sun 9AM-8PM ET
Student Support
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 2
Mon-Fri 9AM-9PM ET
Sat-Sun 8:30AM-5PM ET
Partnerships
- Teach or Tutor for Us
College Readiness
International
Advertising
Affiliate/Other
- Enrollment Terms & Conditions
- Accessibility
- Cigna Medical Transparency in Coverage
Register Book
Local Offices: Mon-Fri 9AM-6PM
- SAT Subject Tests
Academic Subjects
- Social Studies
Find the Right College
- College Rankings
- College Advice
- Applying to College
- Financial Aid
School & District Partnerships
- Professional Development
- Advice Articles
- Private Tutoring
- Mobile Apps
- Local Offices
- International Offices
- Work for Us
- Affiliate Program
- Partner with Us
- Advertise with Us
- International Partnerships
- Our Guarantees
- Accessibility – Canada
Privacy Policy | CA Privacy Notice | Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information | Your Opt-Out Rights | Terms of Use | Site Map
©2024 TPR Education IP Holdings, LLC. All Rights Reserved. The Princeton Review is not affiliated with Princeton University
TPR Education, LLC (doing business as “The Princeton Review”) is controlled by Primavera Holdings Limited, a firm owned by Chinese nationals with a principal place of business in Hong Kong, China.
Northern Illinois University College of Law David C. Shapiro Memorial Law Library
- University Libraries
- David C. Shapiro Memorial Law Library
Basic Legal Research
- Commonly Used Legal Terminology
- Welcome to Basic Legal Research!
Legal Dictionaries
Legal terminology: general terms, legal terminology: case law, legal terminology: codes, statutes & administrative law.
- Court Systems & Legal Authority
- Fact Pattern Analysis
- Secondary Legal Sources
- Understanding Case Citations
- Case Law Reporters
- Using Digests to Find Case Law
- Statutes & Codes
- Illinois Administrative Materials
- Federal Administrative Materials
- Terms and Connectors Searching
- Creating/Determining the "Best" Online Search
- Integrating Print & Online Resources
- Updating Your Research Using Shepard's & KeyCite
- Illinois Legislative History
- Federal Legislative History
- Appendix: Illinois Materials
- Appendix: Sample Bluebook Citations
- Appendix: Study Aids
Need more help? Contact us!

- Law library faculty & staff directory
- Schedule an online appointment with a Reference Librarian (Limited to College of Law students, faculty and staff)
- Law library home page
- The Law Library has several print legal dictionaries available. One of the most frequently used is Black's Law Dictionary , 10th ed. (copies on Reserve and located elsewhere in the library)
- The major legal databases ( Bloomberg , Lexis Advance , Westlaw ) have online legal dictionaries (login required to access)
- Law.com has a free online legal dictionary at http://dictionary.law.com/
- Words and Phrases is a useful source similar to a dictionary. It provides judicial definitions of legal and non-legal terms. Information is compiled from headnotes containing judicial definitions. It is useful for discovering if any court, or a specific court, has ever defined a term or phrase. The Law Library's print copy (KF 156 .W57) is no longer updated as of 2015, but an up-to-date online version is available on Westlaw .
Analogize: To take the facts, rationale or argument of a written decision and explain how the argument relates to your case/issue.
Citation: A reference to a legal precedent or authority (primary or secondary) such as a case, statute or treatise. Case citation: The alpha numeric identifier provided to enable researchers to locate written decisions. The format usually consists of a volume number, the abbreviated reporter name, and a page or paragraph number. (e.g. 268 N.E.2d 1247)
Citators: A tool used in legal research to update legal authorities by listing their subsequent history and treatment. Also provide additional research references to primary and secondary resources citing your original document.
Civil Law: The body of law imposed by the state; the law of civil or private rights; a civil law system relies on codes that provide explicit rules of a situation. A judge's decision in a civil law system does not become binding or form a precedent. Many European countries are civil law countries.
Constitution: A type of primary authority that is a set of principles that a country or state is governed by. Constitutions generally establish the branches of government, the scope of powers for each branch, and a set of guaranteed civil rights and civil liberties.
Criminal Law: The body of law defining offenses against the community at large, regulating how suspects are investigated, charged and tried, and establishing punishment for convicted offenders.
Court Rules: Rules that control the operation of the courts and the conduct of the litigants appearing before the court.
Distinguishing an Authority: Taking the facts, rationale or arguments of a written decision or other primary authority and showing the differences between that authority and your case, even if on the surface they seem similar.
Federal Jurisdiction: A federal court's power to hear matters. Under this type of jurisdiction federal courts may decide a question of civil and/or criminal federal law.
Index: An alphabetical listing of items (topics or names) available in the resource along with an indication of where each item may be found within the work. This finding tool is available in both print and electronic resources.
Hypothetical: Discussion of a legal principle based on a fictitious or assumed set of facts.
Mandatory (Binding) Authority: A primary legal authority that is binding on a court. Jurisdiction and court level determine whether a primary legal authority is mandatory or persuasive.
Moot Court: A fictitious court held, usually in law schools, to argue hypothetical cases, especially at the appellate level.
Persuasive Authority: A primary or secondary authority. The legal authority is not binding on a court, but the court may still rely on the authority when making its determination. Jurisdiction and court level determine whether a primary legal authority is persuasive or mandatory/binding. Secondary authority is always only persuasive.
Pinpoint Citation: The page on which a quotation or relevant passage appears, as opposed to
the page on which a case or article begins.
Procedural Law: Rules that describe the steps for having a right or duty judicially enforced,
as opposed to the law that defines the specific rights and duties themselves.
Primary Legal Authority: Authority that issues directly from a lawmaking body such as constitutions, legislation, regulations, and the reports of litigated cases (court opinions) among others.
Relevance: Relation or pertinence to the issue at hand.
Relief: The compensation (monetary or other- e.g., injunction) or benefit that a party asks of another party, sometimes received through settlement and other times received through the courts.
Secondary Legal Authority: Authority that explains the law but does not itself establish the law, such as a treatise, annotation, or law review article among others.
State Jurisdiction: A state court's power to hear matters. Under this type of jurisdiction state courts may decide a question of civil and/or criminal state law.
Socratic Method: A technique of law school instruction, whereby a professor questions one or more students, building on each answer with another question.
Substantive Law: The part of the law that creates, defines and regulates the rights, duties and powers of parties.
Table of Contents: Usually located at the beginning of the work, it provides a list of chapters/sections within the work, often in outline form, and the page numbers where the topics for each chapter/section begin. Some resources provide tables of contents for each chapter. Electronic resources provide them through a separate link. This finding tool is available in both print and electronic resources.
Uniform Laws: An unofficial law proposed as legislation for all the states to adopt exactly as written, the purpose being to promote greater consistency among the states.
Appeal: To seek review by a higher court. (e.g. appeal trial court decisions to the appropriate higher court; appeal appellate court decisions to the appropriate highest court.)
Appellant: One who brings the appeal of the lower court decision (the loser in the lower court).
Appellate Briefs: Written argument submitted to the appellate court in support of a position on appeal (not the same as a case brief).
Appellee: One against whom the appeal is brought and must respond to the appeal (the winner in the lower court). Also called respondent.
Case: Generally used in law to refer to the written decision of a court.
Case Law: All reported decisions within a jurisdiction. May consist of common law decisions as well as judicial decisions interpreting statutes, regulations, constitutions etc.
Case Reporters: Court opinions that are gathered together and published in chronological order. The books containing these cases are called case reporters. Even though most cases are available online, they are still organized and cited to according to the print reporter system. Cases are primary sources regardless of publication in an official or unofficial reporter, the case decision is the primary source. Case reporters can be official or unofficial.
- Official Reporter : The governmentally approved publication reproducing reported cases within a given jurisdiction. The official reporter is the reporter that should be cited when submitting documents to the court.
- Unofficial Reporter : Reporters published by commercial publishers (West, Lexis, BNA) in either print or online formats, reproducing the reported decisions within a given jurisdiction. Commercially published reporters are considered unofficial reporters.
Citator: A tool used in legal research to update legal authorities by listing their subsequent history and treatment. With case law, legal citators indicate when a case has been cited by a later case, and what effect, if any, the later citation had on the original case. The three main citators are Shepard's on Lexis, KeyCite on Westlaw and Bcite on Bloomberg Law.
Common Law: The body of judge-made law having no basis in statutes. NOTE: Case law that interprets a statue is NOT common law.
Common Law Tradition: The basis for the American legal system where courts create rules called common-law rules and those rules govern future cases in that particular area. For example, Tort cases are governed by common law rules.
Concurring Opinion: A separate written opinion explaining a vote cast by one or more judges in favor of the judgment reached, often on grounds different from those expressed in the opinion explaining the judgment.
Defendant: A person sued in a civil proceeding or accused in a criminal proceeding.
Dicta: A comment by a court that is unnecessary to a decision and therefore not precedential. There are several types of dicta in Black's. You do rely on judicial dictum, but dicta is actually short for obiter dictum. Judicial dictum is considered binding by courts while obiter dictum is not.
Digest: A case finding tool that organizes cases by subject. Within each subject digests provide summaries of cases that discuss the law on that subject. Digests allow you to find cases on a particular point of law in a particular jurisdiction. Online services also provide digests for particular topics.
Dissenting Opinion: An opinion by one or more judges who disagree with the decision reached by the majority.
Docket Number: Courts assign each newly filed action with a number. The number usually refrences the year the case was commenced followed by a series of numbers or letters that represent the type of action (civil, criminal, family court, etc.) or location of filing.
Federal Circuit Courts: The appellate court level in the federal court system. There are 13.
Federal District Courts: The trial court level in the federal court system. There are 94.
Headnote: A brief summary of a specific point of law decided in a case. Headnotes appear before the judicial opinion, and are generally written by a publisher's editors. Headnotes are a great research tool, but are not considered legal authority and should never be cited to.
Illinois Circuit Courts: The trial court level in the Illinois state court system. There are 24.
Illinois District Courts: The appellate court level in the Illinois state court system. There are 5.
Intermediate Appellate Courts: Appellate courts that are in the middle of the judicial hierarchy in a jurisdiction, they are above the trial court and below the highest court/court of last resort. Their opinions are binding on the courts below them (trial courts).
Judge: A public official appointed or elected to hear and decide legal matters in court.
Judiciary: The branch of government responsible for interpreting the laws and administering justice; a body of judges.
Justice: A judge, especially of an appellate court.
Litigation: The process of carrying on a lawsuit; the lawsuit itself.
Litigator: A lawyer who prepares cases for trial as by conducting discovery and pretrial motions, trying cases and handling appeals; a trial lawyer.
Litigant: A party to a lawsuit.
Majority Opinion: see Opinion.
Minority Opinion: see Opinion.
Official Reporter: see Case Reporter.
Opinion: The written decision of a court.
- Majority Opinion: An opinion joined in by more than half of the judges considering a given case.One judge writes the opinion when a majority of judges agree with the holding.
- Minority Opinion: An opinion by one or more judges who disagree with the decision reached by the majority - also called a dissenting opinion.
- Concurring Opinion: A judge who voted with the majority opinion, but writes separately because her reasoning is different.
- Dissenting Opinion: A judge who writes a separate opinion where the reasoning and the holding are different from the majority.
- Per Curiam Opinion : Literally "By the Court." This happens when the court issues a unanimous opinion, typically on a controversial topic, so that no single author can be identified.
Opinions, unpublished : An opin io n is considered publish ed unless it is specifically designated as "unpublished." The court typically designates an opinion as "unpublished" if it doesn't add anything new to the body of law. Courts have different rules about whether they will accept citations to unpublished opinions.
Parallel Citation: An additional reference to a case that has been reported in more than one reporter. Example: Morgan v. United States, 304 U.S. 1, 58 S. Ct. 773, 82 L. Ed. 1129 (1938), where 58 S. Ct. 773 and 82 L. Ed. 1129 are parallel citations to the decision cited in the official reporter at 304 U.S. 1 .
Petitioner: A party who presents a petition to a court or other official body, especially when seeking relief on appeal (where the Petitioner is the Appellant).
Plaintiff: The party who brings a civil suit in a court of law.
Precedent: A decided case that furnishes a basis for determining later cases involving similar facts or issues.
Reporter: see Case Reporters.
Respondent: The party against whom an appeal is taken (appellee); the party against whom a motion or petition is filed.
Slip Opinion : The opinion issued by the court as a stand-alone document on the day it is decided, before it has been assigned a volume and page number in the official reporter.
Star Pagination: A device, typically one or more asterisks (*), used in in cases online to designate differences in pagination of the case as it would appear in print in different reporters.
Stare Decisis: "To stand by things decided." An American legal system doctrine of precedent under which it is necessary for a court to follow earlier judicial decisions when the same points are again in litigation.
Supreme Court: This is the court of last resort, or the highest court in the judicial hierarchy. The opinions of a supreme court are binding on all the courts below it (Trial and Appellate). Note that some jurisdictions refer to the highest court as a Court of Appeals or Court of Last Resort, e.g., in New York State the Supreme Court is not the highest court in the state.
Syllabus/Synopsis: A summary of the case. It will usually describe the procedural posture (how the case made it to to the court) and the holding. It is not part of the official opinion.
Table of Authorities: The list of primary authorities (cases, statutes, regulations, or constitutions) and secondary authorities relied upon in the document you are viewing.
Topic & Key Number System : A proprietary system developed by West Publishing (now ThomsonReuters) to identify related cases on a similar issue. Each headnote in cases published by West will be assigned a corresponding topic and key number.
Trial Courts: Trial courts are at the bottom of the judicial hierarchy in a jurisdiction. They are usually persuasive primary authority. Trial court opinions bind only the parties involved in the case, other trial courts hearing similar cases are not bound by the opinions, and the appellate courts in the jurisdiction are not bound by the trial court opinions.
Code: The subject arrangement of the laws or regulations of a jurisdiction.
- Annotated Code: A publication of all the laws of a jurisdiction organized by subject matter which contains research references that include summaries of cases or citations to secondary sources that discuss that particular law. Annotated codes only contain select case law interpreting the statute, not every case ever citing the statute.
- Unannotated Code: A publication of all the laws of a jurisdiction organized by subject matter. No research references are included in unannotated codes.
Legislative History: The proceedings leading up to the enactment of a statute. This includes hearings, committee reports, and floor debates among other resources. Legislative history is recorded so that it can be used to interpret the statute at a later date. Legislative history records are available for federal statutes. Many states keep records of legislative history, but the extent of the record varies from state to state. Legislative history is considered a primary authority.
Regulation: In administrative law, a primary authority that stems from the executive branch. It is a directive issued by a government agency that implements and/or carries out a governmental policy or program. The directive must be within the agency's statutory authority.
Session Laws: A body of statutes enacted by a legislature during a particular annual or biennial session; the books containing these statutes. Maintained in public act or public law format.
Statute: A law passed by a legislative body. Often also called laws and codes.
- Federal Statute: Written laws passed by the United States Congress. Statutes are primary authority.
- State Statute: Written laws passed by the state legislature. Statutes are primary authority.
Statutes at Large: An official compilation of the acts and resolutions that become law from each session of the United States Congress. They are printed in chronological order.
Statutory Annotations: In statutory research, the term is used to refer to brief summaries of court decisions interpreting and applying statutes as well as summaries of secondary materials referencing the statutory section. These summaries appear in annotated statutory compilations, after the text of individual statutes. They are also referred to as research references.
- << Previous: Welcome to Basic Legal Research!
- Next: Court Systems & Legal Authority >>
- Last Updated: May 2, 2024 12:02 PM
- URL: https://libguides.niu.edu/basic-legal-research
© 2024 Board of Trustees of Northern Illinois University. All rights reserved.
Legal Dictionary
The Law Dictionary for Everyone
The term case law refers to law that comes from decisions made by judges in previous cases. Case law, also known as “ common law ,” and “case precedent ,” provides a common contextual background for certain legal concepts, and how they are applied in certain types of case. How much sway case law holds may vary by jurisdiction , and by the exact circumstances of the current case. To explore this concept, consider the following case law definition.
Definition of Case Law
- The law as established in previous court rulings; like common law, which springs from judicial decisions and tradition.
1860-1865 English common law
What is Case Law
Statutory laws are those created by legislative bodies, such as Congress at both the federal and state levels. While this type of law strives to shape our society, providing rules and guidelines, it would be impossible for any legislative body to anticipate all situations and legal issues. The court system is then tasked with interpreting the law when it is unclear how it applies to any given situation, often rendering judgments based on the intent of lawmakers and the circumstances of the case at hand. Such decisions become a guide for future similar cases.
In order to preserve a uniform enforcement of the laws, the legal system adheres to the doctrine of stare decisis , which is Latin for “stand by decided matters.” This means that a court will be bound to rule in accordance with a previously made ruling on the same type of case. Precedent, or case law, is binding on courts of the same level or lower, and applies only if there is no legislative statute created, or higher court ruling, that overrules it.
Example of Case Law Application
Stacy, a tenant in a duplex owned by Martin, filed a civil lawsuit against her landlord, claiming he had not given her enough notice before raising her rent, citing a new state law that requires a minimum of 90 days’ notice. Martin argues that the new law applies only to landlords of large multi-tenant properties. When the state court hearing the case reviews the law, he finds that, while it mentions large multi-tenant properties in some context, it is actually quite vague about whether the 90-day provision applies to all landlords. The judge , based on the specific circumstances of Stacy’s case, decides that all landlords are held to the 90-day notice requirement, and rules in Stacy’s favor.
A year later, Frank and Adel have a similar problem. When they sue their landlord, the court must use the previous court’s decision in applying the law. This example of case law refers to two cases heard in the state court, at the same level. The ruling of the first court created case law that must be followed by other courts until or unless either new law is created, or a higher court rules differently.
Case Law by Jurisdiction
Case law is specific to the jurisdiction in which it was rendered. For instance, a ruling in a California appellate court would not usually be used in deciding a case in Oklahoma. While there is no prohibition against referring to case law from a state other than the state in which the case is being heard, it holds little sway. Still, if there is no precedent in the home state, relevant case law from another state may be considered by the court.
Rulings made by federal appellate courts, and the U.S. Supreme Court, however, are binding on state courts. Such rulings become “binding precedent,” which must be adhered to by lower courts in future similar cases. Rulings by courts of “lateral jurisdiction” are not binding, but may be used as persuasive authority, which is to give substance to the party’s argument, or to guide the present court.
Case Law Search
Just a few years ago, searching for case precedent was a difficult and time consuming task, requiring people to search through print copies of case law, or to pay for access to commercial online databases. Today, the internet has opened up a host of case law search possibilities, and many sources offer free access to case law. Doing a case law search may be as easy as entering specific keywords or citation into a search engine. There are, however, certain websites that facilitate case law searches, including:
- Google Scholar – a vast database of state and federal case law, which is searchable by keyword, phrase, or citations. Google Scholar also allows searchers to specify which level of court cases to search, from federal, to specific states.
- Justia – a comprehensive resource for federal and state statutory laws , as well as case law at both the federal and state levels.
- Public Library of Law – offers access to cases from the U.S. Supreme court since 1754, the U.S. Circuit Courts of Appeal since 1951, and from each state since 1997. In addition to allowing users to search by keyword, court, and case, the website provides tutorials on “ Finding a Case ,” and “ Searching Statutes .”
In addition, the Law Library of Congress offers a great deal of information on statutes, case law, and other legal issues. This includes a Guide to Law Online .
Dissecting Case Law Citations
Finding a relevant case law ruling, and inserting a reference to that case into a current legal pleading , is not enough to direct the court to the specific issue. In many instances, court rulings in the U.S. deal with multiple issues, and include drawn-out descriptions of how the court, especially an appellate or supreme court, came to its conclusion. Because of this, simply citing the case is more likely to annoy a judge than help the party’s case. Think of it as calling someone to tell them you’ve found their lost phone, then telling them you live in such-and-such neighborhood, without actually giving them an address. Driving around the neighborhood trying to find their phone is likely to be more frustrating than it’s worth.
For legal professionals, there are specific rules regarding case citation, which vary depending on the court and jurisdiction hearing the case. Proper case law citation in a state court may not be appropriate, or even accepted, at the U.S. Supreme Court. Generally speaking, proper case citation includes the names of the parties to the original case, the court in which the case was heard, the date it was decided, and the book in which it is recorded. Different citation requirements may include italicized or underlined text, and certain specific abbreviations.
In the United States, people are not required to hire an attorney to represent them in either civil or criminal matters. Laypeople navigating the legal system on their own can remember one rule of thumb when it comes to referring to case law or precedent in court documents: be as specific as possible, leading the court, not only to the case, but to the section and paragraph containing the pertinent information. The Cornell Law School website offers a variety of information on legal topics, including citation of case law, and even provides a video tutorial on case citation .
Case Law Example in Civil Lawsuit Against Child Services
In 1996, the Nevada Division of Child and Family Services (“DCFS”) removed a 12-year old boy from his home to protect him from the horrible physical and sexual abuse he had suffered in his home, and to prevent him from abusing other children in the home. The boy was placed in an emergency foster home, and was later shifted around within the foster care system. The DCFS social worker in charge of the boy’s case had the boy made a ward of DCFS, and in her 6-month report to the court, the worker elaborated on the boy’s sexual abuse history, and stated that she planned to move him from a facility into a “more homelike setting.” The court approved her plan.
In 1997, the boy was placed into the home of John and Jane Roe as a foster child. Although the couple had two young children of their own at home, the social worker did not tell them about the boy’s history of both being abused, and abusing other children. When she made her report to the court the following day, the worker reported the boy’s placement in the Roe’s home, but didn’t mention that the couple had young children. She did note that the boy still needed extensive therapy in order to cope with his abusive past, and “to reach the point of being safe with other children.” The boy was receiving counseling with a DCFS therapist. Again, the court approved of the actions.
The Roes accompanied the boy to his therapy sessions. When they were told of the boy’s past, they asked if their children were safe with him in their home. The therapist assured them that they had nothing to worry about. Unfortunately, that was not true. Just two months after being placed with the Roe family, the Roe’s son told his parents that the boy had molested him. The boy was arrested two days later, and admitted to having sexually molested the couple’s son several times.
On June 16, 1999, a lawsuit was filed on behalf of the boy by a guardian ad litem , against DCFS, the social worker, and the therapist. A similar lawsuit was also filed on behalf of the Roe’s victimized son by a different guardian ad litem. The defendants petitioned the trial court for a dismissal based on absolute immunity , as they were all acting in their jobs with DCFS. If granted absolute immunity, the parties would not only be protected from liability in the matter, but could not be answerable in any way for their actions. When the court delayed making such a ruling, the defendants took their request to the appellate court.
In determining whether employees of DCFS are entitled to absolute immunity, which is generally held by certain government officials acting within the scope of their employment, the appellate court referred to case law previously rendered on similar cases. The appellate court determined that the trial court had not erred in its decision to allow more time for information to be gathered by the parties – specifically regarding the issue of absolute immunity.
Related Legal Terms and Issues
- Binding Precedent – A rule or principle established by a court, which other courts are obligated to follow.
- Lateral Jurisdiction – A court at the same level.
- Persuasive Authority – Prior court rulings that may be consulted in deciding a current case. It may be used to guide the court, but is not binding precedent.

- How to Prepare for Law School
- How to brief a case
- E-mail This Page
- Print This Page
How to write a case brief for law school: Excerpt reproduced from Introduction to the Study of Law: Cases and Materials ,
Third edition (lexisnexis 2009) by michael makdisi & john makdisi.
C. HOW TO BRIEF
The previous section described the parts of a case in order to make it easier to read and identify the pertinent information that you will use to create your briefs. This section will describe the parts of a brief in order to give you an idea about what a brief is, what is helpful to include in a brief, and what purpose it serves. Case briefs are a necessary study aid in law school that helps to encapsulate and analyze the mountainous mass of material that law students must digest. The case brief represents a final product after reading a case, rereading it, taking it apart, and putting it back together again. In addition to its function as a tool for self-instruction and referencing, the case brief also provides a valuable “cheat sheet” for class participation.
Who will read your brief? Most professors will espouse the value of briefing but will never ask to see that you have, in fact, briefed. As a practicing lawyer, your client doesn’t care if you brief, so long as you win the case. The judges certainly don’t care if you brief, so long as you competently practice the law. You are the person that the brief will serve! Keep this in mind when deciding what elements to include as part of your brief and when deciding what information to include under those elements.
What are the elements of a brief? Different people will tell you to include different things in your brief. Most likely, upon entering law school, this will happen with one or more of your instructors. While opinions may vary, four elements that are essential to any useful brief are the following:
(a) Facts (name of the case and its parties, what happened factually and procedurally, and the judgment)
(b) Issues (what is in dispute)
(c) Holding (the applied rule of law)
(d) Rationale (reasons for the holding)
If you include nothing but these four elements, you should have everything you need in order to recall effectively the information from the case during class or several months later when studying for exams.
Because briefs are made for yourself, you may want to include other elements that expand the four elements listed above. Depending on the case, the inclusion of additional elements may be useful. For example, a case that has a long and important section expounding dicta might call for a separate section in your brief labeled: Dicta. Whatever elements you decide to include, however, remember that the brief is a tool intended for personal use. To the extent that more elements will help with organization and use of the brief, include them. On the other hand, if you find that having more elements makes your brief cumbersome and hard to use, cut back on the number of elements. At a minimum, however, make sure you include the four elements listed above.
Elements that you may want to consider including in addition to the four basic elements are:
(e) Dicta (commentary about the decision that was not the basis for the decision)
(f) Dissent (if a valuable dissenting opinion exits, the dissent’s opinion)
(g) Party’s Arguments (each party’s opposing argument concerning the ultimate issue)
(h) Comments (personal commentary)
Personal comments can be useful if you have a thought that does not fit elsewhere. In the personal experience of one of the authors, this element was used to label cases as specific kinds (e.g., as a case of vicarious liability) or make mental notes about what he found peculiar or puzzling about cases. This element allowed him to release his thoughts (without losing them) so that he could move on to other cases.
In addition to these elements, it may help you to organize your thoughts, as some people do, by dividing Facts into separate elements:
(1) Facts of the case (what actually happened, the controversy)
(2) Procedural History (what events within the court system led to the present case)
(3) Judgment (what the court actually decided)
Procedural History is usually minimal and most of the time irrelevant to the ultimate importance of a case; however, this is not always true. One subject in which Procedure History is virtually always relevant is Civil Procedure.
When describing the Judgment of the case, distinguish it from the Holding. The Judgment is the factual determination by the court, in favor of one party, such as “affirmed,” “reversed,” or “remanded.” In contrast, the Holding is the applied rule of law that serves as the basis for the ultimate judgment.
Remember that the purpose of a brief is to remind you of the important details that make the case significant in terms of the law. It will be a reference tool when you are drilled by a professor and will be a study aid when you prepare for exams. A brief is also like a puzzle piece.
The elements of the brief create the unique shape and colors of the piece, and, when combined with other pieces, the picture of the common law takes form. A well-constructed brief will save you lots of time by removing the need to return to the case to remember the important details and also by making it easier to put together the pieces of the common law puzzle.
D. EXTRACTING THE RELEVANT INFORMATION: ANNOTATING AND HIGHLIGHTING
So now that you know the basic elements of a brief, what information is important to include under each element? The simple answer is: whatever is relevant. But what parts of a case are relevant? When you read your first few cases, you may think that everything that the judge said was relevant to his ultimate conclusion. Even if this were true, what is relevant for the judge to make his decision is not always relevant for you to include in your brief. Remember, the reason to make a brief is not to persuade the world that the ultimate decision in the case is a sound one, but rather to aid in refreshing your memory concerning the most important parts of the case.
What facts are relevant to include in a brief? You should include the facts that are necessary to remind you of the story. If you forget the story, you will not remember how the law in the case was applied. You should also include the facts that are dispositive to the decision in the case. For instance, if the fact that a car is white is a determining factor in the case, the brief should note that the case involves a white car and not simply a car. To the extent that the procedural history either helps you to remember the case or plays an important role in the ultimate outcome, you should include these facts as well.
What issues and conclusions are relevant to include in a brief? There is usually one main issue on which the court rests its decision. This may seem simple, but the court may talk about multiple issues, and may discuss multiple arguments from both sides of the case. Be sure to distinguish the issues from the arguments made by the parties. The relevant issue or issues, and corresponding conclusions, are the ones for which the court made a final decision and which are binding. The court may discuss intermediate conclusions or issues, but stay focused on the main issue and conclusion which binds future courts.
What rationale is important to include in a brief? This is probably the most difficult aspect of the case to determine. Remember that everything that is discussed may have been relevant to the judge, but it is not necessarily relevant to the rationale of the decision. The goal is to remind yourself of the basic reasoning that the court used to come to its decision and the key factors that made the decision favor one side or the other.
A brief should be brief! Overly long or cumbersome briefs are not very helpful because you will not be able to skim them easily when you review your notes or when the professor drills you. On the other hand, a brief that is too short will be equally unhelpful because it lacks sufficient information to refresh your memory. Try to keep your briefs to one page in length. This will make it easy for you to organize and reference them.
Do not get discouraged. Learning to brief and figuring out exactly what to include will take time and practice. The more you brief, the easier it will become to extract the relevant information.
While a brief is an extremely helpful and important study aid, annotating and highlighting are other tools for breaking down the mass of material in your casebook. The remainder of this section will discuss these different techniques and show how they complement and enhance the briefing process.
Annotating Cases
Many of you probably already read with a pencil or pen, but if you do not, now is the time to get in the habit. Cases are so dense and full of information that you will find yourself spending considerable amounts of time rereading cases to find what you need. An effective way to reduce this time is to annotate the margins of the casebook. Your pencil (or pen) will be one of your best friends while reading a case. It will allow you to mark off the different sections (such as facts, procedural history, or conclusions), thus allowing you to clear your mind of thoughts and providing an invaluable resource when briefing and reviewing.
You might be wondering why annotating is important if you make an adequate, well-constructed brief. By their very nature briefs cannot cover everything in a case. Even with a thorough, well-constructed brief you may want to reference the original case in order to reread dicta that might not have seemed important at the time, to review the complete procedural history or set of facts, or to scour the rationale for a better understanding of the case; annotating makes these tasks easier. Whether you return to a case after a few hours or a few months, annotations will swiftly guide you to the pertinent parts of the case by providing a roadmap of the important sections. Your textual markings and margin notes will refresh your memory and restore specific thoughts you might have had about either the case in general or an individual passage.
Annotations will also remind you of forgotten thoughts and random ideas by providing a medium for personal comments.
In addition to making it easier to review an original case, annotating cases during the first review of a case makes the briefing process easier. With adequate annotations, the important details needed for your brief will be much easier to retrieve. Without annotations, you will likely have difficulty locating the information you seek even in the short cases. It might seem strange that it would be hard to reference a short case, but even a short case will likely take you at least fifteen to twenty-five minutes to read, while longer cases may take as much as thirty minutes to an hour to complete. No matter how long it takes, the dense material of all cases makes it difficult to remember all your thoughts, and trying to locate specific sections of the analysis may feel like you are trying to locate a needle in a haystack. An annotation in the margin, however, will not only swiftly guide you to a pertinent section, but will also refresh the thoughts that you had while reading that section.
When you read a case for the first time, read for the story and for a basic understanding of the dispute, the issues, the rationale, and the decision. As you hit these elements (or what you think are these elements) make a mark in the margins. Your markings can be as simple as “facts” (with a bracket that indicates the relevant part of the paragraph). When you spot an issue, you may simply mark “issue” or instead provide a synopsis in your own words. When a case sparks an idea — write that idea in the margin as well — you never know when a seemingly irrelevant idea might turn into something more.
Finally, when you spot a particularly important part of the text, underline it (or highlight it as described below).
With a basic understanding of the case, and with annotations in the margin, the second read-through of the case should be much easier. You can direct your reading to the most important sections and will have an easier time identifying what is and is not important. Continue rereading the case until you have identified all the relevant information that you need to make your brief, including the issue(s), the facts, the holding, and the relevant parts of the analysis.
Pencil or pen — which is better to use when annotating? Our recommendation is a mechanical pencil. Mechanical pencils make finer markings than regular pencils, and also than ballpoint pens. Although you might think a pencil might smear more than a pen, with its sharp point a mechanical pencil uses very little excess lead and will not smear as much as you might imagine. A mechanical pencil will also give you the freedom to make mistakes without consequences. When you first start annotating, you may think that some passages are more important than they really are, and therefore you may resist the urge to make a mark in order to preserve your book and prevent false guideposts. With a pencil, however, the ability to erase and rewrite removes this problem.
Highlighting
Why highlight? Like annotating, highlighting may seem unimportant if you create thorough, well-constructed briefs, but highlighting directly helps you to brief. It makes cases, especially the more complicated ones, easy to digest, review and use to extract information.
Highlighting takes advantage of colors to provide a uniquely effective method for reviewing and referencing a case. If you prefer a visual approach to learning, you may find highlighting to be a very effective tool.
If annotating and highlighting are so effective, why brief? Because the process of summarizing a case and putting it into your own words within a brief provides an understanding of the law and of the case that you cannot gain through the process of highlighting or annotating.
The process of putting the case into your own words forces you to digest the material, while annotating and highlighting can be accomplished in a much more passive manner.
What should you highlight? Similar to annotating, the best parts of the case to highlight are those that represent the needed information for your brief such as the facts, the issue, the holding and the rationale.
Unlike annotating, highlighting provides an effective way to color code, which makes referring to the case even easier. In addition, Highlighters are particularly useful in marking off entire sections by using brackets. These brackets will allow you to color-code the case without highlighting all the text, leaving the most important phrases untouched for a more detailed highlight marking or underlining.
Highlighting is a personal tool, and therefore should be used to the extent that highlighting helps, but should be modified in a way that makes it personally time efficient and beneficial. For instance, you might combine the use of annotations in the margins with the visual benefit of highlighting the relevant text. You may prefer to underline the relevant text with a pencil, but to use a highlighter to bracket off the different sections of a case. Whatever you choose to do, make sure that it works for you, regardless of what others recommend. The techniques in the remainder of this section will describe ways to make full use of your highlighters.
First, buy yourself a set of multi-colored highlighters, with at least four, or perhaps five or six different colors. Yellow, pink, and orange are usually the brightest. Depending on the brand, purple and green can be dark, but still work well. Although blue is a beautiful color, it tends to darken and hide the text.
Therefore we recommend that you save blue for the elements that you rarely highlight.
For each different section of the case, choose a color, and use that color only when highlighting the section of the case designated for that color. Consider using yellow for the text that you tend to highlight most frequently. Because yellow is the brightest, you may be inclined to use yellow for the Conclusions in order to make them stand out the most. If you do this, however, you will exhaust your other colors much faster than yellow and this will require that you purchase an entire set of new highlighters when a single color runs out because colors such as green are not sold separately. If instead you choose to use yellow on a more frequently highlighted section such as the Analysis, when it comes time to replace your yellow marker, you will need only to replace your yellow highlighter individually. In the personal experience on one of the authors, the sections of cases that seemed to demand the most highlighter attention were the
Facts and the Analysis, while the Issues and Holdings demanded the least. Other Considerations and
Procedural History required lots of highlighting in particular cases although not in every case.
Experiment if you must, but try to choose a color scheme early on in the semester and stick with it. That way, when you come back to the first cases of the semester, you will not be confused with multiple color schemes. The basic sections of a case for which you should consider giving a different color are:
Procedural History
Issue (and questions presented)
Holding (and conclusions)
Analysis (rationale)
Other Considerations (such as dicta)
Not all of these sections demand a separate color. You may find that combining Facts and Procedural History or Issues and Holdings works best. Furthermore, as mentioned above, some sections may not warrant highlighting in every case (e.g., dicta probably do not need to be highlighted unless they are particularly important). If you decide that a single color is all that you need, then stick to one, but if you find yourself highlighting lots of text from many different sections, reconsider the use of at least a few different colors. Highlighters make text stand out, but only when used appropriately. The use of many colors enables you to highlight more text without reducing the highlighter’s effectiveness. Three to four colors provides decent color variation without the cumbersomeness of handling too many markers.
Once you are comfortable with your color scheme, determining exactly what to highlight still may be difficult. Similar to knowing what to annotate, experience will perfect your highlighting skills. Be careful not to highlight everything, thus ruining your highlighters’ effectiveness; at the same time, do not be afraid to make mistakes.
Now that we have covered the basics of reading, annotating, highlighting, and briefing a case, you are ready to start practicing. Keep the tips and techniques mentioned in this chapter in mind when you tackle the four topics in the remainder of this book. If you have difficultly, refer back to this chapter to help guide you as you master the case method of study and the art of using the common law.
Have questions about law school? Check out our Facebook page , follow us on Twitter or start networking with law students and lawyers on LexTalk .
More Helpful Links
- The American Legal System
- How to Brief a Case
- How to Read a Casebook 101
- Top 20 Things You Need to Know About Law School
- Learn to Spot Issues Like a Lawyer
- Why an Internet Search is Not Legal Research
- Why go to Law School?
- What’s the Most Challenging Part of Law School?
- What advice would you give yourself about law school?

Get advice about law school from law students and legal professionals at the LexTalk legal community
Legal Research & Practical Guidance
Build your legal strategy and do vital work using authoritative primary law, analysis, guidance, court records and validation tools.
Search vast LexisNexis resources without selecting sources or using search commands.
Federal and state court dockets and documents for research, tracking, and profiling.
Practical Guidance
Current practical guidance from leading practitioners for managing transactional matters.
Lexis Securities Mosaic
Track and analyze SEC filings, U.S. agency information, industry news and current awareness.
News, Company Research & Media Monitoring Solutions
Quickly uncover up-to-date facts, news and insight essential to your decisions and business development.
LexisNexis Newsdesk
A fresh take on media monitoring & analysis to help you find the hidden gems that can impact your business.
Current, authoritative news, social media, company, financial and industry sources.
Media Intelligence Research & Analytics
Identify prospects and compile business profiles that help you close more deals.
Lexis Diligence
Corporate due diligence research tool.
- Intellectual Property
Stay up to speed with trends, track your competition, promote innovation and protect your intellectual assets.
TotalPatent One
The world's largest collection of full-text and bibliographic patent databases.
Patent Advisor
Predictive and revealing analytics for more efficient patent prosecution.
PatentOptimizer
Patent application drafting and analysis tools.
The CaseMap Suite of Litigation Tools
Comprised of four unique components, the CaseMap Suite can help you organize, analyze and present your entire case.
Compile relevant case facts, documents, research and issues into a centralized location for better assessment.
Manage litigation documents—share, search, review, produce, etc.—across your discovery team.
Quickly assemble your data and produce impactful timelines for pennies apiece.
See case presentations from a new angle with technology-driven Sanction software.
Practice & Legal Department Management
Address the business side of your legal activities with solutions to manage, track and analyze matters, finances, critical processes, relationships and performance.
CounselLink
A centralized repository for matter, e-billing and spend management.
Dashboards that display, track and manage your practice, clients and business tasks.
TimeMatters
Organize, associate and track case contacts, documents, events, phone calls, billing, etc.
InterAction
Comprehensive customer relationship management system for law firms.
Compliance & Due Diligence
Stay on top of regulatory and legislative changes, perform due diligence and manage compliance with ease, speed and confidence.
Customizable tools for tracking and reporting legislative and regulatory activity.
IntegraCheck | Integrity Due Diligence
In-depth due-diligence investigation reports.
Just for you Solutions & resources for your organization, department, role or individual work:
- Corporate Communications
- Information Professional
- Marketing & Competitive Intelligence
- Media Organizations
- Political Organizations
- Third-Party Due Diligence
- Sales & Business Development Professionals
- Strategy & Business Development Professionals
- Non-Profit Organizations
- Professional Services
- Technology Professionals
- Librarians & Information Professionals
- Paralegals & Legal Assistants
- Marketing Directors
- Law Department Management
- Litigation Management
- Tax Accounting
- View All »
- Faculty & Adminstration
- Public Libraries
- University & High School Students
- Law School Student Publications
- Portal Sign In
Browse by Industry
- Financial Services
- Health Care
- Life Sciences
- Manufacturing
- Retail & Sales
Browse by Department
- Corporate Compliance
- Corporate Counsel
- Procurement & Supply Chain
- Tax & Accounting
Visit the LexisNexis Store to purchase products that will assist you in your professional success Shop by :
- Jurisdiction
- Practice Area
- Banking Compliance
- Immigration
- Real Estate
- Workers' Comp
- Business Solutions
- Partner Products
- American Health Lawyers Association
- NITA: National Institute for Trial Advocacy
- The Florida Bar
Support & Training
Quick links.
- Lexis+ Support
- Lexis Support
- Nexis Support
- Practical Guidance Support
- CourtLink Support
- Lexis Securities Mosaic Support
- Digital Library Support
- LexTalk: Gain peer-to-peer, product support
- LexisNexis University
- Request Telephonic Training
- Support Center Resources
- Training on the Go
Communities & Blogs
Our Blogs and Communities feature a broad array of trending news and topics within socially interactive environments. Connect, explore and find the answers you need to further your goals.
- Blogs & Newsletters
- Blog Mosaic
- Business of Law Blog
- Corporate Law Advisory
- Legal Content Insider
- State Net Capitol Journal
- News & Trending Topics
- Legal Insights & Trends
- Practical Guidance Journal
- Professional Communities
- Business Insight Solutions – Partner Portal
- Corporate InfoPro (Corporate Information Professionals)
- InfoPro (Legal Information Professionals)
- LexisNexis for Developers
- Litigators Verdict & Settlement Exchange
- Global directory Global directory
- Product logins Product logins
- Contact us Contact us
Our Privacy Statement & Cookie Policy
All Thomson Reuters websites use cookies to improve your online experience. They were placed on your computer when you launched this website. You can change your cookie settings through your browser.
- Privacy Statement
- Cookie Policy

Legal precedents play an important role in decision-making and aids the judicial officers in referring to similar case laws, ultimately saving time and scrutinizing results. And of course, it’s usually a research paralegal or associate tasked with a case law study and discovery concerning a legal matter. This case-building work takes thorough research, where paralegals or associates comb through law books, legal databases, and case law statutes in both physical and digital form. Researching large databases can understandably be a tedious job, but with the most practical case law research tools these tasks can be simplified.
Legal precedent example
In Kudlacik v Johnnys Shawnee Inc , it was observed that once a legal principle has been established by a court, as per the doctrine of stare decisis , it will typically be upheld by the same court when the same legal issue is brought up in consecutive instances, and in all courts of lower rank.
So what transpired? The Supreme Court upheld a district court’s decision to dismiss the plaintiff’s lawsuit against the defendants (two commercial drinking establishments) for injuries sustained in a collision with a vehicle whose driver had consumed alcoholic beverages at the defendants’ establishments prior to the collision.
On appeal, the plaintiff urged the Supreme Court to re-examine the district court’s case law shielding commercial drinking facilities from liability for the wrongs perpetrated by their inebriated customers. The Supreme Court upheld the district court’s ruling after restating the common law in accordance with the stare decisis principle, ruling:
- This court declines to overturn Ling v. Jan’s Liquors, 703 P.2d 731 (Kan. 1985), and the plaintiff failed to state a claim for negligence; and
- Plaintiff failed to state a claim for aiding and abetting under Restatement (Second) of Torts.
“Legal researchers have one perennial question: Have I done enough?” Helping the legal researcher feel confident they’ve done enough – Read the full white paper .
How to use case law as a precedent in a report
Legal reports are typically prepared in one of two ways: in a straightforward, neutral-explanatory tone or in a more persuasive manner.

Include basic elements of a brief
Though writing styles and document templates differ, a report should contain:
- A brief description of the issue that is to be explained in detail further with a simple resolution;
- A statement of facts at hand;
- A comparative study drawn analytically with the facts and the issue concerning the laws;
- A conclusion to the issue, its facts, and its legal analysis.
Align facts and legal issues
Legal precedents are when a case’s circumstances and legal requirements match those of a contemporary legal dispute; unless a party can demonstrate that it was incorrectly resolved or that it differed materially, the precedent will typically govern the outcome of a later similar case.
For judges, it is important to discern the “ratio decidendi,” or the grounds for the decisions taken in previous cases, to apply the precedents stated in a report. In cases where the reasoning is similar enough to lead to the same or similar conclusion, it is the reasons—and nothing else—that “link” subsequent cases.
Additional citations and considerations
When reviewing law reports to cite valid case law it is important for lawyers, paralegals, and students to understand the significance of learning how to navigate and analyze a law report swiftly. The judgment is only one part of a legal report. It starts off with the names of the parties, the hearing date, the judge or judges’ names, and, typically, the court. The headnote includes a summary of the relevant facts and the judge’s decision, followed by catchwords and indexing terms. While working on the report, it is important to ascertain the precedents referred to in drawing the conclusion and upon whom the decision has been relied upon.
Following are the points to be kept in mind while citing case law and constructing a reliable report:
- Write in simple and standard legal language
- Use short sentences
- Employ fewer jargons
- Follow the IRAC Method (Issue, Reasoning, Analysis, and Conclusion)
- Create sub-topics to improve readability
- Maintain the flow of the report
Final thoughts on precedents
It’s often challenging to determine what “the law” is in any given legal situation. In order to determine the actual law that applies to your case, you may need to compare many different instances to the particular facts of your case.
Do you know the laws and rules that apply to your case? Have you located a case or cases from the past that have similar facts and legal issues to yours? Finding a case that is on point or similar enough demands a lot of time and cumbersome research. If that’s where you find yourself today, request a free trial of Westlaw Precision to drastically streamline your case law research or try Practical Law to get access to thousands of expert-written how-to guides, forms, templates, checklists, and more across all major practice areas today.
The content appearing on this website is not intended as, and shall not be relied upon as, legal advice. It is general in nature and may not reflect all recent legal developments. Thomson Reuters is not a law firm and an attorney-client relationship is not formed through your use of this website. You should consult with qualified legal counsel before acting on any content found on this website.
- Legal Topics

Join our community
Sign up for industry-leading insights, updates, and all things AI @ Thomson Reuters.

The past, present, and future of legal research with generative AI
Legal technology has quickly evolved from a books-only exercise to outmatched AI-supported technology - with predictive analytics, precision research capabilities and powerful new citator tools.

Build a career without boundaries
Learn more about how Thomson Reuters informs the way forward in The Power of Purpose
Related posts

What to do if you think your company breached a contract?

How to succeed as a summer law associate

Commercially reasonable efforts explained
More answers.

Everything you need to know about instant payment financial fraud

What does productive legal financial management software look like?

Mind your gaps – Are you making well-being a priority?
- Privacy Policy

Home » Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Table of Contents

A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation.
It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied. Case studies typically involve multiple sources of data, including interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, which are analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, and grounded theory. The findings of a case study are often used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Types of Case Study
Types and Methods of Case Study are as follows:
Single-Case Study
A single-case study is an in-depth analysis of a single case. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand a specific phenomenon in detail.
For Example , A researcher might conduct a single-case study on a particular individual to understand their experiences with a particular health condition or a specific organization to explore their management practices. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a single-case study are often used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Multiple-Case Study
A multiple-case study involves the analysis of several cases that are similar in nature. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to identify similarities and differences between the cases.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a multiple-case study on several companies to explore the factors that contribute to their success or failure. The researcher collects data from each case, compares and contrasts the findings, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as comparative analysis or pattern-matching. The findings of a multiple-case study can be used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Exploratory Case Study
An exploratory case study is used to explore a new or understudied phenomenon. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to generate hypotheses or theories about the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an exploratory case study on a new technology to understand its potential impact on society. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as grounded theory or content analysis. The findings of an exploratory case study can be used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Descriptive Case Study
A descriptive case study is used to describe a particular phenomenon in detail. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to provide a comprehensive account of the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a descriptive case study on a particular community to understand its social and economic characteristics. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a descriptive case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Instrumental Case Study
An instrumental case study is used to understand a particular phenomenon that is instrumental in achieving a particular goal. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand the role of the phenomenon in achieving the goal.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an instrumental case study on a particular policy to understand its impact on achieving a particular goal, such as reducing poverty. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of an instrumental case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Case Study Data Collection Methods
Here are some common data collection methods for case studies:
Interviews involve asking questions to individuals who have knowledge or experience relevant to the case study. Interviews can be structured (where the same questions are asked to all participants) or unstructured (where the interviewer follows up on the responses with further questions). Interviews can be conducted in person, over the phone, or through video conferencing.
Observations
Observations involve watching and recording the behavior and activities of individuals or groups relevant to the case study. Observations can be participant (where the researcher actively participates in the activities) or non-participant (where the researcher observes from a distance). Observations can be recorded using notes, audio or video recordings, or photographs.
Documents can be used as a source of information for case studies. Documents can include reports, memos, emails, letters, and other written materials related to the case study. Documents can be collected from the case study participants or from public sources.
Surveys involve asking a set of questions to a sample of individuals relevant to the case study. Surveys can be administered in person, over the phone, through mail or email, or online. Surveys can be used to gather information on attitudes, opinions, or behaviors related to the case study.
Artifacts are physical objects relevant to the case study. Artifacts can include tools, equipment, products, or other objects that provide insights into the case study phenomenon.
How to conduct Case Study Research
Conducting a case study research involves several steps that need to be followed to ensure the quality and rigor of the study. Here are the steps to conduct case study research:
- Define the research questions: The first step in conducting a case study research is to define the research questions. The research questions should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the case study phenomenon under investigation.
- Select the case: The next step is to select the case or cases to be studied. The case should be relevant to the research questions and should provide rich and diverse data that can be used to answer the research questions.
- Collect data: Data can be collected using various methods, such as interviews, observations, documents, surveys, and artifacts. The data collection method should be selected based on the research questions and the nature of the case study phenomenon.
- Analyze the data: The data collected from the case study should be analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, or grounded theory. The analysis should be guided by the research questions and should aim to provide insights and conclusions relevant to the research questions.
- Draw conclusions: The conclusions drawn from the case study should be based on the data analysis and should be relevant to the research questions. The conclusions should be supported by evidence and should be clearly stated.
- Validate the findings: The findings of the case study should be validated by reviewing the data and the analysis with participants or other experts in the field. This helps to ensure the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Write the report: The final step is to write the report of the case study research. The report should provide a clear description of the case study phenomenon, the research questions, the data collection methods, the data analysis, the findings, and the conclusions. The report should be written in a clear and concise manner and should follow the guidelines for academic writing.
Examples of Case Study
Here are some examples of case study research:
- The Hawthorne Studies : Conducted between 1924 and 1932, the Hawthorne Studies were a series of case studies conducted by Elton Mayo and his colleagues to examine the impact of work environment on employee productivity. The studies were conducted at the Hawthorne Works plant of the Western Electric Company in Chicago and included interviews, observations, and experiments.
- The Stanford Prison Experiment: Conducted in 1971, the Stanford Prison Experiment was a case study conducted by Philip Zimbardo to examine the psychological effects of power and authority. The study involved simulating a prison environment and assigning participants to the role of guards or prisoners. The study was controversial due to the ethical issues it raised.
- The Challenger Disaster: The Challenger Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Space Shuttle Challenger explosion in 1986. The study included interviews, observations, and analysis of data to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
- The Enron Scandal: The Enron Scandal was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Enron Corporation’s bankruptcy in 2001. The study included interviews, analysis of financial data, and review of documents to identify the accounting practices, corporate culture, and ethical issues that led to the company’s downfall.
- The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster : The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the nuclear accident that occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan in 2011. The study included interviews, analysis of data, and review of documents to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
Application of Case Study
Case studies have a wide range of applications across various fields and industries. Here are some examples:
Business and Management
Case studies are widely used in business and management to examine real-life situations and develop problem-solving skills. Case studies can help students and professionals to develop a deep understanding of business concepts, theories, and best practices.
Case studies are used in healthcare to examine patient care, treatment options, and outcomes. Case studies can help healthcare professionals to develop critical thinking skills, diagnose complex medical conditions, and develop effective treatment plans.
Case studies are used in education to examine teaching and learning practices. Case studies can help educators to develop effective teaching strategies, evaluate student progress, and identify areas for improvement.
Social Sciences
Case studies are widely used in social sciences to examine human behavior, social phenomena, and cultural practices. Case studies can help researchers to develop theories, test hypotheses, and gain insights into complex social issues.
Law and Ethics
Case studies are used in law and ethics to examine legal and ethical dilemmas. Case studies can help lawyers, policymakers, and ethical professionals to develop critical thinking skills, analyze complex cases, and make informed decisions.
Purpose of Case Study
The purpose of a case study is to provide a detailed analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. A case study is a qualitative research method that involves the in-depth exploration and analysis of a particular case, which can be an individual, group, organization, event, or community.
The primary purpose of a case study is to generate a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case, including its history, context, and dynamics. Case studies can help researchers to identify and examine the underlying factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and detailed understanding of the case, which can inform future research, practice, or policy.
Case studies can also serve other purposes, including:
- Illustrating a theory or concept: Case studies can be used to illustrate and explain theoretical concepts and frameworks, providing concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Developing hypotheses: Case studies can help to generate hypotheses about the causal relationships between different factors and outcomes, which can be tested through further research.
- Providing insight into complex issues: Case studies can provide insights into complex and multifaceted issues, which may be difficult to understand through other research methods.
- Informing practice or policy: Case studies can be used to inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
Advantages of Case Study Research
There are several advantages of case study research, including:
- In-depth exploration: Case study research allows for a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. This can provide a comprehensive understanding of the case and its dynamics, which may not be possible through other research methods.
- Rich data: Case study research can generate rich and detailed data, including qualitative data such as interviews, observations, and documents. This can provide a nuanced understanding of the case and its complexity.
- Holistic perspective: Case study research allows for a holistic perspective of the case, taking into account the various factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the case.
- Theory development: Case study research can help to develop and refine theories and concepts by providing empirical evidence and concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Practical application: Case study research can inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
- Contextualization: Case study research takes into account the specific context in which the case is situated, which can help to understand how the case is influenced by the social, cultural, and historical factors of its environment.
Limitations of Case Study Research
There are several limitations of case study research, including:
- Limited generalizability : Case studies are typically focused on a single case or a small number of cases, which limits the generalizability of the findings. The unique characteristics of the case may not be applicable to other contexts or populations, which may limit the external validity of the research.
- Biased sampling: Case studies may rely on purposive or convenience sampling, which can introduce bias into the sample selection process. This may limit the representativeness of the sample and the generalizability of the findings.
- Subjectivity: Case studies rely on the interpretation of the researcher, which can introduce subjectivity into the analysis. The researcher’s own biases, assumptions, and perspectives may influence the findings, which may limit the objectivity of the research.
- Limited control: Case studies are typically conducted in naturalistic settings, which limits the control that the researcher has over the environment and the variables being studied. This may limit the ability to establish causal relationships between variables.
- Time-consuming: Case studies can be time-consuming to conduct, as they typically involve a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific case. This may limit the feasibility of conducting multiple case studies or conducting case studies in a timely manner.
- Resource-intensive: Case studies may require significant resources, including time, funding, and expertise. This may limit the ability of researchers to conduct case studies in resource-constrained settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Qualitative Research Methods

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide

Survey Research – Types, Methods, Examples
Skip to main navigation
- Email Updates
- Federal Court Finder
Glossary of Legal Terms
A jury verdict that a criminal defendant is not guilty, or the finding of a judge that the evidence is insufficient to support a conviction.
A judge in the full-time service of the court. Compare to senior judge.
The federal agency responsible for collecting court statistics, administering the federal courts' budget, and performing many other administrative and programmatic functions, under the direction and supervision of the Judicial Conference of the United States.
A term used to describe evidence that may be considered by a jury or judge in civil and criminal cases.
A lawsuit arising in or related to a bankruptcy case that begins by filing a complaint with the court, that is, a "trial" that takes place within the context of a bankruptcy case.
A written or printed statement made under oath.
In the practice of the court of appeals, it means that the court of appeals has concluded that the lower court decision is correct and will stand as rendered by the lower court.
A juror selected in the same manner as a regular juror who hears all the evidence but does not help decide the case unless called on to replace a regular juror.
A procedure for settling a dispute outside the courtroom. Most forms of ADR are not binding, and involve referral of the case to a neutral party such as an arbitrator or mediator.
Latin for "friend of the court." It is advice formally offered to the court in a brief filed by an entity interested in, but not a party to, the case.
The formal written statement by a defendant in a civil case that responds to a complaint, articulating the grounds for defense.
A request made after a trial by a party that has lost on one or more issues that a higher court review the decision to determine if it was correct. To make such a request is "to appeal" or "to take an appeal." One who appeals is called the "appellant;" the other party is the "appellee."
The party who appeals a district court's decision, usually seeking reversal of that decision.
About appeals; an appellate court has the power to review the judgment of a lower court (trial court) or tribunal. For example, the U.S. circuit courts of appeals review the decisions of the U.S. district courts.
The party who opposes an appellant's appeal, and who seeks to persuade the appeals court to affirm the district court's decision.
A proceeding in which a criminal defendant is brought into court, told of the charges in an indictment or information, and asked to plead guilty or not guilty.
A federal judge who is appointed for life, during "good behavior," under Article III of the Constitution. Article III judges are nominated by the President and confirmed by the Senate.
Property of all kinds, including real and personal, tangible and intangible.
An agreement to continue performing duties under a contract or lease.
An injunction that automatically stops lawsuits, foreclosures, garnishments, and most collection activities against the debtor the moment a bankruptcy petition is filed.
The release, prior to trial, of a person accused of a crime, under specified conditions designed to assure that person's appearance in court when required. Also, can refer to the amount of bond money posted as a financial condition of pretrial release.
A legal procedure for dealing with debt problems of individuals and businesses; specifically, a case filed under one of the chapters of title 11 of the United States Code (the Bankruptcy Code).
An officer of the Judiciary serving in the judicial districts of Alabama and North Carolina who, like the United States trustee, is responsible for supervising the administration of bankruptcy cases, estates, and trustees; monitoring plans and disclosure statements; monitoring creditors' committees; monitoring fee applications; and performing other statutory duties.
The informal name for title 11 of the United States Code (11 U.S.C. §§ 101-1330), the federal bankruptcy law.
The bankruptcy judges in regular active service in each district; a unit of the district court.
All interests of the debtor in property at the time of the bankruptcy filing. The estate technically becomes the temporary legal owner of all of the debtor's property.
A judicial officer of the United States district court who is the court official with decision-making power over federal bankruptcy cases.
A formal request for the protection of the federal bankruptcy laws. (There is an official form for bankruptcy petitions.)
A private individual or corporation appointed in all Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 cases to represent the interests of the bankruptcy estate and the debtor's creditors.
A trial without a jury, in which the judge serves as the fact-finder.
A written statement submitted in a trial or appellate proceeding that explains one side's legal and factual arguments.
The duty to prove disputed facts. In civil cases, a plaintiff generally has the burden of proving his or her case. In criminal cases, the government has the burden of proving the defendant's guilt. (See standard of proof.)
A bankruptcy case in which the debtor is a business or an individual involved in business and the debts are for business purposes.
A crime punishable by death.
A complete collection of every document filed in court in a case.
The law as established in previous court decisions. A synonym for legal precedent. Akin to common law, which springs from tradition and judicial decisions.
The number of cases handled by a judge or a court.
A legal claim.
The offices of a judge and his or her staff.
A reorganization bankruptcy, usually involving a corporation or partnership. A Chapter 11 debtor usually proposes a plan of reorganization to keep its business alive and pay creditors over time. Individuals or people in business can also seek relief in Chapter 11.
The chapter of the Bankruptcy Code providing for adjustment of debts of a "family farmer" or "family fisherman," as the terms are defined in the Bankruptcy Code.
The chapter of the Bankruptcy Code providing for the adjustment of debts of an individual with regular income, often referred to as a "wage-earner" plan. Chapter 13 allows a debtor to keep property and use his or her disposable income to pay debts over time, usually three to five years.
A person appointed to administer a Chapter 13 case. A Chapter 13 trustee's responsibilities are similar to those of a Chapter 7 trustee; however, a Chapter 13 trustee has the additional responsibilities of overseeing the debtor's plan, receiving payments from debtors, and disbursing plan payments to creditors.
The chapter of the Bankruptcy Code dealing with cases of cross-border insolvency.
The chapter of the Bankruptcy Code providing for "liquidation," that is, the sale of a debtor's nonexempt property and the distribution of the proceeds to creditors. In order to be eligible for Chapter 7, the debtor must satisfy a "means test." The court will evaluate the debtor's income and expenses to determine if the debtor may proceed under Chapter 7.
A person appointed in a Chapter 7 case to represent the interests of the bankruptcy estate and the creditors. The trustee's responsibilities include reviewing the debtor's petition and schedules, liquidating the property of the estate, and making distributions to creditors. The trustee may also bring actions against creditors or the debtor to recover property of the bankruptcy estate.
The chapter of the Bankruptcy Code providing for reorganization of municipalities (which includes cities and towns, as well as villages, counties, taxing districts, municipal utilities, and school districts).
The judge who has primary responsibility for the administration of a court; chief judges are determined by seniority
A creditor's assertion of a right to payment from a debtor or the debtor's property.
A lawsuit in which one or more members of a large group, or class, of individuals or other entities sue on behalf of the entire class. The district court must find that the claims of the class members contain questions of law or fact in common before the lawsuit can proceed as a class action.
The court officer who oversees administrative functions, especially managing the flow of cases through the court. The clerk's office is often called a court's central nervous system.
Property that is promised as security for the satisfaction of a debt.
The legal system that originated in England and is now in use in the United States, which relies on the articulation of legal principles in a historical succession of judicial decisions. Common law principles can be changed by legislation.
A special condition the court imposes that requires an individual to work – without pay – for a civic or nonprofit organization.
A written statement that begins a civil lawsuit, in which the plaintiff details the claims against the defendant.
Prison terms for two or more offenses to be served at the same time, rather than one after the other. Example: Two five-year sentences and one three-year sentence, if served concurrently, result in a maximum of five years behind bars.
Approval of a plan of reorganization by a bankruptcy judge.
Prison terms for two or more offenses to be served one after the other. Example: Two five-year sentences and one three-year sentence, if served consecutively, result in a maximum of 13 years behind bars.
A bankruptcy case filed to reduce or eliminate debts that are primarily consumer debts.
Debts incurred for personal, as opposed to business, needs.
A claim that may be owed by the debtor under certain circumstances, e.g., where the debtor is a cosigner on another person's loan and that person fails to pay.
An agreement between two or more people that creates an obligation to do or not to do a particular thing.
A judgment of guilt against a criminal defendant.
Legal advice; a term also used to refer to the lawyers in a case.
An allegation in an indictment or information, charging a defendant with a crime. An indictment or information may contain allegations that the defendant committed more than one crime. Each allegation is referred to as a count.
Government entity authorized to resolve legal disputes. Judges sometimes use "court" to refer to themselves in the third person, as in "the court has read the briefs."
A person who makes a word-for-word record of what is said in court, generally by using a stenographic machine, shorthand or audio recording, and then produces a transcript of the proceedings upon request.
Generally refers to two events in individual bankruptcy cases: (1) the "individual or group briefing" from a nonprofit budget and credit counseling agency that individual debtors must attend prior to filing under any chapter of the Bankruptcy Code; and (2) the "instructional course in personal financial management" in chapters 7 and 13 that an individual debtor must complete before a discharge is entered. There are exceptions to both requirements for certain categories of debtors, exigent circumstances, or if the U.S. trustee or bankruptcy administrator have determined that there are insufficient approved credit counseling agencies available to provide the necessary counseling.
A person to whom or business to which the debtor owes money or that claims to be owed money by the debtor.
Money that a defendant pays a plaintiff in a civil case if the plaintiff has won. Damages may be compensatory (for loss or injury) or punitive (to punish and deter future misconduct).
Latin, meaning "in fact" or "actually." Something that exists in fact but not as a matter of law.
Latin, meaning "in law." Something that exists by operation of law.
Latin, meaning "anew." A trial de novo is a completely new trial. Appellate review de novo implies no deference to the trial judge's ruling.
A person who has filed a petition for relief under the Bankruptcy Code.
A debtor's detailed description of how the debtor proposes to pay creditors' claims over a fixed period of time.
A judge's statement about someone's rights. For example, a plaintiff may seek a declaratory judgment that a particular statute, as written, violates some constitutional right.
A judgment awarding a plaintiff the relief sought in the complaint because the defendant has failed to appear in court or otherwise respond to the complaint.
An individual (or business) against whom a lawsuit is filed.
In a civil case, the person or organization against whom the plaintiff brings suit; in a criminal case, the person accused of the crime.
An oral statement made before an officer authorized by law to administer oaths. Such statements are often taken to examine potential witnesses, to obtain discovery, or to be used later in trial. See discovery.
A release of a debtor from personal liability for certain dischargeable debts. Notable exceptions to dischargeability are taxes and student loans. A discharge releases a debtor from personal liability for certain debts known as dischargeable debts and prevents the creditors owed those debts from taking any action against the debtor or the debtor's property to collect the debts. The discharge also prohibits creditors from communicating with the debtor regarding the debt, including through telephone calls, letters, and personal contact.
A debt for which the Bankruptcy Code allows the debtor's personal liability to be eliminated.
A written document prepared by the chapter 11 debtor or other plan proponent that is designed to provide "adequate information" to creditors to enable them to evaluate the chapter 11 plan of reorganization.
Procedures used to obtain disclosure of evidence before trial.
Court action that prevents an identical lawsuit from being filed later.
Court action that allows the later filing.
Income not reasonably necessary for the maintenance or support of the debtor or dependents. If the debtor operates a business, disposable income is defined as those amounts over and above what is necessary for the payment of ordinary operating expenses.
A log containing the complete history of each case in the form of brief chronological entries summarizing the court proceedings.
In criminal law, the constitutional guarantee that a defendant will receive a fair and impartial trial. In civil law, the legal rights of someone who confronts an adverse action threatening liberty or property.
French, meaning "on the bench." All judges of an appellate court sitting together to hear a case, as opposed to the routine disposition by panels of three judges. In the Ninth Circuit, an en banc panel consists of 11 randomly selected judges.
Pertaining to civil suits in "equity" rather than in "law." In English legal history, the courts of "law" could order the payment of damages and could afford no other remedy (see damages). A separate court of "equity" could order someone to do something or to cease to do something (e.g., injunction). In American jurisprudence, the federal courts have both legal and equitable power, but the distinction is still an important one. For example, a trial by jury is normally available in "law" cases but not in "equity" cases.
The value of a debtor's interest in property that remains after liens and other creditors' interests are considered. (Example: If a house valued at $60,000 is subject to a $30,000 mortgage, there is $30,000 of equity.)
Information presented in testimony or in documents that is used to persuade the fact finder (judge or jury) to decide the case in favor of one side or the other.
A proceeding brought before a court by one party only, without notice to or challenge by the other side.
Doctrine that says evidence obtained in violation of a criminal defendant's constitutional or statutory rights is not admissible at trial.
Evidence indicating that a defendant did not commit the crime.
Contracts or leases under which both parties to the agreement have duties remaining to be performed. If a contract or lease is executory, a debtor may assume it (keep the contract) or reject it (terminate the contract).
Property that a debtor is allowed to retain, free from the claims of creditors who do not have liens on the property.
Certain property owned by an individual debtor that the Bankruptcy Code or applicable state law permits the debtor to keep from unsecured creditors. For example, in some states the debtor may be able to exempt all or a portion of the equity in the debtor's primary residence (homestead exemption), or some or all "tools of the trade" used by the debtor to make a living (i.e., auto tools for an auto mechanic or dental tools for a dentist). The availability and amount of property the debtor may exempt depends on the state the debtor lives in.
A bankruptcy case filed either without schedules or with incomplete schedules listing few creditors and debts. (Face sheet filings are often made for the purpose of delaying an eviction or foreclosure
An individual, individual and spouse, corporation, or partnership engaged in a farming operation that meets certain debt limits and other statutory criteria for filing a petition under Chapter 12.
An attorney employed by the federal courts on a full-time basis to provide legal defense to defendants who are unable to afford counsel. The judiciary administers the federal defender program pursuant to the Criminal Justice Act.
As provided for in the Criminal Justice Act, an organization established within a federal judicial circuit to represent criminal defendants who cannot afford an adequate defense. Each organization is supervised by a federal public defender appointed by the court of appeals for the circuit.
Jurisdiction given to federal courts in cases involving the interpretation and application of the U.S. Constitution, acts of Congress, and treaties.
A serious crime, usually punishable by at least one year in prison.
To place a paper in the official custody of the clerk of court to enter into the files or records of a case.
A transfer of a debtor's property made with intent to defraud or for which the debtor receives less than the transferred property's value.
The characterization of a debtor's status after bankruptcy, i.e., free of most debts. (Giving debtors a fresh start is one purpose of the Bankruptcy Code.)
A body of 16-23 citizens who listen to evidence of criminal allegations, which is presented by the prosecutors, and determine whether there is probable cause to believe an individual committed an offense. See also indictment and U.S. attorney.
Latin, meaning "you have the body." A writ of habeas corpus generally is a judicial order forcing law enforcement authorities to produce a prisoner they are holding, and to justify the prisoner's continued confinement. Federal judges receive petitions for a writ of habeas corpus from state prison inmates who say their state prosecutions violated federally protected rights in some way.
Evidence presented by a witness who did not see or hear the incident in question but heard about it from someone else. With some exceptions, hearsay generally is not admissible as evidence at trial
A special condition the court imposes that requires an individual to remain at home except for certain approved activities such as work and medical appointments. Home confinement may include the use of electronic monitoring equipment – a transmitter attached to the wrist or the ankle – to help ensure that the person stays at home as required.
1. The process of calling a witness's testimony into doubt. For example, if the attorney can show that the witness may have fabricated portions of his testimony, the witness is said to be "impeached;" 2. The constitutional process whereby the House of Representatives may "impeach" (accuse of misconduct) high officers of the federal government, who are then tried by the Senate.
Latin, meaning in a judge's chambers. Often means outside the presence of a jury and the public. In private.
"In the manner of a pauper." Permission given by the court to a person to file a case without payment of the required court fees because the person cannot pay them.
Evidence indicating that a defendant did commit the crime.
The formal charge issued by a grand jury stating that there is enough evidence that the defendant committed the crime to justify having a trial; it is used primarily for felonies. See also information.
A formal accusation by a government attorney that the defendant committed a misdemeanor. See also indictment.
A court order preventing one or more named parties from taking some action. A preliminary injunction often is issued to allow fact-finding, so a judge can determine whether a permanent injunction is justified.
A director, officer, or person in control of the debtor; a partnership in which the debtor is a general partner; a general partner of the debtor; or a relative of a general partner, director, officer, or person in control of the debtor.
Any relative of the debtor or of a general partner of the debtor; partnership in which the debtor is a general partner; general partner of the debtor; or corporation of which the debtor is a director, officer, or person in control.
A form of discovery consisting of written questions to be answered in writing and under oath.
1. The disputed point between parties in a lawsuit; 2. To send out officially, as in a court issuing an order.
A court-approved mechanism under which two or more cases can be administered together. (Assuming no conflicts of interest, these separate businesses or individuals can pool their resources, hire the same professionals, etc.)
One bankruptcy petition filed by a husband and wife together.
An official of the Judicial branch with authority to decide lawsuits brought before courts. Used generically, the term judge may also refer to all judicial officers, including Supreme Court justices.
The position of judge. By statute, Congress authorizes the number of judgeships for each district and appellate court.
The official decision of a court finally resolving the dispute between the parties to the lawsuit.
The policy-making entity for the federal court system. A 27-judge body whose presiding officer is the Chief Justice of the United States.
The legal authority of a court to hear and decide a certain type of case. It also is used as a synonym for venue, meaning the geographic area over which the court has territorial jurisdiction to decide cases.
The study of law and the structure of the legal system
The group of persons selected to hear the evidence in a trial and render a verdict on matters of fact. See also grand jury.
A judge's directions to the jury before it begins deliberations regarding the factual questions it must answer and the legal rules that it must apply.
A legal action started by a plaintiff against a defendant based on a complaint that the defendant failed to perform a legal duty which resulted in harm to the plaintiff.
A charge on specific property that is designed to secure payment of a debt or performance of an obligation. A debtor may still be responsible for a lien after a discharge.
A creditor's claim for a fixed amount of money.
The sale of a debtor's property with the proceeds to be used for the benefit of creditors.
A case, controversy, or lawsuit. Participants (plaintiffs and defendants) in lawsuits are called litigants.
A judicial officer of a district court who conducts initial proceedings in criminal cases, decides criminal misdemeanor cases, conducts many pretrial civil and criminal matters on behalf of district judges, and decides civil cases with the consent of the parties.
Section 707(b)(2) of the Bankruptcy Code applies a "means test" to determine whether an individual debtor's chapter 7 filing is presumed to be an abuse of the Bankruptcy Code requiring dismissal or conversion of the case (generally to chapter 13). Abuse is presumed if the debtor's aggregate current monthly income (see definition above) over 5 years, net of certain statutorily allowed expenses is more than (i) $10,000, or (ii) 25% of the debtor's nonpriority unsecured debt, as long as that amount is at least $6,000. The debtor may rebut a presumption of abuse only by a showing of special circumstances that justify additional expenses or adjustments of current monthly income.
Special condition the court imposes to require an individual to undergo evaluation and treatment for a mental disorder. Treatment may include psychiatric, psychological, and sex offense-specific evaluations, inpatient or outpatient counseling, and medication.
An offense punishable by one year of imprisonment or less. See also felony.
An invalid trial, caused by fundamental error. When a mistrial is declared, the trial must start again with the selection of a new jury.
Not subject to a court ruling because the controversy has not actually arisen, or has ended
A request by a litigant to a judge for a decision on an issue relating to the case.
A pretrial motion requesting the court to prohibit the other side from presenting, or even referring to, evidence on matters said to be so highly prejudicial that no steps taken by the judge can prevent the jury from being unduly influenced.
A request by a creditor to allow the creditor to take action against the debtor or the debtor's property that would otherwise be prohibited by the automatic stay.
A Chapter 7 case in which there are no assets available to satisfy any portion of the creditors' unsecured claims.
No contest. A plea of nolo contendere has the same effect as a plea of guilty, as far as the criminal sentence is concerned, but may not be considered as an admission of guilt for any other purpose.
A debt that cannot be eliminated in bankruptcy. Examples include a home mortgage, debts for alimony or child support, certain taxes, debts for most government funded or guaranteed educational loans or benefit overpayments, debts arising from death or personal injury caused by driving while intoxicated or under the influence of drugs, and debts for restitution or a criminal fine included in a sentence on the debtor's conviction of a crime. Some debts, such as debts for money or property obtained by false pretenses and debts for fraud or defalcation while acting in a fiduciary capacity may be declared nondischargeable only if a creditor timely files and prevails in a nondischargeability action.
Property of a debtor that can be liquidated to satisfy claims of creditors.
A trustee's or creditor's objection to the debtor being released from personal liability for certain dischargeable debts. Common reasons include allegations that the debt to be discharged was incurred by false pretenses or that debt arose because of the debtor's fraud while acting as a fiduciary.
A trustee's or creditor's objection to the debtor's attempt to claim certain property as exempt from liquidation by the trustee to creditors.
A judge's written explanation of the decision of the court. Because a case may be heard by three or more judges in the court of appeals, the opinion in appellate decisions can take several forms. If all the judges completely agree on the result, one judge will write the opinion for all. If all the judges do not agree, the formal decision will be based upon the view of the majority, and one member of the majority will write the opinion. The judges who did not agree with the majority may write separately in dissenting or concurring opinions to present their views. A dissenting opinion disagrees with the majority opinion because of the reasoning and/or the principles of law the majority used to decide the case. A concurring opinion agrees with the decision of the majority opinion, but offers further comment or clarification or even an entirely different reason for reaching the same result. Only the majority opinion can serve as binding precedent in future cases. See also precedent.
An opportunity for lawyers to summarize their position before the court and also to answer the judges' questions.
1. In appellate cases, a group of judges (usually three) assigned to decide the case; 2. In the jury selection process, the group of potential jurors; 3. The list of attorneys who are both available and qualified to serve as court-appointed counsel for criminal defendants who cannot afford their own counsel.
The release of a prison inmate – granted by the U.S. Parole Commission – after the inmate has completed part of his or her sentence in a federal prison. When the parolee is released to the community, he or she is placed under the supervision of a U.S. probation officer.
The Sentencing Reform Act of 1984 abolished parole in favor of a determinate sentencing system in which the sentence is set by sentencing guidelines. Now, without the option of parole, the term of imprisonment the court imposes is the actual time the person spends in prison.
A party who has standing to be heard by the court in a matter to be decided in the bankruptcy case. The debtor, U.S. trustee or bankruptcy administrator, case trustee, and creditors are parties in interest for most matters.
Latin, meaning "for the court." In appellate courts, often refers to an unsigned opinion.
A district court may grant each side in a civil or criminal trial the right to exclude a certain number of prospective jurors without cause or giving a reason.
A group of citizens who hear the evidence presented by both sides at trial and determine the facts in dispute. Federal criminal juries consist of 12 persons. Federal civil juries consist of at least six persons.
The document that initiates the filing of a bankruptcy proceeding, setting forth basic information regarding the debtor, including name, address, chapter under which the case is filed, and estimated amount of assets and liabilities.
A business not authorized to practice law that prepares bankruptcy petitions.
A federal misdemeanor punishable by six months or less in prison.
A person or business that files a formal complaint with the court.
In a criminal case, the defendant's statement pleading "guilty" or "not guilty" in answer to the charges. See also nolo contendere.
Written statements filed with the court that describe a party's legal or factual assertions about the case.
A transfer of the debtor's property made after the commencement of the case.
The arrangement (or rearrangement) of a debtor's property to allow the debtor to take maximum advantage of exemptions. (Prebankruptcy planning typically includes converting nonexempt assets into exempt assets.)
A court decision in an earlier case with facts and legal issues similar to a dispute currently before a court. Judges will generally "follow precedent" - meaning that they use the principles established in earlier cases to decide new cases that have similar facts and raise similar legal issues. A judge will disregard precedent if a party can show that the earlier case was wrongly decided, or that it differed in some significant way from the current case.
A debt payment made to a creditor in the 90-day period before a debtor files bankruptcy (or within one year if the creditor was an insider) that gives the creditor more than the creditor would receive in the debtor's chapter 7 case.
A report prepared by a court's probation officer, after a person has been convicted of an offense, summarizing for the court the background information needed to determine the appropriate sentence.
A meeting of the judge and lawyers to plan the trial, to discuss which matters should be presented to the jury, to review proposed evidence and witnesses, and to set a trial schedule. Typically, the judge and the parties also discuss the possibility of settlement of the case.
A function of the federal courts that takes place at the very start of the criminal justice process – after a person has been arrested and charged with a federal crime and before he or she goes to trial. Pretrial services officers focus on investigating the backgrounds of these persons to help the court determine whether to release or detain them while they await trial. The decision is based on whether these individuals are likely to flee or pose a threat to the community. If the court orders release, a pretrial services officer supervises the person in the community until he or she returns to court.
The Bankruptcy Code's statutory ranking of unsecured claims that determines the order in which unsecured claims will be paid if there is not enough money to pay all unsecured claims in full.
An unsecured claim that is entitled to be paid ahead of other unsecured claims that are not entitled to priority status. Priority refers to the order in which these unsecured claims are to be paid.
A slang expression sometimes used to refer to a pro se litigant. It is a corruption of the Latin phrase "in propria persona."
Representing oneself. Serving as one's own lawyer.
Sentencing option in the federal courts. With probation, instead of sending an individual to prison, the court releases the person to the community and orders him or her to complete a period of supervision monitored by a U.S. probation officer and to abide by certain conditions.
Officers of the probation office of a court. Probation officer duties include conducting presentence investigations, preparing presentence reports on convicted defendants, and supervising released defendants.
The rules for conducting a lawsuit; there are rules of civil procedure, criminal procedure, evidence, bankruptcy, and appellate procedure.
A written statement describing the reason a debtor owes a creditor money, which typically sets forth the amount of money owed. (There is an official form for this purpose.)
All legal or equitable interests of the debtor in property as of the commencement of the case.
To charge someone with a crime. A prosecutor tries a criminal case on behalf of the government
An agreement by a debtor to continue paying a dischargeable debt after the bankruptcy, usually for the purpose of keeping collateral or mortgaged property that would otherwise be subject to repossession.
A written account of the proceedings in a case, including all pleadings, evidence, and exhibits submitted in the course of the case.
A procedure in a Chapter 7 case whereby a debtor removes a secured creditor's lien on collateral by paying the creditor the value of the property. The debtor may then retain the property.
The act of a court setting aside the decision of a lower court. A reversal is often accompanied by a remand to the lower court for further proceedings.
A penalty or other type of enforcement used to bring about compliance with the law or with rules and regulations.
Lists submitted by the debtor along with the petition (or shortly thereafter) showing the debtor's assets, liabilities, and other financial information. (There are official forms a debtor must use.)
A secured creditor is an individual or business that holds a claim against the debtor that is secured by a lien on property of the estate. The property subject to the lien is the secured creditor's collateral.
Debt backed by a mortgage, pledge of collateral, or other lien; debt for which the creditor has the right to pursue specific pledged property upon default. Examples include home mortgages, auto loans and tax liens.
A federal judge who, after attaining the requisite age and length of judicial experience, takes senior status, thus creating a vacancy among a court's active judges. A senior judge retains the judicial office and may cut back his or her workload by as much as 75 percent, but many opt to keep a larger caseload.
The punishment ordered by a court for a defendant convicted of a crime.
A set of rules and principles established by the United States Sentencing Commission that trial judges use to determine the sentence for a convicted defendant.
To separate. Sometimes juries are sequestered from outside influences during their deliberations.
The delivery of writs or summonses to the appropriate party.
Parties to a lawsuit resolve their dispute without having a trial. Settlements often involve the payment of compensation by one party in at least partial satisfaction of the other party's claims, but usually do not include the admission of fault.
A special type of chapter 11 case in which there is no creditors' committee (or the creditors' committee is deemed inactive by the court) and in which the debtor is subject to more oversight by the U.S. trustee than other chapter 11 debtors. The Bankruptcy Code contains certain provisions designed to reduce the time a small business debtor is in bankruptcy.
Degree of proof required. In criminal cases, prosecutors must prove a defendant's guilt "beyond a reasonable doubt." The majority of civil lawsuits require proof "by a preponderance of the evidence" (50 percent plus), but in some the standard is higher and requires "clear and convincing" proof.
A series of questions the debtor must answer in writing concerning sources of income, transfers of property, lawsuits by creditors, etc. (There is an official form a debtor must use.)
A declaration made by a chapter 7 debtor concerning plans for dealing with consumer debts that are secured by property of the estate.
A law passed by a legislature.
The time within which a lawsuit must be filed or a criminal prosecution begun. The deadline can vary, depending on the type of civil case or the crime charged.
Latin, meaning "of its own will." Often refers to a court taking an action in a case without being asked to do so by either side.
The act or process by which a person's rights or claims are ranked below those of others.
A command, issued under a court's authority, to a witness to appear and give testimony.
A command to a witness to appear and produce documents.
Akin to a preliminary injunction, it is a judge's short-term order forbidding certain actions until a full hearing can be conducted. Often referred to as a TRO.
Evidence presented orally by witnesses during trials or before grand juries.
See statute of limitations.
A civil, not criminal, wrong. A negligent or intentional injury against a person or property, with the exception of breach of contract.
A written, word-for-word record of what was said, either in a proceeding such as a trial, or during some other formal conversation, such as a hearing or oral deposition
Any mode or means by which a debtor disposes of or parts with his/her property.
The representative of the bankruptcy estate who exercises statutory powers, principally for the benefit of the unsecured creditors, under the general supervision of the court and the direct supervision of the U.S. trustee or bankruptcy administrator. The trustee is a private individual or corporation appointed in all chapter 7, chapter 12, and chapter 13 cases and some chapter 11 cases. The trustee's responsibilities include reviewing the debtor's petition and schedules and bringing actions against creditors or the debtor to recover property of the bankruptcy estate. In chapter 7, the trustee liquidates property of the estate, and makes distributions to creditors. Trustees in chapter 12 and 13 have similar duties to a chapter 7 trustee and the additional responsibilities of overseeing the debtor's plan, receiving payments from debtors, and disbursing plan payments to creditors.
A lawyer appointed by the President in each judicial district to prosecute and defend cases for the federal government. The U.S. Attorney employs a staff of Assistant U.S. Attorneys who appear as the government's attorneys in individual cases.
An officer of the U.S. Department of Justice responsible for supervising the administration of bankruptcy cases, estates, and trustees; monitoring plans and disclosure statements; monitoring creditors' committees; monitoring fee applications; and performing other statutory duties.
A debt secured by property that is worth less than the amount of the debt.
The most widely used test for evaluating undue hardship in the dischargeability of a student loan includes three conditions: (1) the debtor cannot maintain – based on current income and expenses – a minimal standard of living if forced to repay the loans; (2) there are indications that the state of affairs is likely to persist for a significant portion of the repayment period; and (3) the debtor made good faith efforts to repay the loans.
A lawsuit brought by a landlord against a tenant to evict the tenant from rental property – usually for nonpayment of rent.
A claim for which a specific value has not been determined.
A debt that should have been listed by the debtor in the schedules filed with the court but was not. (Depending on the circumstances, an unscheduled debt may or may not be discharged.)
A claim or debt for which a creditor holds no special assurance of payment, such as a mortgage or lien; a debt for which credit was extended based solely upon the creditor's assessment of the debtor's future ability to pay.
The appellate court agrees with the lower court decision and allows it to stand. See affirmed.
The geographic area in which a court has jurisdiction. A change of venue is a change or transfer of a case from one judicial district to another.
The decision of a trial jury or a judge that determines the guilt or innocence of a criminal defendant, or that determines the final outcome of a civil case.
Jury selection process of questioning prospective jurors, to ascertain their qualifications and determine any basis for challenge.
A transfer of a debtor's property with the debtor's consent.
A nonbankruptcy legal proceeding whereby a plaintiff or creditor seeks to subject to his or her claim the future wages of a debtor. In other words, the creditor seeks to have part of the debtor's future wages paid to the creditor for a debt owed to the creditor.
Court authorization, most often for law enforcement officers, to conduct a search or make an arrest.
A person called upon by either side in a lawsuit to give testimony before the court or jury.
A written court order directing a person to take, or refrain from taking, a certain act.
An order issued by the U.S. Supreme Court directing the lower court to transmit records for a case which it will hear on appeal.
A Case Study: Translation of Legal Terms
- First Online: 13 January 2023
Cite this chapter

- Xiaobo Dong 3 &
- Yafang Zhang 3
160 Accesses
One of the difficulties in legal English translation lies in how translators understand and convey legal terminology. For one reason, it requires functional equivalence in language; for another, legal functional equivalence is also needed. According to the Equivalence Theory of Sarcevic and given the different levels of language and legal functional equivalence in the corresponding words from the source language to the target language, the following measures can be taken in legal terminology translation: using the exact words when concepts are equivalent; using functional equivalent words when concepts are nearly or partly equivalent; using paraphrase, neutral, borrowed or new words when concepts are totally different.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Bao, K. (2011). On the unequivalence of English and Chinese legal terms and their translation strategies. Chinese Science and Technology Translators Journal, 4 , 32–34.
Google Scholar
Chen, Z. (2000). Laws translation . China Legal Publishing House.
Dong, X. (2011). Translation of legal texts . University of International Business and Economics Press.
Du, J. (2004). Forensic linguistics . Shanghai Foreign Language Education Press.
Garner, B. A. (2004). Black’s law dictionary (8th ed.). Thomson West Group.
Li, K., & Zhang, X. (2006). Legal texts and legal translation . China Translation and Publishing Corporation.
Liang, S. (2014). A study of textual translation and the subjectivity of translators from the perspective of intertextuality. Research, 9 , 120–124.
Liu, R. (2010). On the accuracy of legal terminology translation. Foreign Language Research, 4 , 125–127.
Sarcevic, S. (1997). New approaches to legal translation . Kluwer Law International.
Tan, F., & Xiang, H. (2012). Cross-cultural translation of legal English terms from functional equivalence theory perspective. Contemporary Foreign Languages Studies, 10 , 52–55.
Xiao, Y. (2001). The characteristics, etymology and translation of English and Chinese legal terms. Chinese Translators Journal, 3 , 44–47.
Xiong, D. (2010). “Prometheus” in legal translation in late Qing Dynasty and its special contribution. Foreign Language Education, 5 , 94–97.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
Xiaobo Dong & Yafang Zhang
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Xiaobo Dong .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Dong, X., Zhang, Y. (2023). A Case Study: Translation of Legal Terms. In: Chinese Legal Translation and Language Planning in the New Era. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-8448-8_7
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-8448-8_7
Published : 13 January 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-19-8447-1
Online ISBN : 978-981-19-8448-8
eBook Packages : Social Sciences Social Sciences (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
What is a Master of Studies in Law? Explore the George Washington University Law School MSL

You don’t have to be a lawyer to earn a living understanding and applying the law. Many professions require — or benefit significantly from — a thorough understanding of how the law impacts an industry or institution. The Master of Studies in Law (MSL), a graduate-level law degree designed for non-lawyers, can prepare you for a career interpreting and navigating legal situations.
You can earn an MSL 100% online from the George Washington University Law School (GW Law); you also have the option to take courses on-campus. The program offers specializations online in three areas: government procurement law, national security and cybersecurity law, and government procurement and cybersecurity law. The university’s location in the heart of Washington, D.C. enables students to benefit from access to the center of national legal and political activity — without ever having to leave their hometowns.
Gain Legal Expertise to Propel Your Career
Choose from three msl concentrations at gw law.
If you aspire to a career engaging with the law, you may be wondering whether a Master of Studies in Law is the right degree for you. How does the MSL differ from the Juris Doctor (JD), the law degree pursued by aspiring attorneys? What careers does each degree facilitate? This article explores those questions to help you decide which option better suits your career goals.
Master of Studies in Law vs. Juris Doctor: Decoding the Differences
A Master of Studies in Law is a master’s-level graduate degree in law and legal systems. A Juris Doctor is a terminal degree at the doctoral level that qualifies recipients to work in the courts as lawyers and judges. Admissions requirements, coursework, and career opportunities for the degrees differ substantially.
Applicants to GW’s MSL program must hold a bachelor’s degree and three to five years of professional experience relevant to the specialization they choose to pursue. Acceptance into a JD program requires a bachelor’s degree and an acceptable score on the Law School Admission Test (LSAT) .
Coursework in the degree programs overlaps somewhat, but the JD is undoubtedly the more comprehensive and detailed of the two. GW’s MSL program requires 24 credit hours of coursework, which can be completed in as few as 12 months (for full-time students). A JD requires 80 credit hours and includes a rigorous first-year law student curriculum, with courses such as Torts, Property, and Contracts. Full-time JD students typically take three years to complete their degrees, after which they must pass their state’s bar exam.
Your professional goals will dictate which degree you choose. JD graduates are trained to practice law (after successfully passing a state or DC bar examination); they typically pursue careers as lawyers, judges and legal scholars. An MSL can be helpful in professions in such varied fields as government, business, finance, real estate, court administration, mediation, insurance, policy, and nongovernmental organizations. Practically every field intersects with the law, creating career opportunities for MSL degree holders.
What Will You Learn in MSL Programs?
Graduates of George Washington University’s Master of Studies in Law are prepared to communicate with lawyers and competently address industry compliance and regulatory issues. Students pursue the specialization most compatible with their current professional experience:
- Government Procurement Law examines how procurement systems operate and the laws and regulations that govern them in the U.S. and abroad. Classwork includes anti-corruption, intellectual property and procurement reform.
- National Security & Cybersecurity Law thoroughly examines legal and policy issues surrounding national security, cybersecurity, AI, big data and new technologies. Classes cover internet law, foreign access to U.S. technology, and artificial intelligence law.
- Government Procurement & Cybersecurity Law prepares professionals to address the rising demand for cybersecurity legal expertise in government procurement law. Topics include cybersecurity law and technology, consumer privacy and data protection, and government procurement of intellectual property.
In all fields, the MSL degree prepares graduates to address challenges from a legal perspective, communicate with lawyers and non-lawyers alike, and assess the legal ramifications of corporate and institutional issues.
Career Pathways with a Master of Studies in Law
An MSL can be especially beneficial for people who work in highly regulated fields, such as government, healthcare, education, nonprofits, manufacturing and finance. Anyone who communicates frequently with lawyers can also benefit from an MSL. Graduates of GW’s MSL program have gone on to work for various employers, including:
- Department of Defense
- Department of Homeland Security
- General Dynamics
- General Services Administration (GSA)
- Lockheed Martin
- Northrop Grumman
Is an MSL the Right Fit for Your Professional Goals?
The GW Law online MSL serves non-lawyer professionals whose work requires a detailed knowledge of the law. An MSL can benefit compliance officers, consultants, government managers, intelligence community analysts, journalists, policy analysts, and procurement specialists, to name just a few.
George Washington University Law School’sMSL program provides the theoretical and practical knowledge necessary to apply the law to today’s organizational legal challenges. Located in our nation’s capital with flexible options to attend from any location, GW Law’s MSL degree delivers a strong law curriculum, respected faculty experts, academic peers from across the globe and over 33,000 living alumni for networking, advice and career development.
If you are ready to explore the law and find your place within it, contact an admissions adviser to learn more about the MSL program or start your application .
Become a Source of Valued Legal Insight in Your Workplace
Learn to identify and address legal risks.
Tell us about yourself.
Sharing some details will help us customize your experience. A bachelor’s degree is required to attend.
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
What a judge’s gag order on Trump means in his hush money case
The judge overseeing Donald Trump’s New York hush money trial has clarified the gag order pertaining to the ex-president doesn’t prohibit him from testifying on his own behalf.

Donald Trump has been fined $9,000 for repeatedly violating a gag order that barred him from making public statements about witnesses, jurors and some others connected to his New York hush money case.
FILE - Former President Donald Trump speaks outside the courtroom in New York, April 30, 2024. A gag order bars him from making public comments on witnesses, jurors and some others connected to the case. The judge found that Trump repeatedly violated the order and he fined Trump $9,000 and warned that jail could follow if Trump keeps it up. The order doesn’t stop Trump from talking about the allegations against him or commenting on the judge or the elected top prosecutor. And it doesn’t stop him from testifying in court if he chooses. (Justin Lane/Pool Photo via AP, File)
- Copy Link copied
Former President Donald Trump returns to the courtroom following a break in his trial at Manhattan criminal court in New York, on Friday, May 3, 2024. (Charly Triballeau/Pool Photo via AP)
Former President Donald Trump speaks to media as he returns to his trial at the Manhattan Criminal Court, Friday, May 3, 2024, in New York. (Curtis Means/Pool Photo via AP)
Former President Donald Trump speaks to media as he returns to his trial at the Manhattan Criminal Court, Friday, May 3, 2024, in New York. (Charly Triballeau/Pool Photo via AP)
NEW YORK (AP) — Virtually every day of his hush money criminal trial , former President Donald Trump talks about how he can’t talk about the case.
A gag order bars Trump from commenting publicly on witnesses, jurors and some others connected to the matter. The New York judge already has found that Trump, the presumptive Republican nominee for president, repeatedly violated the order, fined him $9,000 and warning that jail could follow if he doesn’t comply.
What to know about Trump’s hush money trial:
- Follow AP’s live updates as the third week of testimony draws to a close.
- A guide to terms used in the Trump trial.
- Trump is the first ex-president on criminal trial. Here’s what to know about the hush money case.
- Trump is facing four criminal indictments, and a civil lawsuit. You can track all of the cases here.
But the order doesn’t stop Trump from talking about the allegations against him or commenting on the judge or the elected top prosecutor. And despite a recent Trump remark, it doesn’t stop him from testifying in court if he chooses .
As he fights the felony charges against him while running for president, Trump has at times stirred confusion about what he can and can’t do in the case. He has pleaded not guilty.
So what does the order do, what doesn’t it and where did it come from?
WHAT IS A GAG ORDER?
Generally speaking, a gag order is a judge’s directive prohibiting someone or people involved in a court case from publicly commenting about some or all aspects of it. In Trump’s case, it’s titled an “Order Restricting Extrajudicial Statements,” with “extrajudicial” meaning outside of court.
Gag orders, particularly in high-profile cases, are intended to prevent information presented outside a courtroom from affecting what happens inside.
Trump also is subject to a gag order in his federal criminal election interference case in Washington. That order limits what he can say about witnesses, lawyers in the case and court staff, though an appeals court freed him to speak about special counsel Jack Smith, who brought the case.
In his recent New York civil fraud trial , Trump was fined a total of $15,000 for comments he made about that judge’s law clerk after a gag order barred participants in the trial from “posting, emailing or speaking publicly” about the court’s staff.
The U.S. Supreme Court has acknowledged that gag orders can pit fair trial rights against free speech rights. The court has struck down some orders that barred the press from reporting on certain cases or court proceedings and rejected as too vague a Nevada court rule that limited what all lawyers could say out of court.
IS TRUMP FIGHTING THE GAG ORDER?
Yes. Before the trial, he asked a state appeals court to postpone the trial while he appeals the gag order , but the court refused. His appeal of the order itself is ongoing.
WHO IS COVERED BY THE GAG ORDER ON TRUMP?
Initially imposed March 26 , the gag order bars Trump from making or directing others to make public statements about any juror and about any “reasonably foreseeable” witness’ participation in the investigation or the trial.
It also bars any statements about lawyers in the case, court staffers, prosecution aides and relatives of all of the above, to the extent that the statements are intended to “materially interfere with, or to cause others to materially interfere with” their work on the case “or with the knowledge that such interference is likely to result.”
The order doesn’t apply to Judge Juan M. Merchan or to Manhattan District Attorney Alvin Bragg, whose office is bringing the case. It does apply to comments about their family members, however. Merchan added that provision on April 1 after Trump lashed out on social media at the judge’s daughter , a Democratic political consultant, and made a claim about her that was later repudiated by court officials.
Trump is also allowed to talk about his political opponents, as Merchan made clear on Thursday.
The order also doesn’t bar witnesses from commenting on Trump. Michael Cohen, Trump’s ex-lawyer and an expected witness, has routinely attacked his former boss, leading Trump to complain about not being able to respond in kind.
CAN TRUMP TESTIFY?
Yes. The U.S. Supreme Court has held that criminal defendants have a constitutional right to take the stand in their own defense — or not to .
There was some confusion after Trump said Thursday that because of the gag order, he was “not allowed to testify.” In context, it appeared he was actually referring to his ability to respond to a reporter’s court-hallway question about a witness’ testimony that afternoon.
Trump clarified to reporters Friday that he understood the order wasn’t a bar on testifying. Merchan emphasized the same in court.
“I want to stress, Mr. Trump, you have an absolute right to testify at trial, if that’s what you decide to do after consultation with your attorneys,” Merchan said.
WHY DID TRUMP GET FINED? WHAT CAN’T HE SAY?
Merchan found that Trump violated the gag order with social media posts that laid into Cohen. Among the offending posts: one that asked whether “disgraced attorney and felon Michael Cohen been prosecuted for LYING,” a repost of a New York Post article that described Cohen as a “serial perjurer,” and a Trump post referring to Fox News host Jesse Watters’ claim that liberal activists were lying to infiltrate the jury.
Merchan noted that Trump’s comment on the Watters segment misstated what the host had actually said, making the comment “the words of Defendant himself.”
On the other hand, Merchan declined to sanction Trump for an April 10 post that referred to Cohen and Stormy Daniels, the porn performer who got a $130,000 hush money payment that’s at the heart of the case, as “sleaze bags.”
Trump contended that he was responding to previous comments by Cohen, and the judge said the back-and-forth gave him pause as to whether that post met the bar for a violation.
COULD TRUMP REALLY GO TO TO JAIL OVER THE GAG ORDER?
When Merchan fined Trump $1,000 apiece for nine violations — the maximum fine allowed by law — he wrote that “jail may be a necessary punishment” for some wealthy defendants who won’t be deterred by such a sum.
Merchan added that he “will not tolerate continued willful violations” of the gag order and that, if “necessary and appropriate,” he “will impose an incarceratory punishment,” meaning jail.
It’s unclear what would rise to the level of “necessary and appropriate.”
Defense lawyer Todd Blanche indicated in court Friday that he plans to appeal the judge’s finding this past week that Trump violated the gag order.
Prosecutors have asked Merchan to hold Trump in contempt again and fine him $1,000 for each of four alleged violations from April 22-25. But the prosecution isn’t asking for the former president to be locked up over those comments because they happened before Merchan’s jail warning and because “we’d prefer to minimize disruption to this proceeding,” prosecutor Christopher Conroy said.
Advertisement
Tracking Abortion Bans Across the Country
By The New York Times Updated May 1, 4:40 P.M. ET
- Share full article
Twenty-one states ban abortion or restrict the procedure earlier in pregnancy than the standard set by Roe v. Wade, which governed reproductive rights for nearly half a century until the Supreme Court overturned the decision in 2022.
In some states, the fight over abortion access is still taking place in courtrooms, where advocates have sued to block bans and restrictions. Other states have moved to expand access to abortion by adding legal protections.
Latest updates
- The Arizona state legislature voted to repeal an 1864 ban on nearly all abortions. Officials warned that the near-total ban may be briefly enforceable this summer until the repeal takes effect in the fall. A 15-week ban remains in effect.
- A ban on abortion after about six weeks of pregnancy took effect in Florida , following a ruling by the Florida Supreme Court that the privacy protections of the state’s Constitution do not extend to abortion.
The New York Times is tracking abortion laws in each state after the Supreme Court’s decision in Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization , which ended the constitutional right to an abortion.
Where abortion is legal
In a few states that have enacted bans or restrictions, abortion remains legal for now as courts determine whether these laws can take effect. Abortion is legal in the rest of the country, and many states have added new protections since Dobbs.
Ban in effect
Note: TK note here.
Legal for now
State details.
More details on the current status of abortion in each state are below.
An earlier version of this article misstated the legal status of abortion in Utah. As of 4 p.m. on June 24, the state attorney general had issued a statement saying the state’s abortion ban had been triggered, but it had not yet been authorized by the legislature’s general counsel. By 8:30 p.m., the counsel authorized the ban and it went into effect.
A table in an earlier version of this article misstated which abortion ban is being challenged in Texas state court. Abortion rights supporters are challenging a pre-Roe ban, not the state’s trigger ban.
An earlier version of this article referred incorrectly to the legal status of abortion in Indiana. While Indiana abortion providers stopped offering abortion services in anticipation of an abortion ban taking effect on Aug. 1, the law did not take effect.
Farmers With Easements Given Safe Harbor Under Wetlands Rule
By Bobby Magill

Upper Midwest farmers who put their land under a conservation easement will be given safe harbor from legal action if they follow specific US Fish and Wildlife Service guidelines in case they accidentally drain certain wetlands unique to the region, according to a rule scheduled to be finalized on May 13.
The Fish and Wildlife Service’s final Drain Tile Setbacks Rule uses conservation easements on farmland to protect wetlands in the Prairie Pothole Region of Iowa, Minnesota, Montana, North Dakota and South Dakota.
The region is pocked with wetlands in prairie depressions formed through glaciation thousands of years ago that ...
Learn more about Bloomberg Law or Log In to keep reading:
Learn about bloomberg law.
AI-powered legal analytics, workflow tools and premium legal & business news.
Already a subscriber?
Log in to keep reading or access research tools.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Introduction. Each branch of government produces a different type of law. Case law is the body of law developed from judicial opinions or decisions over time (whereas statutory law comes from legislative bodies and administrative law comes from executive bodies). This guide introduces beginner legal researchers to resources for finding judicial ...
This article reviews classic and contemporary case study research in law and social science. Taking as its starting point that legal scholars engaged in case studies generally have a set of questions distinct from those using other research approaches, the essay offers a detailed discussion of three primary contributions of case studies in legal scholarship: theory building, concept formation ...
While we have not yet seen a study on the efficacy of the case study method vs. the Langdell method in law schools, research from political science professor Matthew Krain suggests that case studies and problem-based activities do enhance certain types of learning over other types of pedagogy. In his investigation, Krain compared the results of ...
Introduction. Every law student and practicing attorney must be able to find, read, analyze, and interpret case law. Under the common law principles of stare decisis, a court must follow the decisions in previous cases on the same legal topic. Therefore, finding cases is essential to finding out what the law is on a particular issue.
The Case Study Teaching Method. It is easy to get confused between the case study method and the case method, particularly as it applies to legal education. The case method in legal education was invented by Christopher Columbus Langdell, Dean of Harvard Law School from 1870 to 1895. Langdell conceived of a way to systematize and simplify legal ...
Cases, in turn, interpret those statutes and regulations. Cases may be the sole source of the law when the doctrine is strictly a common law doctrine. Even when law is based on a statute, cases interpreting the terms and intent of the statute are invaluable tools for legal writers. Some methods for using cases, discussed in detail below ...
case law. Case law is law that is based on judicial decisions rather than law based on constitutions, statutes, or regulations. Case law concerns unique disputes resolved by courts using the concrete facts of a case. By contrast, statutes and regulations are written abstractly. Case law, also used interchangeably with common law, refers to the ...
Case Study Research. Last update: April 07, 2022. A legal scholar who uses the term 'case' will probably first think of a legal case. From a socio-legal perspective, the understanding of this concept is, however, slightly different. Case study research is a methodology that is useful to study 'how' or 'why' questions in real-life.
Harvard Education Press provides access to cases in higher education and K-12 education. Topics include administration and finance, curriculum development, external relations and public affairs, faculty, human resources, leadership, marketing, planning, student affairs, data use, and community organizing. Harvard Kennedy School Case Program.
These case studies expose participants to real-world problems that lawyers and firm leaders confront, and help them work through possible approaches and solutions. CDI was founded by Professor Ashish Nanda and is now directed by Dr. Lisa Rohrer. Great for: discussion-based case studies, law and business, management, professional development.
The case method eschews explanation and encourages exploration. In a course that relies entirely on the casebook, you will never come across a printed list of "laws." Indeed, you will learn that in many areas of law there is no such thing as a static set of rules, but only a constantly evolving system of principles.
Legal Terminology: Case Law. Appeal: To seek review by a higher court. (e.g. appeal trial court decisions to the appropriate higher court; appeal appellate court decisions to the appropriate highest court.) Appellant: One who brings the appeal of the lower court decision (the loser in the lower court).
The term case law refers to law that comes from decisions made by judges in previous cases. Case law, also known as "common law," and "case precedent," provides a common contextual background for certain legal concepts, and how they are applied in certain types of case.How much sway case law holds may vary by jurisdiction, and by the exact circumstances of the current case.
Case briefs are a necessary study aid in law school that helps to encapsulate and analyze the mountainous mass of material that law students must digest. The case brief represents a final product after reading a case, rereading it, taking it apart, and putting it back together again.
Case Study Law and Legal Definition. A case study involves a detailed intensive study of a unit. A case study can be of a person, a group or a social phenomenon. In order to seek patterns and causes for behavior in a case study, every aspect of a subject's life and history is analyzed. The purpose of case study is to generalize learned ...
March 15, 2023 · 5 minute read. Generally, there are two types of legal precedents: Binding precedent - Precedent that a court must abide by in its adjudication of a case. Persuasive precedent - Precedent that a court may, but is not required to, rely on in deciding a case. Definition taken from the Practical Law glossary pictured below.
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation. It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied.
The Texas State Law Library provides access to several case law databases that will allow you to conduct case law research online. These databases are complex and can be intimidating, but knowing a few tips will allow you to locate cases relevant to your research in no time at all. This page will discuss a few things you should keep in mind ...
A bankruptcy case in which the debtor is a business or an individual involved in business and the debts are for business purposes. Go to top. C Capital offense . A crime punishable by death. Case file . A complete collection of every document filed in court in a case. Case law . The law as established in previous court decisions.
A system of instruction or study of law focused upon the analysis of court opinions rather than lectures and textbooks; the predominant method of teaching in U.S. law schools today. Christopher Columbus Langdell, a law professor, often receives credit for inventing the case method although historians have found evidence that others were ...
Legal terms generally have the following characteristics: 1. The Meaning of Legal Terms Is Professional. Legal terminology is the core part of the legal system, and it's fixed down after the use of a long period of time in the gradual precipitation. A term may mean a legal concept (such as "object", "legal person", "person having no ...
In the translation of legal terms, we must first study the meaning of the source legal terms to be translated, compare the legal system involved, and try to find the target term with the same content. ... Dong, X., Zhang, Y. (2023). A Case Study: Translation of Legal Terms. In: Chinese Legal Translation and Language Planning in the New Era ...
The Master of Studies in Law (MSL), a graduate-level law degree designed for non-lawyers, can prepare you for a career interpreting and navigating legal situations. You can earn an MSL 100% online from the George Washington University Law School (GW Law); you also have the option to take courses on-campus. The program offers specializations ...
A guide to terms used in the Trump trial. Trump is the first ex-president on criminal trial. Here's what to know about the hush money case. Trump is facing four criminal indictments, and a civil lawsuit. You can track all of the cases here.
The Supreme Court is set to issue decisions in the coming weeks in more than a dozen cases involving issues like abortion, guns and sweeping immunity for former President Donald Trump.
Saturday, May 11, 2024 Seattle's Law Mandating Higher Pay for Food Delivery Workers Is a Case Study in Backfire Economics Seattle politicians chose to abandon sound free-market policies in favor of coercive wage controls—and workers, consumers, and small business owners are all paying the price.
State law protects abortion, but a 1984 law prohibits using state funds to cover the cost of most abortions. A 2023 law shields those seeking or providing abortions in Colorado from laws in other ...
The law would impose new disclosure rules and oblige these civic institutions to state they are "pursuing the interests of a foreign power." The model is Russia's foreign agent law, adopted ...
Upper Midwest farmers who put their land under a conservation easement will be given safe harbor from legal action if they follow specific US Fish and Wildlife Service guidelines in case they accidentally drain certain wetlands unique to the region, according to a rule scheduled to be finalized on May 13.