Your Complete Guide to Pursuing a PhD in Robotics: Scope, Schools & Careers
Embarking on a PhD in robotics positions you at the intersection of technology and innovation, opening pathways to academia, private sector research, and cutting-edge industry applications. In this straightforward guide, delve into the essential aspects of a Robotics PhD—including the scope, exemplary schools, and the promising careers it can lead to, ensuring you make an informed decision about your academic future.
Key Takeaways
A PhD in Robotics is an interdisciplinary program that blends computer science, engineering, and other related fields, focusing on cutting-edge research in areas such as machine learning, human-robot interaction, and autonomous systems, which prepares graduates for diverse careers in academia, research, or the private sector.
Top universities offering esteemed PhD programs in Robotics include Carnegie Mellon University, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and Stanford University, known for their outstanding faculty, comprehensive curricula, and innovative research opportunities.
The application process for a PhD in Robotics typically requires a bachelor’s or master’s degree in a related field, standardized test scores like the GRE, English proficiency tests for non-native speakers, recommendation letters, a statement of purpose, and in some cases, a resume.

Understanding PhD in Robotics: An Overview

Robotic technologies, now integral to our societies, are shaping a technological revolution. A PhD in Robotics provides the skills necessary to lead in this field. This program is an interdisciplinary blend of:
computer science
electrical and computer engineering
mathematics
mechanical engineering
This interdisciplinary approach, which includes systems engineering, offers students a comprehensive understanding of robotics, preparing them to contribute to a variety of sectors.
A key aspect of a doctoral program in Robotics is the focus on cutting-edge research. Some areas of research in these programs include:
Enhancing machine learning algorithms
Advancing human-robot interaction
Developing autonomous systems
Improving computer vision and perception
Designing and controlling robotic systems
These programs encourage students to push the boundaries of existing knowledge and technology.
The career opportunities post a PhD in Robotics are diverse and exciting. Graduates have the choice to pursue academia, engage in research, or utilize their skills within the private sector. From healthcare to manufacturing and autonomous vehicles, the demand for robotics expertise is growing, offering promising career prospects to Robotics PhD graduates.
Interdisciplinary Nature
The Robotics PhD program epitomizes the interdisciplinary study. It incorporates principles of computer science, engineering, and other related disciplines, creating a holistic view of robotics. This unique blend of disciplines fosters innovation and collaboration, empowering students to explore intricate problems and contribute to the advancement of robotics.
Research Focus
Research forms the backbone of any PhD program, and Robotics is no exception. The program motivates students to investigate various areas such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and computer vision. The objective is to equip students with the ability to conduct in-depth research, enabling them to solve complex problems and further advance knowledge in the field of robotics.
Career Opportunities
A PhD in Robotics opens a gateway to a plethora of career opportunities. Graduates can pursue:
Academic roles such as researchers and professors
Contribute to research and development in the private sector
Venture into sectors like healthcare and manufacturing.
As digitization proliferates worldwide, the need for robotics expertise escalates, suggesting that a Robotics PhD is a promising career pathway.
Top Universities Offering PhD Programs in Robotics

Several esteemed universities offer a PhD program in Robotics. Some of the notable institutions include Carnegie Mellon University, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), and Stanford University. These universities, celebrated for their outstanding faculty, broad curriculum, and pioneering research initiatives, are excellent choices for aspiring Robotics PhD students.
Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University’s Robotics Institute offers a renowned PhD program in Robotics. The program is recognized for its:
Interdisciplinary nature
Cutting-edge research initiatives
Faculty composed of eminent individuals
Cooperative opportunities for students
Empowerment of students to promote robotics advancement
Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT)
MIT’s Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) is distinguished for its Robotics PhD program. The program is recognized for its focus on robotic hardware and algorithms that incorporate sensing, control, perception, and manipulation. The distinguished faculty members guide students through their research journey, fostering innovation and excellence in robotics.
Stanford University
Stanford University’s Artificial Intelligence Laboratory offers a unique Robotics PhD program. The program presents unique research opportunities in areas like humanoid robots, bio-inspired robots, and cooperative robots. Guided by a team of esteemed faculty members, students are encouraged to push the boundaries of robotics research and contribute to its advancement.
Admission Requirements and Application Process

The admission requirements for a Robotics PhD program typically include:
A bachelor’s or master’s degree in a related field
Relevant coursework
Standardized tests like the GRE
TOEFL or IELTS for non-native English speakers
However, it’s important to note that the specific requirements may vary across universities.
The application process for a Robotics PhD program usually involves:
Submitting transcripts
Submitting recommendation letters
Submitting a statement of purpose
Some universities may also require a resume
Every university has unique application procedures and deadlines, thus checking the respective university’s website for precise information is necessary.
Prerequisites
Applicants for a Robotics PhD program usually need:
A strong foundation in mathematics
Proficiency in computer science, including programming and data analysis
Research experience, although not necessarily in the field of robotics, enhances the application.
A solid academic performance, demonstrated through a minimum undergraduate GPA requirement, is also often a prerequisite for students in their second or third year.
GRE Scores and Standardized Tests
GRE scores and other standardized tests are integral to the admission process for Robotics PhD programs. However, these scores are evaluated in conjunction with other elements such as GPA, recommendation letters, and essays.
For non-native English speakers, proof of English proficiency through TOEFL or IELTS scores, which assess verbal skills, may also be required.
Supporting Documents
Supporting documents such as:
Transcripts
Letters of recommendation
A statement of purpose
are crucial components of a Robotics PhD application. These documents provide a comprehensive picture of the applicant’s academic journey, achievements, and research capabilities, aiding the admissions committee in making an informed decision.
Curriculum and Coursework

The curriculum of a Robotics PhD program typically includes:
Core courses that provide a solid foundation in robotics, encompassing mechanics, controls, perception, artificial intelligence, and human-robot interaction
Electives that allow students to specialize in specific areas of robotics
A significant research component that allows students to conduct original research in the field of robotics
This comprehensive curriculum is designed to provide students with a deep understanding of robotics and prepare them for careers in academia, industry, or research.
Elective courses allow students to delve deeper into specific areas of interest, enabling them to specialize in a particular aspect of robotics. The research component, a significant part of the program, permits students to undertake independent study and promote knowledge in the robotics field.
Core Courses
The core courses in a Robotics PhD program cover fundamental topics such as:
Artificial Intelligence
Human-Robot Interaction
These courses provide the students with a comprehensive understanding of the field, equipping them with the necessary skills to engage in advanced research and pursue a master’s degree.
Elective courses in Robotics PhD programs offer the opportunity to focus on specific areas of interest. These courses equip students with specialized knowledge and skills, enabling them to conduct focused research in their chosen area. Some examples of areas of focus in Robotics PhD programs include:
Computer vision
Human-robot interaction
Artificial intelligence
Machine learning
Control systems
Autonomous systems
By taking elective courses in these areas, students can deepen their understanding and expertise in their chosen field of study.
Research Components
The research component of a Robotics PhD program typically involves independent study, laboratory work, and a dissertation. This component allows students to apply the knowledge and skills gained from their coursework to solve complex problems, contributing to the advancement of robotics.
Online and Part-Time Options for Robotics PhD Programs
In addition to traditional full-time programs, many universities offer online and part-time options for Robotics PhD programs. These flexible options provide an opportunity for those who wish to balance their studies with work or other responsibilities.
Online Programs
Some universities, like Capitol Technology University, offer fully online PhD programs in Robotics. These programs provide the flexibility to study from any location, making them ideal for individuals who cannot commit to on-campus studies.
Part-Time Study
Part-time study options for Robotics PhD programs offer the following benefits:
Students can balance their education with work or other responsibilities
The programs retain the rigorous curriculum of their full-time counterparts
The coursework is extended over an extended duration
Funding Opportunities and Financial Aid
Pursuing a PhD in Robotics is a significant financial commitment. However, there are various funding opportunities and financial aid options available to help offset the cost. These include fellowships, grants, and teaching or research assistantships.
Fellowships and grants, providing financial assistance, can help alleviate tuition and research expenses. Teaching and research assistantships, aside from offering financial support, provide worthwhile experience to refine students’ skills and elevate their career possibilities.
Fellowships
Fellowships offer the following benefits to Robotics PhD students:
Financial aid to offset tuition costs and research expenses
Opportunity to engage in independent research
Contribution to the advancement of knowledge in the field of robotics
Grants and Scholarships
Grants and scholarships are another form of financial aid available to Robotics PhD students. These funding options can help cover tuition costs and research expenses, making the pursuit of a PhD more accessible.
Teaching and Research Assistantships
Teaching and research assistantships provide financial support and valuable experience for Robotics PhD students. These assistantships involve assisting in teaching or research activities, providing a practical perspective to the theoretical knowledge gained through coursework. Research advisors play a crucial role in guiding students through these assistantships.
Real-World Applications and Impact of Robotics Research

Robotics research has significant real-world applications, impacting various sectors from healthcare to manufacturing and autonomous vehicles. Robotics advancements carry the potential to transform these sectors, boosting efficiency and productivity.
In healthcare, robotics research has led to the development of surgical robots and assistive devices, improving patient care and treatment outcomes. In manufacturing, robotics has enabled automation and improved efficiency. And in the realm of autonomous vehicles, advancements in AI, machine learning, and computer vision have paved the way for self-driving cars.
In the healthcare sector, Robotics research has led to significant advancements. Surgical robots have enhanced the efficiency and precision of medical procedures. Assistive devices have improved the quality of life for individuals with disabilities. These developments have revolutionized patient care, making healthcare more accessible and effective.
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing industry, robotics research has enabled automation of laborious tasks, leading to increased efficiency and productivity. Robots can handle repetitive and physically strenuous roles, allowing for greater precision and reduced likelihood of human error. These advancements have led to improved quality control and lower production costs.
Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles are an exciting application of robotics research. Advances in AI, machine learning, and computer vision have enabled vehicles to navigate autonomously, understanding their environment and making informed decisions.
These developments could transform transportation, rendering it safer and more efficient.
Pursuing a PhD in Robotics offers the opportunity to contribute to a field that is shaping the future. This program equips students with a comprehensive understanding of robotics, preparing them to address complex problems and advance knowledge in this exciting field. With the interdisciplinary nature of the program, the focus on cutting-edge research, and the wide range of career opportunities, a PhD in Robotics is a promising choice for those interested in this dynamic field.
The advancements in robotics are revolutionizing various sectors, from healthcare to manufacturing and autonomous vehicles. As the demand for robotics expertise grows, the opportunities for Robotics PhD graduates are expanding, making it an exciting time to embark on this academic journey. So, are you ready to step into the future and make your mark in the world of robotics?
Frequently Asked Questions
Can you get a phd in robotics.
Yes, you can get a PhD in robotics, and one example of such a program is offered jointly by the College of Computing and the College of Engineering at Georgia Institute of Technology.
How long is a PhD in robotics?
A PhD in robotics typically takes about five to six years to complete. The program includes coursework, a research qualifier, and the submission of a thesis.
What is the starting salary for robotics PhD?
The starting salary for a robotics PhD can range from $83,500 to $127,000 annually in the United States, with some top earners making up to $156,000 annually.
Why PhD in robotics?
A PhD in robotics will provide graduates with a diverse skill set encompassing mathematical thinking and technological proficiency, positioning them for careers in technology design, programming, and equipment maintenance in the field of robotics.
What are the prerequisites for a Robotics PhD program?
To apply for a Robotics PhD program, you’ll need a bachelor’s or master’s degree in a related field, relevant coursework, and a strong background in mathematics and computer science. These are the typical prerequisites for admission.
PhD in Robotics Engineering
WPI’s PhD in Robotics Engineering is one of the few worldwide where students can earn a doctorate in the field. We take robotics seriously, yet our approach is creative and innovative. Our world-class facilities and industry-leading faculty encourage originality and allow candidates to lead novel, cutting-edge research that crosses disciplines.
Value Proposition Description
The open atmosphere builds collaborative opportunities where students generate solutions that often lead to breakthroughs in robotics technology. And WPI’s location in the heart of the robotics industry opens doors to research, collaboration, internships, and networking with the world’s leading robotics companies.

The PhD in Robotics Engineering doctoral program is groundbreaking and internationally known for its outstanding faculty and advanced research projects. A small student-to-faculty ratio means students work side by side with world-class professors who are exploring everything from medical robotic devices and multi-robot systems to the ethical implications of human-robot interaction.
Course work across disciplines includes computer science, electrical and computer engineering, mathematics, and mechanical engineering and gives candidates depth and breadth in robotics expertise. Students may enter with a BS or an MS degree and will propose a plan of study and potential research leading up to dissertation studies.
Research for Robotics Engineering PhD
Faculty research is wide-ranging and involves students in every step of research and exploration, so robotics engineering PhD students have nearly endless choices. Working in this wide-ranging field means you’re always innovating on exciting new problems and challenges in real-time. The energy in our labs is contagious and breeds revolutionary approaches to robotics.
WPI’s robotics faculty research is supported through federal and industry funding. Some areas of faculty specialization:
- Assistive and Augmentative Robotics
- Human-Robot Interaction
- Kinematics, Dynamics, and Control
- Manipulation
- Medical and Surgical Robotics
- Motion Planning

As a robotics graduate student, you’ll work side-by-side with faculty on research that pushes the boundaries of what seems possible—whether it’s developing robotic medical instruments or fine-tuning the smallest, multi-robot swarm robotics.

WPI has a long history as a pioneer in robotics engineering education, giving it a depth and breadth of knowledge. IT was the first university to offer BS through PhD degrees in robotics, and its comprehensive curriculum reflects that deep experience.

As a multidisciplinary field, robotics researchers collaborate to extend their impact.

Robotics impacts humanity in levels as varied as manufacturing to the most delicate surgery. A degree in robotics gives you plentiful job opportunities.

You’ll develop varied skills working within the robotics field. Depending on goals and interests, students can write the software to operate robots, build robots, or explore the ethical implications of robots in a complex human world.

New England is considered the global epicenter for the robotics industry. Opportunities to contribute to important advances in the field exist in nearby academia, established organizations and industries, and start-ups.

The robotics curriculum is purposefully varied. The industry is multilayered, so students take classes that have a business, systems engineering, or entrepreneurial approach.
- Multi-robot Systems
- Origami-inspired Foldable Robot Design and Fabrication
- Real-time Motion Planning
- Robot Learning
- Soft/Flexible Robotic Systems
- Tactile Sensing
The extensive robotics labs and facilities at WPI cater to the various interests and the collaborative and independent research projects of students. All around campus, students pursue advances using the latest technology in labs outfitted for robots for medical, social, military, communication, and even artistic uses.
Refer a Friend
Do you have a friend, colleague, or family member who might be interested in Worcester Polytechnic Institute’s (WPI) graduate programs? Click below to tell them about our programs.
Faculty Profiles

My research spans robotics, haptics, multi-modal perception, and artificial intelligence, at the intersection of computer science and engineering. There are two highly related themes in my robotics research: one is the focus on “contact sport”, i.e., the contact and interaction between a robot or a part/tool it holds and the environment, and the other is real-time adaptiveness of robots to uncertainty and uncertain changes in an environment based on perception.

An integral part of a rewarding academic career is being an educator. It is a wonderful opportunity to work with students and guide their development to fulfill their potential. I enjoy teaching the fundamentals of robotics engineering, science and technology as well as training students in advanced independent research. I aim to teach students about research-based thinking and problem solving, to give them a real career choice to determine their future in further research or the industry.

Berk's research primarily focuses on problems related to robotic manipulation, which is a key functionality largely missing from the current state of the art in robotics for unstructured environments, including homes, modern warehouses, and collaborative manufacturing stations. He develops multi-modal robotic manipulation strategies mainly focusing on the role of vision feedback for coping with uncertainties of unstructured environments.

My research interests are in the application of robotics and computer science to enhance medicine, and particularly surgery. What gets me out of bed in the morning is the prospect of helping doctors save lives and improve the quality of life of their patients. My students and I work side-by-side with clinical collaborators to create technology that presents a tangible clinical value – for instance, making an existing surgical procedure more accurate or enabling new procedures that are not feasible with current instrumentation.
Professor Fischer is the William Smith Dean's Professor and a faculty member in Robotics Engineering with a appointments in Mechanical Engineering and Biomedical Engineering at WPI. He received his PhD in Mechanical Engineering in 2008 from Johns Hopkins University, where he was part of the NSF Engineering Research Center for Computer Integrated Surgery. At WPI he has been an integral part of developing the Robotics Engineering program and teaches primarily junior-level and graduate courses in Robotics.

My research leverages control theory, formal methods, and machine learning to construct adaptive, provably correct cyber-physical systems with respect to complex specifications. The challenges I am currently interested in include: reactive robotic systems under partial information and modeling uncertainty, multi-robot coordination, optimal control of hybrid systems, and design of adaptive semi-autonomous systems.

The focus of my research is designing innovative tools for swarm robotics. I am developing Buzz, a programming language specifically designed for real-world robot swarms. During my Ph.D., I have designed ARGoS, which is currently the fastest general-purpose robot simulator in the literature. Recent work focuses on human-swarm interaction and multi-robot learning. I am also working on swarm robotics solutions for disaster response scenarios, such as search-and-rescue and firefighting.
Ready to Work on Innovative Robots, But Need Your Masters? Explore Our Online & On Campus Options.
If you’re interested in working on breakthrough robotics discoveries through serious research and an innovative imagination, our master’s in robotics engineering may be a good fit for you. A first-of-its-kind degree in the nation, our MS in robotics is offered online and on-campus in which you will advance knowledge in fundamental areas of computer science, ECE, mathematics, and mechanical engineering to tackle real-world problems.
Gain a Foundation in Robotics With a Graduate Certificate
Whether you’re hoping to gain a solid base in the robotics field or want to stay ahead of the curve, our robotics engineering graduate certificates are a great starting point. WPI’s on campus robotics engineering graduate certificate covers the fundamentals of robotics to provide students a strong understanding of how robots are engineered. This 15-credit certificate dives into robot dynamics, systems engineering, and more. Prefer to study online at your own convenience? We also offer our robotics engineering graduate certificates 100% online so you can advance your skills in robotics while continuing your career. Maybe you’re interested in complementing your technical skills with a leadership edge? Our robotics engineering management certificate covers how robotics systems are engineered through management contexts.
Are you interested in majoring in robotics? Do you want to learn more?
If you’re interested in robotics and want to dive right into a top-rated program, a bachelor’s in robotics engineering at WPI lets you do everything from researching how the field of robotics works to actually building robotic devices, interacting with them, and exploring the uses and ethics of robotics. Our first-in-the-nation bachelor’s degree in robotics engineering delivers the kind of expertise and comprehensive approach you need to understand the use and implications of robotics. If robotics interests you but your major is in a different discipline, try our minor in robotics engineering. Our minor in robotics engineering includes course work in disciplines such as ECE, mechanical engineering, computer science, and others, so you’ll be able to apply what you learn in the minor program to your major discipline.
WPI is proud to be the recipient of not one, but two National Science Foundation Research Traineeship programs. The programs provide exceptionally talented graduate students with specialized training and funding assistance to join careers at the forefront of technology and innovation. The programs are for graduate students in research-based master's and doctoral degree programs in STEM. Learn more .
The BioPoint Program for Graduate Students has been designed to complement traditional training in bioscience, digital and engineering fields. Students accepted into one of the home BioPoint programs will have the flexibility to select research advisors and take electives in other departments to broaden their skills. BioPoint curriculum is designed to be individual, interactive, project-focused and diverse, and includes innovative courses, seminars, journal clubs and industrial-based projects. Learn more .
- College of Computing

Ph.D. in Robotics
The Institute for Robotics and Intelligent Machines (IRIM ) serves as the flagship for Tech’s robotics efforts and therefore, the research institute has an integral relationship with the program. Almost all of IRIM faculty members serve as research advisors to students pursuing the robotics degree.
The program supports Tech’s mission to provide education in disciplines related to science, technology, and interdisciplinary areas, and to recruit and educate outstanding students who will provide leadership in a world that is increasingly dependent on technology. Currently, Tech has more than 40 faculty members actively engaged in the Ph.D. robotics program.
Admission Requirements
The Georgia Tech criteria used in determining each applicant’s eligibility for consideration includes:
- A bachelor’s degree or its equivalent (prior to matriculation) from a recognized institution; graduation in the upper quarter of their class; students must show evidence of preparation in their chosen field sufficient to ensure profitable graduate study;
- GRE scores (General Test is required for all; Subject Tests in Computer Science, Math or Physics recommended but not required);
- For international applicants, satisfactory scores on the Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL). Minimum scores are 100 (Internet-based test), 250 (computer-based) or 600 (paper-based).
Students enroll for the Robotics Ph.D. Program through one of the participating units:
- Aerospace Engineering
- Biomedical Engineering
- Electrical and Computer Engineering
- Mechanical Engineering
Students should indicate that they are applying for the Robotics Program through that unit by marking a check box. As minimum requirements, students must satisfy all of the specific admission requirements of the home unit.
The Robotics Ph.D. Program Committee will make final admission decisions in coordination with the home units.
Decisions are based on a combination of factors:
- Academic degrees and records
- Statement of purpose
- Letters of recommendation
- GRE and TOEFL test scores
- Relevant work experience
Also considered is the appropriateness of the applicant’s goals to the Robotics Ph.D. Program, their expected abilities in carrying out original research, and the faculty research interests.
Complete the online application .
Program of Study
The main emphasis of the Robotics Ph.D. program is the successful completion of an original and independent research thesis. The degree requirements are designed around this goal.
Minimum Requirements
- Completion of 36 semester hours of courses with a letter grade
- Passing a comprehensive qualifying exam with written and oral components.
- Successfully conducting, documenting, and defending a piece of original research culminating in a doctoral thesis.
Ph.D. Candidacy
Prior to completing all of these requirements, Georgia Tech defines the Ph.D Candidate milestones. Admission to candidacy requires that the student:
- Complete all course requirements (except the minor);
- Achieve a satisfactory scholastic record;
- Pass the comprehensive examination;
- Submit and receive approval naming the dissertation topic and delineating the research topic.
Core Area Courses
The core areas of robotics consist of: Mechanics, Control, Perception, Artificial Intelligence, Autonomy and Human-Robot Interaction (HRI). They are used to select three foundation courses and three targeted elective courses. Visit phdrobotics.gatech.edu/program for a full list of core area courses.
Qualifying Exam
The purpose of the comprehensive exam is to assess the student’s general knowledge of the degree area and specialized knowledge of the chosen research area. The comprehensive examination provides an early assessment of the student's potential to satisfactorily complete the requirements for the doctoral degree. As such, it requires that fundamental principles be mastered and integrated so that they can be applied to solving problems relevant to robotics.
After three regular semesters (Fall or Spring) from entering the Ph.D. program the student must take the comprehensive examination at the next scheduled offering, usually during the fourth regular semester. If the comprehensive examination is failed, the student may have one additional opportunity at the next scheduled offering. The examination will be offered at least once every year.
The comprehensive exam is a written and oral examination and is administered by a faculty committee, selected by the thesis advisor in consultation with the student, and approved by the Robotics Program Committee. The committee consists of:
- Three faculty members consistent with the student's graduate coursework and research area.
- The thesis advisor as a non-voting observer.
From the Catalog:
- College of Computing
Ph.D. in Robotics
The Institute for Robotics and Intelligent Machines (IRIM ) serves as the flagship for Tech’s robotics efforts and therefore, the research institute has an integral relationship with the program. Almost all of IRIM faculty members serve as research advisors to students pursuing the robotics degree.
The program supports Tech’s mission to provide education in disciplines related to science, technology, and interdisciplinary areas, and to recruit and educate outstanding students who will provide leadership in a world that is increasingly dependent on technology. Currently, Tech has more than 40 faculty members actively engaged in the Ph.D. robotics program.
Admission Requirements
The Georgia Tech criteria used in determining each applicant’s eligibility for consideration includes:
- A bachelor’s degree or its equivalent (prior to matriculation) from a recognized institution; graduation in the upper quarter of their class; students must show evidence of preparation in their chosen field sufficient to ensure profitable graduate study;
- GRE scores (General Test is required for all; Subject Tests in Computer Science, Math or Physics recommended but not required);
- For international applicants, satisfactory scores on the Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL). Minimum scores are 100 (Internet-based test), 250 (computer-based) or 600 (paper-based).
Students enroll for the Robotics Ph.D. Program through one of the participating units:
- Aerospace Engineering
- Biomedical Engineering
- Electrical and Computer Engineering
- Mechanical Engineering
Students should indicate that they are applying for the Robotics Program through that unit by marking a check box. As minimum requirements, students must satisfy all of the specific admission requirements of the home unit.
The Robotics Ph.D. Program Committee will make final admission decisions in coordination with the home units.
Decisions are based on a combination of factors:
- Academic degrees and records
- Statement of purpose
- Letters of recommendation
- GRE and TOEFL test scores
- Relevant work experience
Also considered is the appropriateness of the applicant’s goals to the Robotics Ph.D. Program, their expected abilities in carrying out original research, and the faculty research interests.
Complete the online application .
Program of Study
The main emphasis of the Robotics Ph.D. program is the successful completion of an original and independent research thesis. The degree requirements are designed around this goal.
Minimum Requirements
- Completion of 36 semester hours of courses with a letter grade
- Passing a comprehensive qualifying exam with written and oral components.
- Successfully conducting, documenting, and defending a piece of original research culminating in a doctoral thesis.
Ph.D. Candidacy
Prior to completing all of these requirements, Georgia Tech defines the Ph.D Candidate milestones. Admission to candidacy requires that the student:
- Complete all course requirements (except the minor);
- Achieve a satisfactory scholastic record;
- Pass the comprehensive examination;
- Submit and receive approval naming the dissertation topic and delineating the research topic.
Core Area Courses
The core areas of robotics consist of: Mechanics, Control, Perception, Artificial Intelligence, Autonomy and Human-Robot Interaction (HRI). They are used to select three foundation courses and three targeted elective courses. Visit phdrobotics.gatech.edu/program for a full list of core area courses.
Qualifying Exam
The purpose of the comprehensive exam is to assess the student’s general knowledge of the degree area and specialized knowledge of the chosen research area. The comprehensive examination provides an early assessment of the student's potential to satisfactorily complete the requirements for the doctoral degree. As such, it requires that fundamental principles be mastered and integrated so that they can be applied to solving problems relevant to robotics.
After three regular semesters (Fall or Spring) from entering the Ph.D. program the student must take the comprehensive examination at the next scheduled offering, usually during the fourth regular semester. If the comprehensive examination is failed, the student may have one additional opportunity at the next scheduled offering. The examination will be offered at least once every year.
The comprehensive exam is a written and oral examination and is administered by a faculty committee, selected by the thesis advisor in consultation with the student, and approved by the Robotics Program Committee. The committee consists of:
- Three faculty members consistent with the student's graduate coursework and research area.
- The thesis advisor as a non-voting observer.
From the Catalog:
Robotics (Ph.D.)
Focus: educating a new breed of multidisciplinary researchers in robotics who will provide leadership in this rapidly evolving discipline and help meet the growing industrial and societal demand for advanced education and research in robotics.
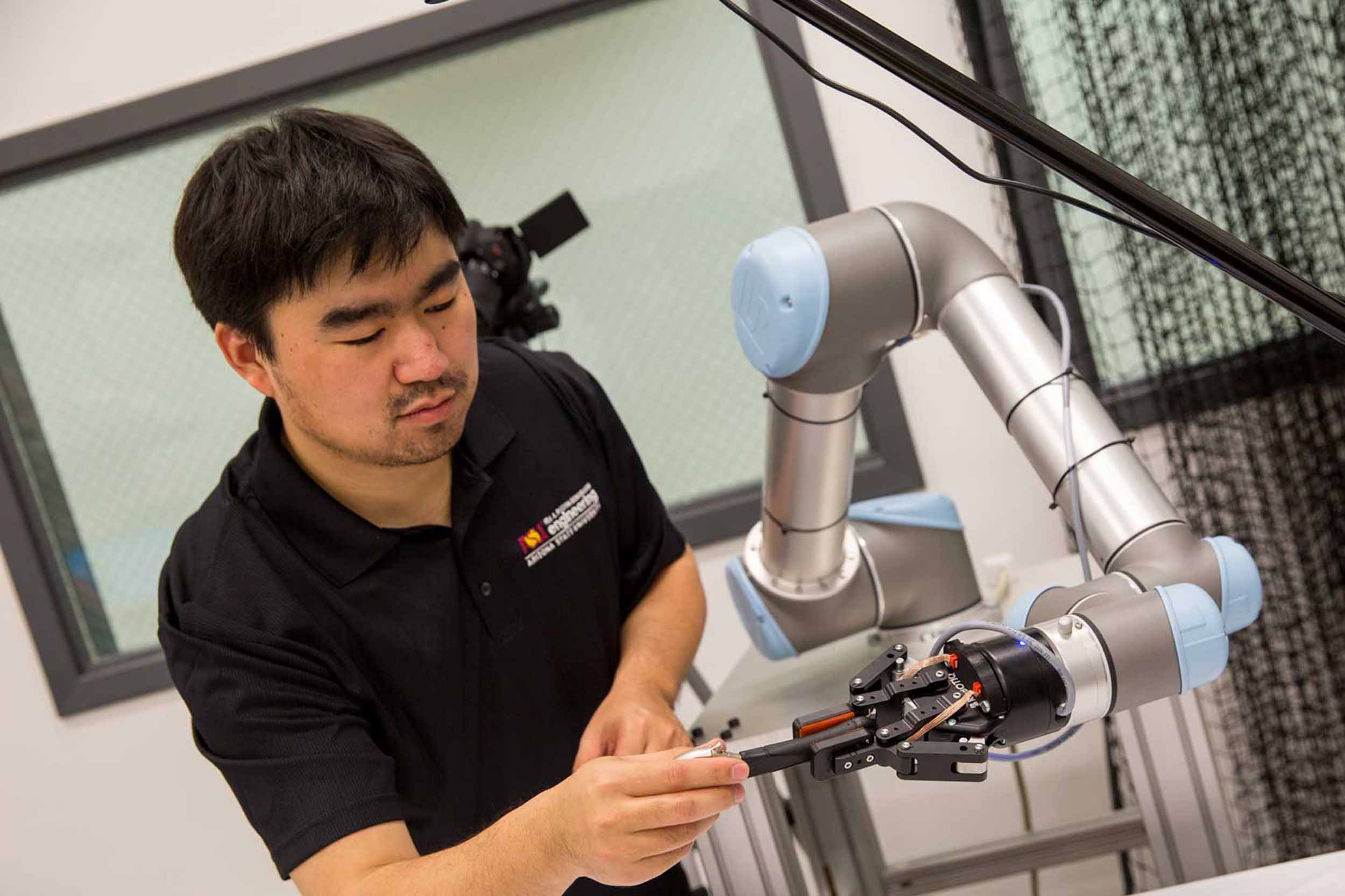
Robotics and autonomous systems (mechatronics and automation), PhD
Master the knowledge, skills and abilities to successfully meet the most difficult challenges of modern robotics and autonomous systems on a global scale.
Program description
The mechatronics and automation concentration of the PhD program in robotics and autonomous systems provides an opportunity for in-depth independent research in a highly focused problem domain approved by the student’s advisory committee.
The robotics and autonomous systems (mechatronics and automation), PhD is intended primarily for those desiring to develop expertise in a particular and focused problem in the field of robotics and autonomous systems, including both traditional and advanced robotics and autonomous systems technologies, systems integration and data fusion techniques, and modeling and simulation development.
Graduates will become trained researchers and scientists who will be able to perform analysis, evaluation and synthesis for a broad range of problems related to the design, implementation and efficient operation of robotics and autonomous systems.
Career outlook
Graduates with a doctorate in robotics and autonomous systems typically seek research-oriented academic appointments or industrial research and development positions.
These professionals have substantial opportunities at all levels in manufacturing engineering in research and development at companies, research institutes and national laboratories (e.g., Department of Defense, Department of Energy, National Aeronautics and Space Administration). Relevant careers and related titles include the following:
- electronics engineer
- industrial engineers
- manufacturing engineers
- mechanical engineers
- mechatronics engineers
- robotics engineer
Admission requirements and application process
Admission requirements.
The applicant must have a master’s degree in a relevant field with a GPA of 3.00 or higher. Relevant fields include mechanical engineering, aerospace engineering, computer science, computer engineering, electrical engineering, industrial engineering, automation engineering, manufacturing engineering, automotive engineering, biomedical engineering and human systems engineering.
Applicants must fulfill the requirements of both the Graduate College and the Ira A. Fulton Schools of Engineering.
Applicants are eligible to apply to the program if they have earned a bachelor’s or master’s degree in robotics and autonomous systems or a related field from a regionally accredited institution.
Applicants must have a minimum cumulative GPA of 3.00 (scale is 4.00 = “A”) in the last 60 hours of their first bachelor’s degree program, or applicants must have a minimum cumulative GPA of 3.00 (scale is 4.00 = “A”) in an applicable master’s degree program.
All applicants are required to submit:
- graduate admissions application and application fee
- official transcripts for undergraduate and graduate degrees
- personal statement
- professional resume
- two letters of recommendation
- proof of English proficiency
An applicant whose native language is not English must provide proof of English proficiency regardless of their current residency.
Applicants need to submit a copy of their unofficial transcripts as part of the online admission application submission. After admission, official transcripts are required to be submitted to the Graduate Admission Services office.
Application process
The admission process begins by applying for graduate admission . The application requires that following items must be submitted:
- Two (2) Letters of Recommendation
- Statement of Purpose: Submit online a 300- to 500-word statement of purpose describing your motivation and rationale for obtaining a PhD in the robotics and autonomous systems program at Arizona State University and how it relates to your long-term career goals.
- Official transcripts from each college or university attended.
- Graduate admission application and application fee
- International applicants must also meet the English proficiency requirements , as defined by Graduate Admissions. Please be sure to review the TOEFL, IELTS, or PTE score requirements , as your application will not be processed without valid proof of English proficiency.
Graduate faculty and funding opportunities
More information.
ASU degree page
Schedule an advising appointment
Degree requirements
A minimum of 84 semester credit hours are required for the PhD degree, distributed as follows:
- 12 credit hours of core courses from approved list
- EGR 546 Robotic Systems II (3)
- EGR 550 Mechatronic Systems (3)
- EGR 545 Robotic Systems I (3)
- EGR 602 Principles of Independent Research (3)
- 12 credit hours, at minimum, of RAS 792 Research
- 12 credit hours of RAS 799, Dissertation
- 36 credit hours, Electives or Research (up to 30 credits from previous completed master’s degree in engineering)
A program handbook with more specifics will be available in January 2024.
Application deadlines
August 15 Spring semester (January) January 15 Fall semester (August)
These are priority deadlines. Applications submitted after this deadline may still be considered.
Course requirements
All students enrolled in the PhD in Robotics and Autonomous Systems with a concentration in Mechatronics and Automation must complete the required courses. Additional curriculum details will be listed in the program handbook, which will be available in Spring 2024.
12 credits of core courses within 4 key areas :
- Conceptualization (Modeling/Theoretical Foundations) of RAS
- Intelligence and Control of RAS
- Embodiment (Mechanics/Actuation) of RAS
- Sociotechnical Implications of RAS
All courses must be chosen from the approved course list.
6 credit hours of other requirements
6 credits of concentration coursework
Additional coursework will fall into three categories: Electives, Research, Dissertation.
[email protected]
Graduate student resources
Academic calendar
Academic standards
Graduate College Policies
Resources and Forms
Institute for Robotics and Intelligent Machines

Ph.D. Program
Ph.d. program in robotics.
Offered jointly by the College of Computing and the College of Engineering, the Ph.D. program in Robotics is the first truly multidisciplinary robotics degree of its kind in the world—and only the second robotics doctorate offered in the U.S. The program involves the schools of Interactive Computing, Electrical & Computer Engineering, Mechanical Engineering, Biomedical Engineering and Aerospace Engineering.
We educate a new generation of robotics researchers who are prepared to be impactful contributors upon entering the high-tech workforce. The Institute for Robotics & Intelligent Machines (IRIM) serves as the flagship for Tech’s robotics efforts; therefore, IRIM has an integral relationship with the program, and many IRIM faculty members serve as research advisors to students pursuing the degree. The Robotics program supports Tech’s mission to provide instruction in disciplines related to science, technology, and interdisciplinary areas.
Program of Study
The main emphasis of the Ph.D. program is the successful completion of an original and independent research thesis. The degree requirements are designed around this goal.
Minimum Requirements
- Completion of 36 semester hours of courses with a letter grade
- Passing a comprehensive qualifying exam with written and oral components.
- Successfully conducting, documenting, and defending a piece of original research culminating in a doctoral thesis.
PLEASE NOTE
Home Unit Teaching Apprenticeship and Extra-curricular Requirements Robotics Ph.D. students are subject to their home unit's teaching apprenticeship requirements (e.g., a certain number of semesters serving as a TA) and other the extra-curricular requirements such as seminar attendance or annual review process. For example, students with home units in BME, IC, and ME are required to do two semesters of teaching practicum or apprenticeship and register for the corresponding courses. Students should contact their home units for details for any departmental requirements that are in addition to the Robotics degree requirements. Students are responsible for ensuring that they understand and satisfy any home unit requirements as well as the Robotics program and Institute requirements.
*A maximum of two classes (6 semester hours) at the 4000 level may be used to satisfy the minor requirements only. No courses used to satisfy any bachelor's degree requirements can be used towards a graduate degree.
DOWNLOAD THE ROBOTICS Ph.D. HANDBOOK HERE
Program director dr. nader sadegh, faculty coordinators .
For questions about academic and research components of the program, contact the faculty member for your area. All questions about application procedures and processes, as well as additional contact information, may be found on the schools’ websites.
- Mechanics: Frank Hammond , ME/BME
- Control: Patricio Vela , ECE
- Perception : Jim Rehg , IC
- HRI: Karen Feigh , AE
The RoboGrads site offers a lot of useful information!

Robotics and Autonomous Systems (Mechatronics and Automation), PhD
- Program description
- At a glance
- Degree requirements
- Admission requirements
- Tuition information
- Application deadlines
- Career opportunities
- Contact information
Autonomous Systems, Autonomous Vehicle Systems, Robotics, approved for STEM-OPT extension
Master the knowledge, skills and abilities to meet the most difficult challenges of modern robotics and autonomous systems on a global scale.
The mechatronics and automation concentration of the PhD program in robotics and autonomous systems provides an opportunity for in-depth independent research in a highly focused problem domain approved by the student's advisory committee. This program is intended primarily for those who desire to develop expertise in a particular and focused problem in the field of robotics and autonomous systems, including both traditional and advanced robotics and autonomous systems technologies, systems integration and data fusion techniques, and modeling and simulation development.
This program may be eligible for an Optional Practical Training extension for up to 36 months. This OPT work authorization term may help international students gain skills and experience in the U.S. Those interested in an OPT extension should review ASU degrees that qualify for the STEM-OPT extension at ASU's International Students and Scholars Center website.
The OPT extension only applies to students on an F-1 visa and does not apply to students completing the degree through ASU Online.
- College/school: Ira A. Fulton Schools of Engineering
- Location: Polytechnic
84 credit hours, an oral comprehensive exam, a written comprehensive exam, a prospectus and a dissertation
Required Core (12 credit hours)
Concentration (6 credit hours) EGR 550 Mechatronic Systems (3) RAS 546 Robotic Systems II (3)
Other Requirements (6 credit hours) EGR 602 Principles of Independent Research (3) RAS 545 Robotic Systems I (3)
Electives or Additional Research (36 credit hours)
Research (12 credit hours)
Culminating Experience (12 credit hours) RAS 799 Dissertation
Additional Curriculum Information For elective courses (depending on concentration), up to six credits of MAE, EEE, MFG, EGR, CSE, AME or RAS 590 Reading and Conference are allowed.
The classes listed under the core requirements can also be taken as electives, if not already counted toward the core requirements.
Applicants must fulfill the requirements of both the Graduate College and the Ira A. Fulton Schools of Engineering.
Applicants are eligible to apply to the program if they have earned a bachelor's or master's degree in robotics and autonomous systems or a related field from a regionally accredited institution.
Applicants must have a minimum cumulative GPA of 3.00 (scale is 4.00 = "A") in the last 60 hours of their first bachelor's degree program or a minimum cumulative GPA of 3.00 (scale is 4.00 = "A") in an applicable master's degree program.
All applicants are required to submit:
- graduate admissions application and application fee
- official transcripts
- personal statement
- professional resume
- two letters of recommendation
- proof of English proficiency
Additional Application Information An applicant whose native language is not English must provide proof of English proficiency regardless of their current residency.
The applicant must have a master's degree in a relevant field with a GPA of 3.00 or higher. Relevant fields include mechanical engineering, aerospace engineering, computer science, computer engineering, electrical engineering, industrial engineering, automation engineering, manufacturing engineering, automotive engineering, biomedical engineering and human systems engineering.
Graduates with a doctorate in robotics and autonomous systems typically seek research-oriented academic appointments or industrial research and development positions. As trained researchers and scientists, graduates perform analysis, evaluation and synthesis for a wide variety of problems related to the design, implementation and efficient operation of robotics and autonomous systems. These professionals have substantial opportunities at all levels in manufacturing engineering in research and development at companies, research institutes and national laboratories (e.g., Department of Defense, Department of Energy, NASA). Relevant careers and related titles include:
- electronics engineer
- industrial engineer
- manufacturing engineer
- mechanical engineer
- mechatronics engineer
- robotics engineer
School of Manufacturing Systems and Networks | TECH 100 [email protected] 480-727-2097 Admission deadlines

Explore your training options in 10 minutes Get Started
- Graduate Stories
- Partner Spotlights
- Bootcamp Prep
- Bootcamp Admissions
- University Bootcamps
- Coding Tools
- Software Engineering
- Web Development
- Data Science
- Tech Guides
- Tech Resources
- Career Advice
- Online Learning
- Internships
- Apprenticeships
- Tech Salaries
- Associate Degree
- Bachelor's Degree
- Master's Degree
- University Admissions
- Best Schools
- Certifications
- Bootcamp Financing
- Higher Ed Financing
- Scholarships
- Financial Aid
- Best Coding Bootcamps
- Best Online Bootcamps
- Best Web Design Bootcamps
- Best Data Science Bootcamps
- Best Technology Sales Bootcamps
- Best Data Analytics Bootcamps
- Best Cybersecurity Bootcamps
- Best Digital Marketing Bootcamps
- Los Angeles
- San Francisco
- Browse All Locations
- Digital Marketing
Machine Learning
- See All Subjects
- Bootcamps 101
- Full-Stack Development
- Career Changes
- View all Career Discussions
- Mobile App Development
- Cybersecurity
- Product Management
- UX/UI Design
- What is a Coding Bootcamp?
- Are Coding Bootcamps Worth It?
- How to Choose a Coding Bootcamp
- Best Online Coding Bootcamps and Courses
- Best Free Bootcamps and Coding Training
- Coding Bootcamp vs. Community College
- Coding Bootcamp vs. Self-Learning
- Bootcamps vs. Certifications: Compared
- What Is a Coding Bootcamp Job Guarantee?
- How to Pay for Coding Bootcamp
- Ultimate Guide to Coding Bootcamp Loans
- Best Coding Bootcamp Scholarships and Grants
- Education Stipends for Coding Bootcamps
- Get Your Coding Bootcamp Sponsored by Your Employer
- GI Bill and Coding Bootcamps
- Tech Intevriews
- Our Enterprise Solution
- Connect With Us
- Publication
- Reskill America
- Partner With Us
- Resource Center
- Bachelor’s Degree
- Master’s Degree
Best Doctorates in Automation and Robotics Engineering: Top PhD Programs, Career Paths, and Salaries
If you are interested in furthering your education and advancing in the engineering field, you should take a look at the best PhDs in Automation and Robotics Engineering. It can be challenging to find the best schools for automation and robotics engineering PhDs, so we have created this comprehensive guide to learn everything you need to know.
We highlight the best automation and robotics engineering PhD programs, their costs, and thesis subjects you should consider. This guide discusses automation and robotics engineering jobs and their respective salaries, so you can be sure to have a long and fruitful career after graduation.
Find your bootcamp match
What is a phd in automation and robotics engineering.
A PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering is the highest academic degree that teaches you how to program, design, and create robots. Usually, a PhD in this field qualifies you to teach in universities and qualifies you for the highest positions in your professional career.
How to Get Into an Automation and Robotics Engineering PhD Program: Admission Requirements
The requirements to get into an automation and robotics engineering PhD program include an application letter and a personal statement. Students should submit a resume that discusses their academic and research background and area of focus during the program. Other admission requirements include letters of recommendation and all school transcripts.
When getting into an automation and robotics engineering PhD program, you want to prove that you are a good fit for the department. Although it is not a requirement, they expect you to be proficient with programming languages like C, Python, Java, and MATLAB.
PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering Admission Requirements
- GRE, GMAT, or TOEFL
- Transcripts from all post-secondary school institutions
- Letters of recommendation
- Statement of purpose
Automation and Robotics Engineering PhD Acceptance Rates: How Hard Is It to Get Into a PhD Program in Automation and Robotics Engineering?
It can be hard to get into a PhD program in automation and robotics engineering. Once you meet the admission requirements for the program, you will need to provide a strong argument about why you want to pursue the program with your select school. Many schools offer part-time, full-time, and online formats, giving you more options to choose from.
Your chances of getting into a PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering program depends on the number of students applying. There could be over 300 students applying for only 25 spots. However, Oregon State University boasts a school acceptance rate of 83,4 percent, higher than Stevens Institute of Technology’s rate of 53 percent.
How to Get Into the Best Universities
[query_class_embed] how-to-get-into-*school
Best PhDs in Automation and Robotics Engineering: In Brief
Best universities for automation and robotics engineering phds: where to get a phd in automation and robotics engineering.
The best universities for automation and robotics engineering PhDs usually have quality curricula, a strong faculty, and cutting-edge research facilities. Some of the best schools have made groundbreaking discoveries or inventions in the field. If you are wondering where to get a PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering, the guide below has all your answers.
Founded in 1900, Carnegie Mellon University is a private research university renowned for its computer science research programs. The US News and World Report rank CMU as the best institution for learning programming languages and artificial intelligence. The Robotics Institute is a wing of Carnegie Mellon University dedicated to robotics research and education.
PhD in Robotics
The PhD in Robotics program at Carnegie Mellon is unique because it offers students a comprehensive and interdisciplinary approach to studying robotics. Students in the PhD program have access to state-of-the-art labs, equipment, and some of the world's leading experts in robotics.
Robotics students will learn cognition core, action core, and math foundation core courses with topics ranging from AI and machine learning to mechanics and applied math. Students improve their writing, speaking, communication, and collaboration skills.
PhD in Robotics Overview
- Program Length: 2 years
- Acceptance Rate: N/A
- Tuition and Fees: $645/ credit
- PhD Funding Opportunities: Graduate Fellowship, Research Fellowship, Project scholarship
PhD in Robotics Admission Requirements
- Minimum of an undergraduate degree
- Application fee: $125
- GRE (optional for 2022-2023 academic year)
- Transcripts
- Three letters of recommendation
The Georgia Institute of Technology is a top choice for students seeking a quality graduate education. The graduate school offers more than 130 programs through six colleges. The school was founded in 1885.
PhD in Robotics
This program helps students develop the skills needed to conduct research and contribute to the advancement of robotics technology. The curriculum provides students with an in-depth knowledge of the principles and theories of robotics and hands-on experience in the design and development of robotic systems.
In addition, students will complete some elective courses that allow them to specialize in a particular area of robotics. Core courses include mechanics, controls, perception, and artificial intelligence.
- Program Length: 1.5 years (15 credits per semester for a total of 36 credits)
- Tuition and Fees: $586/credit (in state); $1,215/credit (out of state)
- PhD Funding Opportunities: Graduate Assistantship, research scholarship, Microsoft Azure Credit Awards
- Bachelor's degree or the equivalent
- Application fee: $75
- GRE is recommended
- Recommendation letters
- Online application
Founded in 1957, Oakland University is a public university that offers a variety of graduate programs that can accommodate students’ needs and interests, including business administration, engineering, education, and information technology. Graduate students conduct research in world-class facilities and access unique learning opportunities.
PhD in Electrical and Computer Engineering
The PhD in Electrical and Computer Engineering program focuses on designing, developing, and deploying new electrical and computer systems. It is research-intensive, and students are expected to complete a dissertation in addition to their coursework.
The focus areas include systems engineering, computer engineering, embedded systems, communications and networking, and control systems. Students will have to study algorithms and complexity, graph theory and application, and computer algebra.
PhD in Electrical and Computer Engineering Overview
- Program Length: 2-4 years
- Tuition and Fees: $807.5/credit (in-state); $1,027/credit (out of state)
- PhD Funding Opportunities: Graduate Future Faculty Fellowship, Research Fellowship, Project scholarship, Graduate Assistantship, Scholarships
PhD in Electrical and Computer Engineering Admission Requirements
- Master’s degree in electrical or computer engineering or a related field
- All official transcripts
- Two official recommendations for graduate admission forms
- Proof of English proficiency
- Application fee: $45
- GRE is required
- Statement of objectives
Oregon State University offers several graduate degree and certificate programs with unique specialties in robotics, computer science, and business. OSU has one of the largest and most diverse research programs in the United States, with more than $400 million in research expenditures. The school was founded in 1868.
This graduate program draws on faculty and resources from the Departments of Mechanical Engineering, Electrical Engineering, and Computer Science. The curriculum covers locomotion and manipulation, machine learning and perception, and human-robot interaction. Students in this program get to choose their major professor who will advise them throughout their studies.
- Program Length: 2 years (6 quarters)
- Acceptance Rate: 83.4%
- Tuition and Fees: $557/credit (in state); $1,105/credit (out of state)
- PhD Funding Opportunities: Graduate Research Assistantship, Graduate Teaching Assistantship, COE Dean’s Scholarship, SSI Scholarship, External Scholarships, Grant Resources
- At least a Bachelor’s Degree in Engineering, Mathematics, or Computer Science
- GRE is not required
Stevens Institute of Technology is a private research university that offers graduate programs in business, engineering, science, and technology. These programs have a strong focus on entrepreneurship and offer a range of programs and resources to help students start their businesses.
Founded in 1870, Stevens also has a well-established network of alumni entrepreneurs who provide mentorship and support and has an enrollment of just under 7,000 students.
PhD in Mechanical Engineering
The Stevens Institute of Technology offers a PhD in Mechanical Engineering program with an option to specialize in robotics engineering. The curriculum is divided into core courses, electives, research, and a thesis.
In addition to completing coursework, students must also pass a qualifying exam and write a dissertation. Students are encouraged to conduct original research under the guidance of a faculty advisor.
PhD in Mechanical Engineering Overview
- Program Length: 2-3 years (84 credits)
- Acceptance Rate: 53%
- Tuition and Fees: $1,776/credit
- PhD Funding Opportunities: Teaching and Research Assistantship
PhD in Mechanical Engineering Admission Requirements
- Minimum of a Bachelor's Degree in Electrical or Computer Engineering
- Application fee: $60
- A statement of purpose
- Official college transcripts
- Two letters of recommendation
Founded in 1876, the University of Colorado offers graduate degrees in various fields, including business, engineering, education, and public health. The school has a strong reputation and offers a variety of programs that can help every doctoral student achieve their goals.
PhD in Robotics and Systems Design
This program is highly interdisciplinary. It is jointly offered by the Department of Electrical, Computer, Energy Engineering, and the Department of Mechanical Engineering. The curriculum for the Robotics and Systems Design PhD program is very flexible, and students can choose from courses such as industrial automation, optimal design, and soft machines.

"Career Karma entered my life when I needed it most and quickly helped me match with a bootcamp. Two months after graduating, I found my dream job that aligned with my values and goals in life!"
Venus, Software Engineer at Rockbot
PhD in Robotics and Systems Design Overview
- Program Length: Five years
- Tuition: $2,562/credit (in state); $5,688/credit (out of state)
- PhD Funding Opportunities: Teaching or Research Assistantship
PhD in Robotics and Systems Design Admission Requirements
- Bachelor's degree in a related field
- Personal statement
The University of Michigan was founded in 1817 and is the oldest university in the state of Michigan. It offers a variety of programs at the graduate level but is renowned for its medical and engineering programs. The university has been ranked highly by various sources, including U.S. News & World Report, Forbes, and the Academic Ranking of World Universities.
The Robotics PhD program at Michigan is interdisciplinary and allows students to specialize in one of four areas, namely robotics engineering, autonomous systems, human-robot interaction, or machine learning. The program has a strong emphasis on hands-on experience, and students are required to complete several robotics projects during their studies.
Students must complete the Comprehensive Qualifying Exam (CQE), a research thesis, and a total of 30 credits to graduate. Students can take courses such as robotic systems laboratory, programming for robotics, and wearable sensors.
- Program Length: 4.5 years
- Tuition and Fees: $1,730/credit (in state); $3,132/credit (out of state)
- PhD Funding Opportunities: Graduate Student Research Assistantship, Graduate Student Instructorship
- Bachelor's degree
- GRE is not required for PhD application
- Transcripts
- Three letters of recommendation
- Academic statement of purpose
- Personal statement
- Curriculum Vitae
The University of Utah has a rich history dating back to 1850 when the state legislature approved the creation of the university. The graduate school offers about 71 programs across 17 colleges and schools. Students can study business, education, engineering, law, medicine, or social work.
PhD in Mechanical Engineering - Robotics Track
The program is designed for students who want to develop the skills necessary to create and manage advanced robotic systems. Students in the Robotics Track will gain experience in computer-aided design, motion planning and control, sensor fusion, and machine learning.
They will also have the opportunity to specialize in one or more areas of robotics, such as medical robotics, service robotics, or unmanned aerial vehicles. Core courses in robotics include intro to robotics, artificial intelligence, and robot design.
PhD in Mechanical Engineering - Robotics Track Overview
- Program Length: 3 years
- Tuition and Fees: $1,805/credit (in state); $5,051.02/credit (out of state)
- PhD Funding Opportunities: Teaching Assistantship, Research Assistantship, and Graduate Assistantship
PhD in Mechanical Engineering - Robotics Track Admission Requirements
- Minimum of a degree in an undergraduate program
- Application fee: None
The University of West Florida was founded in 1963 as a junior college and became a four-year university in 1971. It offers graduate programs in business, education, engineering, health, and science. The majority of the graduate programs offered are asynchronous, which means that students can access the course materials at any time that is convenient for them.
PhD in Intelligent Systems and Robotics
The program provides students with a strong foundation in intelligent systems theory and practice and robotics. It is jointly offered by the Department of Computer Science and Engineering and the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering.
The coursework covers artificial intelligence, machine learning, robotics, computer vision, sensor fusion, and data mining. Graduates can work in development, healthcare, and high-tech industries.
PhD in Intelligent Systems and Robotics Overview
- Program Length: Three years
- Tuition and Fees: $377.60/credit (in state); $1,037.24/credit (out of state)
- PhD Funding Opportunities: Graduate assistantships, UWF Graduate Grand
PhD in Intelligent Systems and Robotics Admission Requirements
- Bachelor’s or master’s degree
- Application fee: $30
- Oral interview (if deemed necessary)
Founded in 1865 as a private research university, Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) focuses on the instruction and research of technical arts and applied sciences. The school offers graduate degrees in science, engineering, technology, business, the social sciences, and the humanities and arts.
PhD in Robotics Engineering
The program covers the design, analysis, and control of robotic systems, with a focus on applications in manufacturing and engineering. Students learn about a variety of robotics technologies, including industrial robots, service robots, micro-robots, and unmanned aerial vehicles.
PhD in Robotics Engineering Overview
- Program Length: Five years
- Tuition and Fees: $28,980/ year
- PhD Funding Opportunities: Graduate Fellowship, Graduate Assistantship, Graduate Research Fellowship
PhD in Robotics Engineering Admission Requirements
- Application fee: $70
- All post-secondary education transcripts
Can You Get a PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering Online?
Yes, you can get a PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering online, even from accredited institutions. Online PhD programs are becoming more popular every year as it allows people to continue their education without having to leave their jobs or families. Online academic programs are also typically cheaper and faster to complete than on-site programs.
Best Online PhD Programs in Automation and Robotics Engineering
How long does it take to get a phd in automation and robotics engineering.
It takes about two to six years to get a PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering. The duration of the program varies with the school, the program schedule, and the mode of delivery. For example, part-time PhD programs typically take longer time to complete compared to full-time PhD degree programs.
A typical PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering program comprises teaching sessions and direct research components. Students will develop a thesis, conduct comprehensive research, and defend their proposal before the end of their program.
Is a PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering Hard?
Yes, a PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering is hard. It is one of the most challenging degrees you can earn. It covers a wide range of topics, from mechanical engineering to computer science. Students should be prepared for a lot of hard work in programming, mathematics, and have an engineering background to excel in an automation engineering program.
The most challenging part of PhD programs in robotics and automation is often the research. From choosing a dissertation topic to conducting the actual research, the program can pose diverse types and levels of difficulties. Depending on the nature of the project, it can also be costly and time-demanding.
How Much Does It Cost to Get a PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering?
It costs $19,314 per year to get a PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering , according to reports from the National Center for Education Statistics. If you are running the program for five years, that adds up to approximately $96,570 for the entire length of the program.
There is a high chance of getting your doctorate at cheaper rates at a government-owned college instead of a private university. Books, accommodation, and expenses for research are some other costs that you may need to consider when preparing for a PhD program.
How to Pay for a PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering: PhD Funding Options
The PhD funding options that students use to pay for a PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering include student or financial loans. These loans often cover tuition expenses, living costs, and other expenses related to the PhD program. They may apply for scholarships or grants.
Students in a graduate PhD program can also apply for fellowships and assistantships such as a teaching assistantship, a graduate assistantship, or a research assistantship. No matter the choice, graduate students have multiple funding options to choose from.
Best Online Master’s Degrees
[query_class_embed] online-*subject-masters-degrees

What Is the Difference Between an Automation and Robotics Engineering Master’s Degree and PhD?
The difference between an automation and robotics master’s degree and a PhD is the amount of research involved. A master’s degree typically requires two years of full-time study, while a PhD can take up to five years. A PhD is the highest level of academic degree and is more research-oriented and involves writing a dissertation on an original topic.
Unlike in master’s degree programs, where you can take an internship in place of a capstone project, a PhD degree requires you to conduct comprehensive research on core research questions relevant to the field. Your thesis prepares you to become a university professor or professional researcher and qualifies you for the highest-level jobs.
Master’s vs PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering Job Outlook
If you have a PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering, you are qualified to teach in a postsecondary position. The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) projects a 12 percent growth rate for this profession . A job you can get with a master’s degree is a computer and information research scientist, which boasts a job outlook growth of 22 percent over the next ten years.
The benefit of getting a PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering is that you qualify for any jobs that require a master’s degree, while master’s degree holders do not qualify for PhD positions. BLS even states that a lot of employers prefer to hire PhD holders .
Difference in Salary for Automation and Robotics Engineering Master’s vs PhD
According to PayScale, the average annual salary for automation and robotics engineering PhD jobs is $107,000. That could be higher depending on the job title and level of experience. PhD holders are qualified to become research and development engineers, engineering project managers, robotics engineers, and senior software engineers.
In contrast, Master’s Degree in Automation and Robotics Engineering salaries average at $90,000 per year. Like the PhD holders, these professionals increase their earning potential as they get more experience and higher job titles. Some jobs that Master’s Degree in Automation and Robotics Engineering grads occupy are a senior mechanical engineer and project engineer.
Related Automation and Robotics Engineering Degrees
[query_class_embed] https://careerkarma.com/blog/robotics-associate-degrees/ https://careerkarma.com/blog/robotics-bachelors-degrees/ https://careerkarma.com/blog/automation/
Why You Should Get a PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering
You should get a PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering because it will give you the skills you need to be at the forefront of this growing industry. It significantly increases your earning potential, opens you up to high-end career opportunities, and helps you fast-track your journey up the career ladder. Below are the benefits of an automation and robotics engineering PhD.
Reasons for Getting a PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering
- Get endless opportunities. Automation and robotics will play an increasingly important role in our lives and in the economy. A PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering will give you the skills you need to be at the forefront of this growing industry.
- Expand your network. The research work of this program helps you to connect with other student researchers and faculty members from various specializations and departments. Workshops and seminars help students connect to leading researchers and scientists worldwide.
- Solve industry-wide problems . Automation and robotics engineering PhD students often conduct research to solve key unanswered questions in the industry. Ground-breaking research and discoveries can get you global recognition and qualify you for many prestigious awards.
- Get equipped for the next big step. A doctoral degree equips you with the skills, knowledge, and experience to dive into various career paths. After the program, you may begin a startup, join academia, advance in a professional tech career, or choose to continue as a computer science researcher.
Getting a PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering: Automation and Robotics Engineering PhD Coursework

With the advent of new technologies, getting a PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering can help you get the skill and exposure you need to stay on top of your career. We provided an overview of a typical automation and robotics engineering coursework that you’ll encounter during your studies.
Artificial Intelligence
The artificial intelligence (AI) course is a core component of the robotics engineering PhD curriculum. Students learn the theories and principles underlying the design and deployment of AI systems. Topics covered in the course include machine learning, probabilistic inference, decision theory, natural language processing, and robotics.
This advanced course covers topics like supervised and unsupervised learning, reinforcement learning, neural language processing, and their application in advanced systems. Throughout the course, students will use a variety of programming languages and tools like Python, MATLAB, TensorFlow, scikit-learn, and Keras to implement machine learning algorithms.
Mechatronics
This course covers topics such as microelectromechanical systems, robotics, control theory, smart materials and structures, and manufacturing processes. You’ll learn how to design and analyze mechatronic systems and how to optimize their performance.
Human-Robot Interaction
Human-robot interaction studies how people interact with robots and vice versa. It encompasses areas such as robotics, psychology, and design. Researchers in human-robot interaction work to create better and more natural interactions between humans and robots. The course also teaches the principles of HRI and ethical concerns surrounding robotics.
Robotic and Dynamic Programming
This course covers the mathematical foundations of optimal control theory and its applications to problems arising in robotics and engineering. Students will study the controllability and observability of linear systems. They will learn optimal control problems for discrete-time and continuous-time systems and discuss the problem of motion planning for robots.
Best Master’s Degrees
[query_class_embed] *subject-masters-degrees
How to Get a PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering: Doctoral Program Requirements
The doctoral program requirements for automation and robotics engineering typically demands students to complete a dissertation on a research topic of their choice. They must complete a certain number of credit hours, which may be earned through coursework or research. We have highlighted below the steps required to know how to get a PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering.
Most schools require students to maintain excellent grades all through the program length. Students have to complete coursework and research work with a grade of B or higher. In addition, they will also have to pass a final exam to get their doctorate.
Doctoral students in the field of automation and robotics engineering can expect to complete a rigorous program that will require them to maintain a GPA of 3.5 or higher. In addition to completing coursework, doctoral students will also be required to complete and defend a dissertation.
The coursework of automation and robotics engineering PhD programs includes core courses in mathematics, engineering, and computer science, along with electives in the student’s chosen specialization. To complete the doctoral program requirements, students must also complete an electives requirement.
To get a PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering, you will need to pass the final exam. This is a comprehensive test that will cover all of the material that you have learned throughout your doctoral program. The exam is usually administered by a panel of professors who are experts in the field and includes both written and oral components.
A thesis is a concrete documentation of a student's original research work carried out throughout the program. Including the research observation, procedure, and conclusion, it is usually 70,000 to 100,000 words long.
A thesis is required to be submitted, defended, and accepted before a Doctorate in Automation and Robotics Engineering is awarded to a student. Your thesis should provide answers to questions, solutions to a problem, or improvements to already existing solutions or theories in the robotics field.
Potential Careers With an Automation and Robotics Engineering Degree
[query_class_embed] how-to-become-a-*profession
PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering Salary and Job Outlook
With a PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering you can work in several industries, institutions, and organizations that involve manufacturing, data, engineering, research, and automation. BLS projects a seven percent growth for robotic engineers in the next decade. The rapid advancement in technology will further positively affect this prediction.
What Can You Do With a PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering?
With a PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering, you can work as a research engineer, a systems engineer, or a product development engineer. These positions all require working with complex machinery and designing new systems or products. You can also work as a professor at a university, teaching students and conducting research about the principles of robotics and automation.
Best Jobs with a PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering
- Engineering project manager
- Computer software research and development engineer
- Senior software engineer
- Senior robotics engineer
- Robotics engineering professor
What Is the Average Salary for a PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering?
The average salary for a graduate with a PhD in Robotics and Automation degree is $138,000 per year, according to PayScale. However, this number can vary depending on the level of experience and position the holder has. Generally, those with a PhD in this field can expect to make a comfortable living.
Highest-Paying Automation and Robotics Engineering Jobs for PhD Grads
Best automation and robotics engineering jobs with a doctorate.
Building a career in automation and robotics engineering typically requires you to have specialized knowledge and skills, and a doctorate gives you that. It also positions you to take on high-paying jobs. Here are some of the best automation and robotics engineering jobs with a doctorate.
These professionals are responsible for planning, organizing, and managing the execution of engineering projects. They work with teams of engineers to make sure projects are completed on time and within budget.
Engineering project managers must be able to juggle multiple tasks and priorities and have a strong understanding of the engineering process. They must also be able to effectively communicate with engineers and clients.
- Salary with an Automation and Robotics Engineering PhD: $152,350
- Job Outlook: 4% job growth from 2020 to 2030
- Number of Jobs: 197,800
- Highest-Paying States: California, New Mexico, Colorado, New Jersey, Texas
Computer software research and development engineers are responsible for designing, creating, testing, and maintaining software applications and programs. They work with teams of programmers and engineers to create new and innovative software products that meet the needs of their company or client.
- Salary with an Automation and Robotics Engineering PhD: $131,490
- Job Outlook: 22% job growth from 2020 to 2030
- Number of Jobs: 33,000
- Highest-Paying States: California, Washington, Maryland, New York, Rhode Island
Senior software engineers develop and manage software applications according to the company's requirements. They work with team members to design and implement solutions, as well as troubleshoot and debug issues. Considering their experience in the field, they mentor junior software engineers and oversee the work of other engineers.
- Salary with an Automation and Robotics Engineering PhD: $110,140
- Number of Jobs: 1,847,900
A robotics engineer is someone who designs and creates robots and robotic systems. They may work on the software, hardware, or mechanics of robots, and are involved in testing and deploying robots. In addition, they train other engineers and staff on the use of robotics in manufacturing and production environments.
- Salary with an Automation and Robotics Engineering PhD : $95,300
- Job Outlook: 7% job growth from 2020 to 2030
- Number of Jobs: 299,200
- Highest-Paying States: New Mexico, Louisiana, District of Columbia, California, Alaska
A robotics engineering professor is someone who teaches students about the design and operation of robots. They help students apply what they learn in the classroom to real-world situations. Beyond teaching, they carry out research on various aspects of automation and robotics.
- Salary with an Automation and Robotics Engineering PhD : $79,640
- Job Outlook: 12% job growth from 2020 to 2030
- Number of Jobs : 1,276,900
- Highest-Paying States: California, Illinois, Rhode Island, Washington, Alabama
Is a PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering Worth It?
Yes, a PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering is worth it. Earning this degree from a reputed university can open up a world of opportunities for you in the field of robotics. You get the opportunity to connect with several leading minds in science and technology.
Automation and robotics engineering PhD students are constantly on the lookout for new technological advancements which have the potential to disrupt entire industries. A breakthrough can bring you to the limelight and be a foundation for starting an entrepreneurship or research career. This degree positions you for the highest-paying jobs in the field.
Additional Reading About Automation and Robotics Engineering
[query_class_embed] https://careerkarma.com/blog/robotics/ https://careerkarma.com/blog/how-to-get-a-job-in-robotics/ https://careerkarma.com/blog/best-programming-languages-for-automation/
PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering FAQ
No, a PhD is not the minimum requirement for employment in robotics. However, it is preferred by most employers. A Master’s Degree in Robotics should suffice for most robotics-related jobs, but a PhD will make you more employable because you will be considered fit to handle advanced-level tasks.
No, although work experience may be a criterion for admission in some schools, it is usually not required. However, it is generally advised to have prior work experience as it will aid you in your pursuit of a doctorate.
Most robotics professionals have a Bachelor’s or Master’s Degree in Electrical, Mechanical, or Computer Engineering. These are the best fields to consider getting a bachelor’s or master’s in, as either of them will prepare you for a professional career in robotics.
On average, it takes about five years to complete a PhD program in robotics. However, the time a student will spend pursuing a PhD depends on the nature of the coursework and the school.
About us: Career Karma is a platform designed to help job seekers find, research, and connect with job training programs to advance their careers. Learn about the CK publication .
What's Next?
Get matched with top bootcamps
Ask a question to our community, take our careers quiz.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *


- Doing a PhD in Robotics
What does a PhD in Robotics Involve?
A PhD in robotics focuses on training researchers in the field of automation and robotics engineering. Doctoral students are characterised by the application of the techniques of this field in solving new problems and technological challenges. Nowadays, the field of automation covers a wide spectrum, ranging from the automation of industrial processes to the development of robotic systems for domestic environments or the pattern recognition for quality control systems.
The speciality areas for a PhD research project in robotics include:
- Intelligent Robotics : This area focuses on the design and development of intelligent and autonomous robotic systems. The aim of this area is to develop systems that understand their physical environment and use intuitive behaviour to adapt to changes.
- Intelligent Interfaces : This line of research deals with projects related to the design and development of interfaces to enable efficient interaction between the human user and the artificial robot system. It aims to develop artificial intelligent interfaces that enable communication and dialogue with the robotic system through voice, emotion and vision – in other words, human-robot interaction.
- Rehabilitation Robotics and Control of Robotic Systems : This line of research includes the development of robotic devices to support therapists and patients in physical rehabilitation therapies . One goal is the design and optimisation of robotic mechanisms and exoskeletons for physical therapy. To achieve this goal, mechanism design, optimisation algorithms, linear and nonlinear control techniques, artificial intelligence and haptic systems are used.
The fundamental aim of a doctoral robotics program is to enable students to become highly specialised by conducting original research in scientific and technological areas of robotics to answer stated research questions that ultimately improve our quality of life.
Browse PhDs in Robotics
Decoherence due to flux noise in superconducting qubits at microkelvin temperatures, demobeccs: the potential and demonstration feasibility of beccs, application of artificial intelligence to multiphysics problems in materials design, from text to tech: shaping the future of physics-based simulations with ai-driven generative models, study of the human-vehicle interactions by a high-end dynamic driving simulator, what are the typical application requirements for a phd in robotics.
A Robotics degree is mainly, but not exclusively, aimed at engineering graduates in the fields of robotics, electrical engineering, electronics, mechanics, industry, mechatronics, computer science, mathematics, physics and related fields .
The typical entry requirement is a relevant Masters qualification with an Upper Second-Class Honours, typically in one of the above-mentioned subjects. In addition, if the candidate is an international student, they will be expected to meet a number of English language requirements set by the university.
Although this is not always the case, some robotic PhD programs require the applicant to submit a research proposal outlining his or her intended research. The supervisor may use this to assess whether the student is suitable for the doctoral program, especially if the position comes with funding.
Personal Profile
The general entrance profile of graduate students in Robotic programs is that of a person interested in the formal development of technology based on design methodologies, interested in research with critical thinking, creativity and inventiveness to address new problems or innovate by offering solutions to real problems of automation and production, willingness to use computer systems, determination and perseverance.
Although not a prerequisite, it is helpful for a prospective PhD student to have knowledge in the following areas:
- Mathematics : numerical methods, linear algebra, numerical analysis, probability and statistics, and differential equations.
- Computing : programming, data structures, algorithms, computer vision, sensors (image, tactile, acoustic, pressure, etc.), speech recognition and synthesis.
- Physics : classical mechanics (kinematics and dynamics), optics.
- Engineering : mechanics (mechanisms and mechanical design), electronics (digital and analogue), control systems and signal processing.
In addition, many universities are also looking for prospective students who can demonstrate that they have the potential:
- Develop a thorough knowledge of the scientific and technological that underlies the field of robotics.
- Master the concepts, methods and techniques of their disciplinary field related to robotics.
- Can plan, carry out and evaluate original research projects, especially in their discipline.
- Train human resources for teaching and research.
- Can form multidisciplinary groups with national and international colleagues to carry out basic and applied research projects.
- Handling of specialised computer tools in the various fields of engineering.
- Communicate ideas as articles and presentations in professional forums.
- Have initiative and strong decision-making skills.
- Have ethical and moral commitment with its social environment for generating and passing on knowledge.
How much does a Robotics PhD cost?
The average university full-time tuition fee for a PhD in Robotics in the UK is approximately £4,407 per academic year for home students and £19,600 per academic year for international students. For part-time study it is approximately £2,203 and £8,800 per academic year for home and international students respectively.
Career and Professional Development Options

The influence of automation and robotics research in today’s society is becoming increasingly evident. Robotics is associated with the desire to synthesise some aspects of human function through mechanisms, sensors, actuators and computers.
The multidisciplinary nature of robotics enables it to include many fields of knowledge such as mathematics, physics, electronics, mechanics, computing, vision and artificial intelligence. Research and development in this area are crucial, and as a result, Robotic PhD graduates are in high demand.
Career options for robotics engineering degree holders include work in the following industries:
- Renewable Energy : developing systems to increase the efficiency of photovoltaic modules and collectors.
- Development of sensors : dedicated to the monitoring of remote variables, suitable for industrial environments such as the food industry.
- Home Automation : automation and control of smart homes.
- GPS : cargo monitoring and fleet tracking and management system.
- AGRO : statistics and data collection for the measurement of soil parameters.
- OEM : Original equipment for residential and industrial products.
- Mining and Military : developing technological equipment to increase field effectiveness.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
We use cookies to help our site work, to understand how it is used, and to tailor ads that are more relevant to you and your interests.
By accepting, you agree to cookies being stored on your device. You can view details and manage settings at any time on our cookies policy page.

Robotics and Autonomous Systems PhD
Key information, full-time - 4 years, part-time - 8 years.
Research brochure
Register for updates
Webinars and events
Why choose this programme
Robots must interact with people and objects, as well as challenging real-world environments. They must simulate human perception mechanisms, shared control and natural multi-modal interfaces. Robots must also exhibit a high degree of autonomy and intelligence when performing highly complex tasks, such as condition monitoring, prognostics and health management, and long-term persistent autonomy, including validation and verification.
Designing and managing robotics and autonomous systems requires diverse skills from various engineering disciplines such as electronics, mechatronics, control and signal processing, together with state-of-the-art micro and nano-sensors, embedded multi-core computing and artificial intelligence. This programme embraces all these disciplines and aims to train the next generation of innovators in the growing field of robotics and autonomous systems.
In the Research Excellence Framework (REF) 2021, the University of Surrey ranks 15th in the UK for research power for engineering and top 20 in the UK for the overall quality of research outputs (research papers and other published works).

Frequently asked questions about doing a PhD
What you will study
Our PhD in Robotics and Autonomous Systems will give you the knowledge, skills and expertise needed for a career in engineering, research or academia. You’ll be intellectually challenged, develop research and management skills, and become an expert in your chosen field of study.
It normally takes around three years to complete a full-time PhD. You will be assigned a minimum of two supervisors, who will guide you through your studies. You will learn how to conduct literature reviews, develop your ideas, and verify them with experiments, and collaborate and perform interdisciplinary research. You will develop your skills over time to become an independent researcher.
Your final assessment will be based on the presentation of your research in a written thesis, which will be discussed in a viva examination with at least two examiners. You have the option of preparing your thesis as a monograph (one large volume in chapter form) or in publication format (including chapters written for publication), subject to the approval of your supervisors.
Research support
The professional development of postgraduate researchers is supported by the Doctoral College , which provides training in essential skills through its Researcher Development Programme of workshops, mentoring and coaching. A dedicated postgraduate careers and employability team will help you prepare for a successful career after the completion of your PhD.

Research themes
- Aerial robotics
- Bioinspired robots
- Field robotics
- Human-robot interaction
- Robots for condition monitoring and prognostics
- Robots for space applications
- Robot-soil interaction
- Robotic sensing and perception
- Soft robotics.
Our academic staff
See a full list of all our academic staff within the School of Mechanical Engineering Sciences.
Research centres

Entry requirements
Applicants are expected to hold a first or upper second-class (2:1) UK degree in a relevant discipline (or equivalent overseas qualification), or a lower-second (2:2) UK degree plus a good UK masters degree - distinction normally required (or equivalent overseas qualification).
International entry requirements by country
English language requirements.
IELTS Academic: 6.5 or above (or equivalent) with 6.0 in each individual category.
These are the English language qualifications and levels that we can accept.
If you do not currently meet the level required for your programme, we offer intensive pre-sessional English language courses , designed to take you to the level of English ability and skill required for your studies here.
Application requirements
Applicants are advised to contact potential supervisors before they submit an application via the website. Please refer to section two of our application guidance .
After registration
Students are initially registered for a PhD with probationary status and, subject to satisfactory progress, subsequently confirmed as having PhD status.
Selection process
Selection is based on applicants:
- Meeting the expected entry requirements
- Being shortlisted through the application screening process
- Completing a successful interview
- Providing suitable references.
Student life
At Surrey we offer the best of both worlds – a friendly campus university, set in beautiful countryside with the convenience and social life of Guildford on your doorstep.
Start date: September 2024
Start date: January 2025
Start date: April 2025
Start date: July 2025
- Annual fees will increase by 4% for each year of study, rounded up to the nearest £100 (subject to legal requirements).
- Any start date other than September will attract a pro-rata fee for that year of entry (75 per cent for January, 50 per cent for April and 25 per cent for July).
Additional costs
There are additional costs that you can expect to incur when studying at Surrey.
A Postgraduate Doctoral Loan can help with course fees and living costs while you study a postgraduate doctoral course.
Apply online
If you are applying for a studentship to work on a particular project, please provide details of the project instead of a research proposal.
Read our application guidance for further information on applying.
To apply online first select the course you'd like to apply for then log in.
1. Select your course
Select the course you wish to apply for.
To apply online sign in or create an account.
Code of practice for research degrees
Surrey’s postgraduate research code of practice sets out the University's policy and procedural framework relating to research degrees. The code defines a set of standard procedures and specific responsibilities covering the academic supervision, administration and assessment of research degrees for all faculties within the University.
Download the code of practice for research degrees (PDF) .
Terms and conditions
When you accept an offer to study at the University of Surrey, you are agreeing to follow our policies and procedures , student regulations , and terms and conditions .
We provide these terms and conditions in two stages:
- First when we make an offer.
- Second when students accept their offer and register to study with us (registration terms and conditions will vary depending on your course and academic year).
View our generic registration terms and conditions (PDF) for the 2023/24 academic year, as a guide on what to expect.
This online prospectus has been published in advance of the academic year to which it applies.
Whilst we have done everything possible to ensure this information is accurate, some changes may happen between publishing and the start of the course.
It is important to check this website for any updates before you apply for a course with us. Read our full disclaimer .
Course location and contact details
Campus location
Stag Hill is the University's main campus and where the majority of our courses are taught.
University of Surrey Admissions
University of Surrey Guildford Surrey GU2 7XH
- Tools & Services
- Chemical, Biological, and Environmental Engineering
- Civil and Construction Engineering
- Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
- Mechanical, Industrial, and Manufacturing Engineering
- Nuclear Science and Engineering
- Biological & Ecological Engineering
- Alumni & Partners
Doctorate Degree in Robotics
The Robotics Ph.D. program of study comprise a minimum of 108 credits, including at least 48 credits of coursework and 36 credits of Thesis (ROB 603). The balance may either constitute additional coursework and/or thesis credits or come from other sources such as research, reading and conference, etc. At least 50 percent of the course credits should represent stand-alone graduate courses (500 level or above). The remaining credits may include the 5XX component of 4XX/5XX-level courses (so-called slash courses). Of the coursework credits, 16 must come from approved core courses.
Robotics Core : The intent of the Robotics core is to ensure each program of study both specializes in robotics, and contains sufficient breadth. To that end, the four-course core comprises one introductory course, one introductory hands-on robotics course, one autonomy course, and one fundamental control/dynamics course: 1. ROB 514 : Introduction to Robotics 2. ROB 515 : Introduction to Robotics II 3. ROB 537 : Learning-Based Control -OR- ROB 534 : Sequential Decision Making in Robotics 4. ME 531 : Linear Multivariate Control Systems I -OR- ROB 545 : Kinematics, Dynamics, and Control
Timeline of a Ph.D. in Robotics: The major milestones in completing a Ph.D. in robotics at Oregon State are listed below. For more information about these milestones, please contact the graduate advising team ( [email protected] ).
Selecting a major professor: Your major professor will serve as your primary advisor throughout your graduate program. While we assign all incoming MIME graduate students an interim advisor, it is your responsibility to select your major professor and assemble your committee as soon as possible. Your Ph.D. program of study, which must be filed with the Graduate School prior to the sixth term of enrollment, requires your committee's approval.
Qualifying examination: The purpose of the Ph.D. qualifying exam is to assess students’ research skills (their ability to analyze, interpret, and communicate fundamental scientific, mathematical, and engineering concepts) for the purpose of determining their aptitude for the Ph.D. program. The examination also includes a diagnostic function to highlight potential weaknesses in the students’ background that can be addressed through additional coursework or independent study.
Qualifying exam format: The qualifying exam consists of:
- A written research paper on a topic selected by the committee. This will generally consist of literature review of two areas, with a discussion highlighting the interesting research directions in that topic and a discussion off the social implications of the research. The committee will specify the format and length of the paper, which will be due one week prior to the scheduled oral examination.
- A 20 minute oral presentation on the topic of the research paper.
- topics presented in the research paper
- topics identified by the committee as a result of evaluating the research paper
Qualifying exam timeline: The qualifying exam is conducted every Winter term. Students entering the program with an MS degree must take the qualifying exam in their first year in graduate school. Students entering the program with a BS degree must take the qualifying exam in their second year in graduate school.
Program of Study meeting : After passing the qualifying examination and establishing a Ph.D. committee, students must convene a program meeting at which all committee members (including the Graduate Council Representative) are present. The purpose of this meeting is for you to present your program of study . At this meeting you will also present an approximate timeline for Ph.D. requirement completion (coursework completion, preliminary exam, and final oral exam).
Preliminary exam: The preliminary examination evaluates a Ph.D. candidate's research methodology, experimental plan, and interpretation of preliminary results (if appropriate). The purpose of the exam is to allow the committee to aid the candidate in planning and implementing the highest quality thesis.
Preliminary exam format: The preliminary exam consists of:
- A written document that summarizes previous work in the area, including the student's, and proposes the novel research needed to complete the thesis.
- A presentation of the proposal to the committee
- An oral examination on the proposal’s content
Preliminary exam timeline: The preliminary exam must be scheduled through the Graduate School using their Exam Scheduling Form , and exam takers must be formally enrolled (for a minimum of 3 credits) during the term in which the exam takes place.
Final Oral Examination: After completing all required coursework and thesis credits and submitting the pretext pages of your thesis to the Graduate School, you must schedule your final oral examination through the Graduate School using their Exam Scheduling Form. Also, you must be formally enrolled (for a minimum of 3 credits) during the term in which the exam takes place.
GRADUATE LEARNING OUTCOMES FOR ROBOTICS PHD PROGRAM
Outcome 1: Scholarship The student will be able to produce and defend a significant contribution to knowledge.
Outcome 2: Mastery of Subject Material The student will be able to demonstrate mastery of subject materials.
Outcome 3: Ethical Conduct Students will be able to conduct scholarly or professional activities in an ethical manner.
Note : For the most recent university guidelines and requirements, please consult the Graduate School . For the latest graduate handbooks, please see here .

Careers in robotics: Should you get a PhD or go into industry?
So you are considering a PhD in robotics! Before you decide to apply, here are some things to consider.
What is a PhD?
A PhD is a terminal degree, meaning it is the highest degree that you can earn. Almost without exception, people only earn one PhD. This degree is required for some jobs, mostly in academia, but is often just considered equivalent to years worked in industry. For some positions, hiring managers may even prefer to hire people without PhDs. A PhD is a paid (though not well paid) position at a university that lasts for between 4 and 10 years. To learn more about the PhD process, check out this previous post .

The author on a field trip to Oceano Dunes in California. She is controlling RHex, a six-legged robot, outfitted with sensors to study dune migration.
The day-to-day life of a PhD student versus an industry professional
The process of earning the PhD is very different from the process of earning a bachelor’s or a master’s degree. It is more like an internship or a job. The first two or so years of any PhD program will be largely coursework, but even at this stage you will be balancing spending time on your courses against spending time on research – either because you are rotating through different labs, because you are performing research for a qualifier, or because your advisor is attaching you to an existing research project to give you some experience and mentorship before you develop your own project. This means that getting a PhD is not actually a way to avoid “getting a job” or to “stay in school” – it is actually a job. This also means that just because you are good at or enjoy coursework does not mean you will necessarily enjoy or excel in a PhD program, and just because you struggled with coursework does not mean you will not flourish in a PhD program. After you are done with coursework, you will spend all of your time on research. Depending on the day, that can mean reading textbooks and research papers, writing papers, making and giving presentations, teaching yourself new skills or concepts, programming or building robots, running experiments, and mentoring younger students. If you excelled at either conducting research as an undergraduate or very open-ended course projects much more than typical coursework, you’ll be much more likely to enjoy research as a PhD student.
Types of goal setting in academia and industry
In course work, and in industry jobs with a good manager, you are given relatively small, well defined goals to accomplish. You have a team (your study group, your coworkers) who are all working towards the same goal and who you can ask for help. In a PhD program, you are largely responsible for narrowing down a big research question (like “How can we improve the performance of a self-driving car?”) into a question that you can answer over the course of a few years’ diligent work (“Can we use depth information to develop a new classification method for pedestrians?”). You define your own goals, often but not always with the advice of your advisor and your committee. Some projects might be team projects, but your PhD only has your name on it: You alone are responsible for this work. If this sounds exciting to you, great! But these are not good working conditions for everybody. If you do not work well under those conditions, know that you are no less brilliant, capable, or competent than someone who does. It just means that you might find a job in industry significantly more fulfilling than a job in academia. We tend to assume that getting a PhD is a mark of intelligence and perseverance, but that is often not the case — sometimes academia is just a bad match to someone’s goals and motivations.
Meaning and impact
Academic research usually has a large potential impact, but little immediate impact. In contrast, industry jobs generally have an impact that you can immediately see, even if it is very small. It is worth considering how much having a visible impact matters to you and your motivation because this is a major source of PhD student burnout. To give a tangible example, let’s say that you choose to do research on bipedal robot locomotion. In the future, your work might contribute to prostheses that can help people who have lost legs walk again, or to humanoid robots that can help with elder care. Is it important to you that you can see these applications come to fruition? If so, you might be more fulfilled working at a company that builds robots directed towards those kinds of tasks instead of working on fundamental research that may never see application in the real world. The world will be better for your contributions regardless of where you make them – you just want to make sure you are going to make those impacts in a way that allows you to find them meaningful!
Pay and lifetime earning potential
Engineers are significantly better paid in industry than academia. Since working in industry for a minimum of five to ten years and getting a PhD are often considered equivalent experience for the purposes of many job applications, even the time spent getting a PhD – where you will earn much less than you would in industry – can mean that you give up a substantial amount of money. Let’s say that an entry-level engineering job makes $100,000 per year, and a graduate student earns $40,000. If your PhD takes 6 years, you lose out on $60,000 x 6 = $360,000 of potential pay. Consider also that a PhD student’s stipend is fairly static, whereas you can expect to have incremental salary increases, bonuses, and promotions in an industry job, meaning that you actually lose out on at least $400,000. This is a totally valid reason to either skip the PhD process completely, or to work in industry for a few years and build up some savings before applying to PhD programs.

Robotics Institute at University of Toronto
How do I know what I want?
It’s hard! If you’re still uncertain, remember that you can gain a few years of work experience in industry before going back to get the PhD, and will likely be considered an even stronger candidate than before. Doing this allows you to build up some savings and become more confident that you really do want to get that PhD.
Thinking through these questions might help you figure out what direction you want to go:
- Are you much more motivated to do class projects that you are allowed to fully design yourself?
- When you think about something small you built being used daily by a neighbor, how do you feel?
- Is your desire to get a PhD because of the prestige associated with the degree, or the specific job opportunities it opens up?

Related posts :
Robot talk episode 85 – margarita chli, what’s coming up at #icra2024, octopus inspires new suction mechanism for robots, open robotics launches the open source robotics alliance, robot talk episode 77 – patricia shaw, robot talk episode 64 – rav chunilal.

Would you like to learn how to tell impactful stories about your robot or AI system?


Oluwami Dosunmu-Ogunbi Makes History As The First Black Woman To Obtain A Ph.D. In Robotics At The University Of Michigan
University of Michigan (U-M) graduate Oluwami Dosunmu-Ogunbi has made history!
The Street Journal reports she has earned a Ph.D. in robotics, the first for a Black woman at the institution.
Reflecting on her milestone and speaking in front of thousands of people during the university’s 2024 commencement ceremony, she said, “If you do not know me right now that is OK, but I want you to remember me as the University of Michigan’s first Black woman to get a Ph.D. in Robotics. We did it class of 2024. We can officially call ourselves Michigan engineers.”
She later took to LinkedIn and commented further stating, “Speaking at Commencement was the experience of a lifetime! To receive a standing ovation from a crowd of over 70,000 people in the largest stadium in North America…. Oh how far have I ascended! That little girl with big dreams is not so little anymore. She has become a GIANT.”
Dosunmu-Ogunbi’s road to her doctoral started in high school. She recalls being “fixated” on the “funny hat” her high school teacher wore at their graduation. She learned a doctorate degree would be required for her to adorn herself with such a hat. As the child of Nigerian immigrants, she adds that when considering her options to pursue a doctorate, she felt her only choices were to become a lawyer, doctor, or engineer, with the latter the most realistic pathway.
“I can’t be a doctor, because I hate blood. Lawyer is out because I would pass out if I had to ever talk in front of a large crowd of people… So I guess that leaves engineer,” she expressed in her speech.
In doing so, Dosunmu-Ogunbi shares that she understood the positive impact she could have on the world. She exemplified this by discussing her journey with high school students from “Girls Who Code,” advocating for college students’ various identities through participation and activities, and earning the U-M Spectrum Center’s Intersectional Advocacy Award in the process, her personal website mentions.
“A Michigan Engineer isn’t solely a beacon of scientific and technological prowess,” Dosunmu-Ogunbi mentioned during her speech. “Rather, they embody intellectual curiosity, social consciousness, and the ability to craft collaborative solutions for societal challenges. They foster inclusively and innovation, fostering a community dedicated to service for the greater good.”
As for what’s ahead for the bright mind, she is a a postdoctoral researcher in U-M Ann Arbor’s Robotics Department with a focus in “controls with applications in bipedal locomotion,” her website notes. Professor Jessy Grizzle serves as her advisor in the Biped Robotics Lab.
Ultimately, her overarching goal is to become a professor so she has the opportunity to break down the complex disciplines of engineering and robotics for a broader audience.


- Sign Up (2)
- f2fafrica.com
Meet the daughter of Nigerian immigrants who is the first Black woman to earn U-M Robotics PhD

Oluwami (Wami) Dosunmu-Ogunbi is the first Black woman to get a PhD in robotics at the University of Michigan . The daughter of Nigerian immigrants set off on her educational career with no clear end goal in mind. After graduating with her bachelor’s degree, she decided to devote the next five years to research, excited by the PhD regalia.
However, it wasn’t until recently that she understood there were several ways she could apply her engineering background to better people’s lives.
At the engineering graduate commencement ceremony on May 1, Ogunbi shared her story of failure and support. “I do not stand here on my own two feet alone. None of us got here by our individual merit alone,” she said, per the University of Michigan .
She entered the U-M mechanical engineering PhD program adorned with academic awards, including her MVP award from the University of Illinois ’ Pi Tau Sigma chapter, the mechanical engineering honor society. Despite this, she failed the U-M mechanical engineering PhD program’s qualifying tests.
She sought counsel from robotics professor Chad Jenkins, her mentor, when she considered leaving during the pandemic. Seeing Ogunbi’s promise, the lecturer worked quickly to put her in contact with robotics professor Jessy Grizzle, who, along with Jenkins, was a major figure in the founding of Michigan’s robotics program.
Grizzle, for his part, postponed his retirement plans and invited Ogunbi to work in his lab as his last PhD student. Ogunbi attempted her qualifying examinations again, and, fortunately, she found inspiration from Kira Barton, a robotics professor, and Robert Gregg, an associate professor of robotics, who asked questions that helped Ogunbi regain her confidence and get back on track.
Surrounded by a group of professors and colleagues who provided the necessary support, Ogunbi completed her study, with the main outcome being the development of a new stair-climbing controller for bipedal walking robots. She even performed the first demonstration of a bipedal robot stepping on, riding, and getting off a moving walkway.
Her most recent accomplishments are just a few of her distinctions. The university stated that Ogunbi has been a prominent member of the robotics community, having been appointed an outreach ambassador by Robotics for three consecutive years, 2021–2023, and receiving an MLK Spirit Award for mentorship and inspiration from the College of Engineering. She also placed second in the College of Engineering’s 3-minute thesis competition.
She has been admitted to the Bouchet Society, which celebrates outstanding scholarly performance and supports diversity in graduate education and the professoriate.
Ogunbi is currently applying for faculty positions.
Conversations

Help us create more content like this
Subscribe to premium
Already a member? Sign in.

Connect with us
Join our Mailing List to Receive Updates
- All Headlines
- Arts & Culture
- Bicentennial
- Human Resources
- Information Technology
- Police Beat
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Global Engagement
- Health & Medicine
- Public Engagement
- State & Community
- Sustainability
- Multimedia Features
- Faculty/Staff Spotlight
- This Week in U-M History
- U-M Heritage
- U-M In the News
- X (Twitter) #URecord
Commencement speaker shares how magic provides insight to shape lives
Brad meltzer offers four tricks to guide graduates — then springs another one.
By Katie Kelton The University Record
- Campus News
Spring Commencement speaker Brad Meltzer told University of Michigan graduates to draw upon the magic in their lives as they enter the world and continue to grow and transform into the best versions of themselves.
“Life will absolutely not be what you think it will be. It will be hard and wonderful and messy and rewarding, with more versions of you than you think possible,” he told the Michigan Stadium crowd at the May 4 ceremony.
“There are past versions of all of us, and the only thing I know for sure is if that past version of you could see you now, they would look at you in awe.”

Of the 15,100 students eligible to graduate, more than 8,500 graduates claimed tickets to attend the ceremony, their seats filling the Big House field, while thousands of family, friends and supporters filled two-thirds of the stadium around them under a sunny spring sky streaked with clouds.
Meltzer, an award-winning author of fiction and non-fiction books, was presented with an honorary Doctor of Laws degree.

Other honorary degree recipients were:
- Alexa I. Canady, groundbreaking neurosurgeon, Doctor of Science.
- Judith and Stanley Frankel, philanthropists, Doctor of Laws.
- Robin D. Givhan, Pulitzer Prize-winning journalist, Doctor of Laws.
A U-M alumnus with a son who graduated on May 4, Meltzer explained there are four types of magic tricks: making something appear, making something disappear, making two things switch places and changing one thing into something else. He said each trick can give valuable insight into how students can shape their lives.
Graduates should keep in mind the first trick — making something appear — as they try to make the best versions of themselves appear. Meltzer told graduates to surround themselves with people who bring out their best traits and drive them to be the best version of themselves.
He said his then-girlfriend, now wife, was the person who gave him the encouragement and support he needed to write his first book.
“When someone you trust sees your potential and says they believe you can be that person, it opens up a path and inspires you to become that version of yourself,” Meltzer said.
Meltzer said the second trick — making something disappear — can be used when faced with challenges that may be intimidating or scary. While it can be tempting to squash feelings of fear, he said, graduates should use these feelings to find momentum.
“So yes, make your fear disappear, but not because fear is bad. Use your fear. Harness it. Let them underestimate you. In the end, don’t vanquish your critics. Prove them wrong,” Meltzer said.
When addressing the third trick — making two things switch places — Meltzer spoke to the power of empathy. He told graduates about a time when he was a teenager living in New York and his father lost his job. His family of four moved into a cramped, one-bedroom apartment in Miami with two of Meltzer’s grandparents. Seeing the family’s predicament, one of their neighbors offered to leave her own apartment to give them more space and comfort.
“As you go through life, every person you encounter is battling something you can’t see. The solution is switching places and feeling empathy,” Meltzer said. “The world needs more empathy, more humility and certainly more decency.”

The final magic trick — changing one thing into something else — is essential, Meltzer said, because the graduates should never stop striving for personal transformation. He said people tend to get locked into a single state of thinking and living. However, if graduates continue their pursuit of knowledge and growth, they will never stop changing.
“As you leave Michigan, write in pencil and be unafraid to use the eraser,” Meltzer said. “The most sophisticated and intelligent people I know are the ones willing to challenge their thinking and admit there’s more to learn.”
Meltzer said all four magic tricks require effort. “Things don’t just appear or disappear by themselves. Making magic — figuring out who you are — takes work, time and intentionality,” he said. Although, the real magic, he said, comes from making memories and forging cherished friendships.
As he finished his remarks, Meltzer added, “The best magicians always have a final trick up their sleeve. Sometimes, magic is hiding in front of you the entire time.”
Gesturing to the rows of university leaders, faculty members and other dignitaries onstage, he introduced Michigan football legend Desmond Howard, who sprung from a seat wearing a black graduation robe and ran to the front of the stage to strike the Heisman Trophy pose.
“Here’s the thing,” Meltzer continued. “If you want to be the best magician, you’ve gotta top your last trick. Class of 2024, it’s your turn now.”
He then brought out J.J. McCarthy and Blake Corum, members of the 2024 national championship football team, who joined Meltzer and Howard onstage where together they revealed Block M shirts from under their robes.
The thousands of students and supporters filling the stadium rose to their feet and roared in surprised cheers.

In his remarks, President Santa J. Ono also congratulated the graduates for reaching this milestone.
“I’d like to offer my most sincere congratulations to our graduates, for all they have done to reach this milestone, and for all you are going to achieve moving forward in your lives,” he said.
“We’re so proud of your achievements, and we look forward to all that you will do. You will always be part of the University of Michigan family.”

Laurie McCauley, provost and executive vice president for academic affairs, praised the graduates for their hard work and fortitude as they completed a rigorous academic journey in spite of their early college years shrouded by the pandemic.
She spoke of the meaning of U-M’s slogan, “leaders and best,” and encouraged students to strive to be the best version of themselves.
“Leadership is not an identity. It is an action, and it takes continuous practice. For the last few years, you’ve practiced and worked hard to become your best self. And in doing so, you join a global community of leaders united under the banner of the maize and blue,” McCauley said.
Related article
- Journalist promotes kindness to graduates at Rackham ceremony
Faculty Senate Chair Tom Braun told graduates that his daughter spoke at her bat mitzvah about the Tower of Babel. God destroyed the tower, Braun said, because people valued its creation and its impressive height more than the human lives that were lost during its creation.
“I personally think we have far too many Towers of Babel being built in our world right now. … Far too much importance is placed on ideals, positions and demands rather than the human lives that they affect,” Braun said. “I hope you are able to peacefully find your way to be heard, and allow others to be heard, in a vast and often confusing world.”
Oluwami Dosunmu-Ogunbi, a doctoral candidate in the College of Engineering and one of three student speakers, congratulated her fellow graduates as she made history as the first Black woman to earn a Ph.D. in robotics from U-M.
Dosunmu-Ogunbi said she felt “small and powerless” when she was younger, but felt a “fundamentally, raw human urge to be great.” She found the support needed to foster this greatness at U-M.
“Though our specific struggles may have been different, we are united in overcoming our challenges. We had the grit, the motivation and the support to be our best selves,” Dosunmu-Ogunbi said.
“As we graduate today, we must honor those who supported us. We do this by embracing their influence to create a better future — for those already here and those yet to come.”

During the ceremony, Reserve Officers Training Corps graduates were commissioned as officers in their respective service branches by U.S. Navy Secretary Carlos Del Toro.
During the commissioning ceremony, approximately 75 pro-Palestinian protesters gathered at the rear of the student section and then moved down the center aisle, waving flags and chanting, “Disclose. Divest. We will not stop. We will not rest.”
About halfway to the stage they were stopped by public safety officers and university officials and then continued chanting throughout the commissioning ceremony and presentation of honorary degrees. At various times, other students shouted at the protesters and chanted in response: “USA! USA!”
After about 15 minutes, the demonstrators moved to the back of the stadium, guided by officers, and continued their protest — albeit less loudly — throughout the rest of the ceremony. The program was not interrupted and no arrests were made.
In his remarks, Del Toro said the newly commissioned officers “will protect the freedoms that we so cherish as Americans in our Constitution of the United States, which includes the right to protest peacefully.”
— James Iseler of The University Record contributed to this article.
- commencement
- honorary degrees
- Michigan Stadium
- Spring Commencement
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Please read our comment guidelines .
In order to leave a comment, you must log in with your U-M credentials.
Today's Headlines
- University proceeds with plan for campus solar power projects
- Alcohol sales at Michigan Stadium to begin this football season
- Friese named vice provost for academic and faculty affairs
- U-M Health to improve access with University Hospital renovation
- Regents authorize various real estate purchases, sales
- Regents approve faculty promotions
- Regents Roundup — May 2024
- New campus parking permit rates will take effect July 1
- Copper cannot be mined fast enough to electrify United States
- Record shifting to reduced summer email, print schedule

- Past Issues
- Michigan Daily
- Michigan News
- Michigan Public
- Michigan Today
- Health System News
- Athletic News
- Undergraduate
- STUDENT LIFE
Robotics and mechatronics major in high demand with students

Randolph’s new robotics and mechatronics engineering major, which will begin this fall, provides students with the best of both worlds—a challenging, high-tech educational foundation in an environment with small classes, accessible professors, and numerous opportunities for real-world research experience.
E v ery major industry—think telecommunications, agriculture, transportation, biotechnology, automobile, national security, and renewable energy—relies heavily on mechatronics, an emerging field at the center of one of Randolph’s newest majors.
While some might think an aspiring engineer would need to go to a big state school to be successful in the field, a liberal arts college provides unique benefits for those pursuing these careers.
“Engineering is a space unto itself in college and naturally takes more credits than most other majors,” said Peter Sheldon, Randolph’s Charles A. Dana Professor and chair of the physics and engineering departments.

“Engineering schools are typically larger, and only a fraction of the students get hands-on opportunities,” he added. “Here at Randolph, you are going to get your hands on the equipment. You are going to get those opportunities to do further research and projects beyond the classroom, and there are also great support systems set up to help students succeed.”
An interdisciplinary branch of engineering, mechatronics involves mechanical, electrical, and computer engineering. Robotics is a subset of that, focusing on applied systems to design, build, and operate smart machines.
“Think about how robots work or how motors work,” Sheldon explained. “There are physical things that you have to put together to, for instance, move a robotic arm. That’s mechanical engineering. Then you’ve got the electrical components that run the robotic or motor parts, and you use computer engineering to program them to do various tasks.”
Mechatronics also plays a big role in industrial engineering, “an industry where you’re putting things together and going from raw materials to finished products,” he said.
Students will gain a foundation in engineering, computer science, physics, mathematics, and chemistry—and receive hands-on experience with robots from the start.

“We have seen a growing interest in majors such as this and believe offering robotics and mechatronics engineering at Randolph will meet the needs of current and future students,” said Travis Carter, dean of admission and financial aid. “This is an exciting addition to our already strong academic program.”
The coursework is varied; students will go from studying the chemistry of materials to electronic circuits to computer programming, which will all be brought together in manufacturing and engineering.
They’ll finish their degree in four years, culminating in a capstone project that Sheldon said is “very much in the field, actually producing something that works, likely with partners in the industry.”
Those partnerships will be easier to come by in Lynchburg.
“While manufacturing and robotics are big everywhere, this is a particular hotbed for that kind of engineering,” Sheldon said. “We are well-situated with a lot of engineering companies and others in the industry, which is one of the reasons why we chose this major. There’s going to be a lot of partnership opportunities.”
The College has hired two new full-time professors of engineering and is renovating an entire floor in Presser Hall, which will be home to a new teaching lab, research spaces, and machine shop—on top of the ongoing multimillion-dollar renovation of Martin Science Building.
“The engineering program at Randolph is a unique liberal arts experience for those who are not sure where they want to go in the field,” said Severin McNulty ’27. “There are lots of opportunities to get out there and try new things. The robotics and mechatronics program will add diversity to the department and bring in more staff with unique backgrounds, allowing for a better education for all students.”

Randolph News
- Vita Abundantior Magazine
- Events Calendar
- Athletics Updates
- For the Media
- Office of College Relations

Skip to Content
Other ways to search:
- Events Calendar
#ComputeHer
Shamika Klassen stands before the CASE building and a window screen featuring Lucille Berkeley Buchanan, who in 1918 became the first Black woman to graduate from the University of Colorado—an achievement the university did not recognize in her lifetime. Klassen called Buchanan ‘a very big influence on me’ while also saying her experience at CMCI was both welcoming and inclusive. She graduated in May with a PhD, the first Black woman to do so from CMCI’s information science department.
You are here
By Joe Arney Photos by Kimberly Coffin (CritMedia, StratComm’18)
Three words you do not want to tell Shamika Klassen: No, you can’t.
Klassen vividly recalls attending a seventh-grade math and engineering camp where she got to hear from a scientist who described what a PhD was. To Klassen, who’d fallen in love with technology, it sounded like a dream opportunity.
“But then he ended his little speech with how it’s really hard to get a PhD, especially if you're a minority—so you shouldn't try,” Klassen, who is Black, said. “So, I raised my hand during the Q&A. I said, ‘My name is Shamika. I just wanted you to know, I'm getting my Phd.’”
More than two decades later, Klassen’s mic-drop moment is here. A first-generation student, she graduates this May with a PhD from the College of Media, Communication and Information at the University of Colorado Boulder, becoming the university’s first Black person to earn a doctoral degree in information science —a discipline she discovered almost by accident, but one that prepared her to join Google as a user experience researcher.
“As I got older, that excitement I had about technology turned into curiosity about how it was falling short of these aspirations and dreams and imaginations that we had for it,” the soft-spoken scholar said. “I wanted to be part of the bridge between where technology is and where it could be.”
That started in her childhood—Klassen still vividly remembers re-engineering an automated stroller for a doll to turn it into a robot—and was a major reason she pursued a master of divinity from Union Theological Seminary after graduating from Stanford University and teaching with AmeriCorps.
But it was through her connection with Nathan Schneider—who she’d already had the opportunity to work with, including during his time with the Social Science Research Council—that Klassen learned about information science, and how it blended her interests in service and technology.
Schneider, an assistant professor of media studies, was already acquainted with Klassen's work, and in her saw his own academic journey, which also offers interdisciplinary intrigue.
“I was trying to find my own path between my background in religion and how to incorporate tech more into my work—and I loved how she was doing that,” he said.
Klassen studies where technology falls short of its professed ideals, and the kinds of people it leaves behind. Specifically, she invites Black women, femmes and nonbinary people to imagine a better, more equal future—part of a concept she calls technowomanism that dates back to the formation of Black Lives Matter and the Gamergate harassment campaign.
Black Twitter, meet Green-Book
“There was this real dissonance between my activism and my academics—I’d be marching in the afternoon, and writing a paper about liberation theology in the evening,” she said. Technowomanism, she said, “is a use of the womanist ethical framework applied to social justice issues in technology–it’s me asking how can we use ethical frameworks that are rooted in the Black feminism traditions when we're talking about technology.”
A digital calling
At Union Theological Seminary, Shamika Klassen became a “tech chaplain”—in the words of one of her professors, her skill at helping others navigate “these moments of issue with their technology with dignity and grace” was similar to a chaplain ministering believers through troubled times.
It’s how she found herself in the crosshairs of Rod Dreher, the deeply conservative columnist and author, who took aim at her in a piece about social justice warriors. He invited Klassen to reply, and wound up publishing her entire 1,700-word response as a follow up.
“I loved the thoughtfulness of her reply,” Nathan Schneider said. “He made this vicious attack on her, she responds with incredible strength—and he just kind of rolled over. And this is not a guy who rolls over.”
It’s why he was excited to recommend her to CMCI’s doctoral program and why he’s enjoyed opportunities to collaborate with her, most notably on the Sacred Stacks project at the Media Economies Design Lab, of which Schneider is director.
“On that project, I got to see how others responded to her, and the kind of awe and admiration that so often follows her presence—and that maybe she doesn’t see,” he said. “It just makes me so hopeful and so excited about what’s next for her.”
For instance, an early project compared Black Twitter to the Jim Crow-era Green-Book ; both offered Black users a sense of community in unfriendly places. As she interviewed participants about what a real Black Twitter—a social network designed by, and intended for, Black users—could look like, she started asking larger questions about the research ethics of public data.
“It was a great opportunity to talk about the history of research in Black communities,” Klassen said. “Instead of just parachuting in, extracting data and leaving, could we build relationships with these communities, and be more honest and sincere about our intentions?”

“As an ethicist who spends a lot of time critiquing big tech, one of the things that makes me feel better about everything is when people like Shamika go to work in big tech,” said Casey Fiesler , an associate professor of information science. “Because having people who care so deeply, and who have different kinds of perspectives and lived experiences, is how change starts to happen.
“I think Google is exceptionally lucky to have her, and the rest of us are exceptionally lucky to have her at Google.”
Klassen knows a thing or two about luck: She considers herself fortunate to have been raised by a single mother, Mary Shelton, who worked tirelessly to support her four children, of whom Klassen is the eldest.
“She has been the most incredible figure in my life,” Klassen said, sharing a story from her Stanford days of being invited to give a talk at a math camp in Texas, but without enough time to visit her San Antonio home.
“My mom got off work at the post office and drove straight to San Marcus from San Antonio—in her uniform—so she could see my talk,” Klassen said. “We didn’t have a lot of money. But we did have that incredible support from someone who made all kinds of sacrifices that helped me get where I am today.
“I hope she’s proud of me. But I also hope my mom and the rest of my family can see my story and be inspired to do something that they want to do.”
‘The opportunity of a lifetime’
“I want to be able to center marginalized voices in the design and development of technology. And I know that being a voice in the room advocating for these things is a big responsibility.” Shamika Klassen (PhDInfoSci’24)
At Google, she hopes to inspire others to rethink technology. The job is, she said, “the opportunity of a lifetime” and follows an internship where she studied assistive technologies that use artificial intelligence to better understand how to help people with disabilities.
“I want to be able to center marginalized voices in the design and development of technology,” Klassen said. “And I know that being a voice in the room advocating for these things is a big responsibility.”
Count Joanna Mendy (PolSci, Soc’22), a master’s student in information science, among those already inspired by Klassen. A few chance encounters while she was working with the university’s BioFrontiers Institute led Mendy to become Klassen’s research assistant; the two share a passion for bringing people from underrepresented and historically excluded backgrounds into the tech design space.
“I have a genuinely hard time articulating what it’s been like to work with someone who’s so brilliant, so caring and so intentional about her work,” Mendy said of her mentor. “She showed me how to really think through a research project—how to make sure you’re hitting all your goals while still being flexible.
“So much of Shamika's research is about making sure that people feel heard and feel seen. That’s important to me, as well, and she’s been a big influence in helping me make sure those voices are part of my work.”
Exclusive: Wayve co-founder Alex Kendall on the autonomous future for cars and robots
U.K.-based autonomous vehicle startup Wayve started life as a software platform loaded into a tiny electric “car” called Renault Twizy . Festooned with cameras, the company’s co-founders and PhD graduates, Alex Kendall and Amar Shah, tuned the deep-learning algorithms powering the car’s autonomous systems until they’d got it to drive around a medieval city unaided.
No fancy lidar cameras or radars were needed. They suddenly realized they were on to something.
Fast-forward to today and Wayve, now an AI model company, has raised a $1.05 billion Series C funding round led by SoftBank, Nvidia and Microsoft. That makes this the U.K.’s largest AI fundraise to date, and among the top 20 AI fundraises globally. Even Meta’s head of AI, Yann LeCun, invested in the company when it was young.
Wayve now plans to sell its autonomous driving model to a variety of auto OEMs as well as to makers of new autonomous robots.

In an exclusive interview, I spoke to Alex Kendall, co-founder and CEO of Wayve, about how the company has been training the model, the new fundraise, licensing plans and the wider self-driving market.
(Note: The following interview has been edited for length and clarity)
TechCrunch: What tipped the balance to attain this level of funding?
Kendall: Seven years ago, we started the company to build an embodied AI. We have been heads-down building technology […] What happened last year was everything really started to work […] All the elements that are required to make this product dream a reality [came together], and, in particular, the first opportunity to get embodied AI deployed at scale.
Now production vehicles are coming out with GPUs, surrounding cameras, radar and, of course, the appetite to now bring AI onto, and enable, an accelerated journey from assisted to automated driving. So this fundraise is a validation of our technological approach and gives us the capital to go and turn this technology into a product and bring it to market.
Very soon you’ll be able to buy a new car and it’ll have Wayve’s AI on it […] Then this goes into enabling all kinds of embodied AI, not just cars, but other forms of robotics. I think what we want to achieve here is to go way beyond where AI is today with language models and chatbots. To really enable a future where we can trust intelligent machines that we can delegate tasks to, and of course, they can enhance our lives. Self-driving will be the first example of that.
How have you been training your self-driving model these last couple of years?
We partnered with Adsa and Ocado to collect data to trial autonomy. That’s been a great way for us to get this technology off the ground, and it continues to be a really important part of our growth story.
What is the plan around licensing the AI to OEMs, to automotive manufacturers? What will be the benefits?
We want to enable all the auto manufacturers around the world to work with our AI, of course, across a wide variety of sources. More importantly, we’ll get diverse data from different cars and markets, and that’s going to produce the most intelligent and capable embodied AI.
Which car makers have you sold it to? Who have you landed?
We’re working with a number of the top 10 automakers in the world. We’re not ready to announce who they are today.
What moved the needle for SoftBank and the other investors in terms of your technology? Was it because you’re effectively platform-independent and every car will now sport cameras around it?
That’s largely correct. SoftBank has publicly commented on their focus on AI and robotics, and self-driving [tech] is just the intersection of that. What we’ve seen so far with the AV 1.0 approaches is where they throw all of the infrastructure, HD maps, etc., in a very constrained setting to prove out this technology. But it’s a very far journey from there to something that’s possible to deploy at scale.
We’ve found that — and this is where SoftBank and Wayve are completely aligned in the vision for creating autonomy at scale — by deploying this software and a diverse set of vehicles around the world, millions of vehicles, we can not only build a sustainable business, we can also get diverse data from around the world to train and validate the safety case to be able to deploy AV at scale through “hands off, eyes off” driving around the world.
This architecture operates with the intelligence onboard to make its own decisions. It’s trained on video as well as language, and we bring in general-purpose reasoning and knowledge into the system, too. So it can deal with the long-tail, unexpected events that you see on the road. This is the path we’re on.
Where do you see yourself in the landscape at the moment in terms of what’s deployed out there already?
There have been a bunch of really exciting proof points, but self-driving has largely plateaued for three years, and there’s been a lot of consolidation in the AV space. What this technology represents, what AI represents, is that it’s completely game-changing. It allows us to drive without the cost and expense of lidar and HD. That allows us to have the onboard intelligence to operate. It can handle the complexities of unclear lane markings, cyclists and pedestrians, and it’s intelligent enough to predict how others are going to move so it can negotiate and operate in very tight spaces. This makes it possible to deploy technology in a city without causing angst or road rage around you, and to drive in a way that conforms with the driving culture.
You did your first experiments back in the day, peppering the Renault Twizy with cameras. What’s going to happen when car manufacturers put lots of cameras around their cars?
Car manufacturers are already building vehicles that make this possible. I wouldn’t name brands, but pick your favorite brand, and particularly with the higher-end vehicles, they have surround cameras, surround radar and an onboard GPU. All of that is what makes this possible. Also, they’ve now put in place Software Defined Vehicles , so we can do over-the-air updates and get data off the vehicles.
What’s been your “playbook”?
We built a company that has all the pillars required to build. Our playbook has been AI, talent, data and compute. On the talent front, we’ve built a brand that’s at the cross-section of AI and robotics, and we’ve been fortunate enough to bring some of the best minds around the world to come work on this problem. Microsoft’s been a long-standing partner of ours, and the amount of GPU compute they’re giving us in Azure is going to allow us to train a model at the scale of something that we haven’t seen before. A truly enormous, embodied AI model that can actually build the safe and intelligent behavior we need for this problem. And then Nvidia, of course. Their chips are best-in-class in the market today and make it possible to deploy this technology.
Will all of the training data you get from the brands you work with be mixed together into your model?
That’s right. That’s exactly the model we’ve been able to prove. No single car manufacturer is going to produce a model that is safe enough on their own. Being able to train an AI on data from many different car manufacturers is going to be safer and more performant than just one. It’s going to come from more markets.
So you’re effectively going to be the holder of probably the largest amount of training data around driving in the world?
That’s certainly our ambition. But we want to make sure that this AI goes beyond driving — like a true embodied AI. It’s the first vision-language-action model that’s capable of driving a car. It’s not just trained on driving data, but also internet-scale text and other sources. We even train our model on the PDF documents from the U.K. government that tell you the highway code. We’re going to different sources of data.
So it’s not just cars, but robots as well?
Exactly. We’re building the embodied AI foundation model as a general-purpose system trained on very diverse data. Think about domestic robotics. The data [from that] is diverse. It’s not some constrained environment like manufacturing.
How do you plan to scale the company?
We continue to grow our AI, engineering and product teams both here [in the U.K.] and in Silicon Valley, and we just started a small team in Vancouver as well. We’re not going to ‘blitzscale’ the company, but use disciplined, purposeful growth. The HQ will remain in the U.K.
Where do you think the centers of talent and innovation are in Europe for AI?
It’s pretty hard to look anywhere outside London. I think London is by far the dominant place in Europe. We’re based in London, Silicon Valley and Vancouver — probably in the top five or six hubs in the world. London has been a great spot for us so far. We grew out of academic innovation in Cambridge to begin with. Where we are now to the next chapter is somewhat a road less well-trodden. But in terms of where we are now, it’s been a brilliant ecosystem [in the U.K.].
There are a lot of good things to be said around corporation, law and tax. On the regulation front, we’ve worked with the government for the last five years now on new legislation for self-driving in the U.K. It passed the House of Lords, it’s almost through the House of Commons, and should soon come into law and make all of this legal in the U.K. The ability for the government to lean into this to work with us […] we’ve really worked in the weeds for that and had over 15 ministers visit. It’s been a really great partnership so far, and we’ve certainly felt the support of the government.
Do you have any comments on the EU’s approach to self-driving?
Self-driving is not part of the AI act. It’s a specific vertical and should be regulated with subject matter experts and as a specific vertical. It’s not some uncoordinated catch-all, and I’m glad about that. It’s not the fastest way to innovate in specific verticals. I think we can do this responsibly by working with specific automotive regulatory bodies that understand the problem space. So sector-specific regulation is really important. I’m pleased the EU has taken that approach to self-driving.
More TechCrunch
Get the industry’s biggest tech news, techcrunch daily news.
Every weekday and Sunday, you can get the best of TechCrunch’s coverage.
Startups Weekly
Startups are the core of TechCrunch, so get our best coverage delivered weekly.
TechCrunch Fintech
The latest Fintech news and analysis, delivered every Sunday.
TechCrunch Mobility
TechCrunch Mobility is your destination for transportation news and insight.
Adobe comes after indie game emulator Delta for copying its logo
After Apple loosened its App Store guidelines to permit game emulators, the retro game emulator Delta — an app 10 years in the making — hit the top of the…

Meta’s latest experiment borrows from BeReal’s and Snapchat’s core ideas
Meta is once again taking on its competitors by developing a feature that borrows concepts from others — in this case, BeReal and Snapchat. The company is developing a feature…
Startups Weekly: It’s the dawning of the age of AI — plus, Musk is raging against the machine
Welcome to Startups Weekly! We’ve been drowning in AI news this week, with Google’s I/O setting the pace. And Elon Musk rages against the machine.

IndieBio’s SF incubator lineup is making some wild biotech promises
IndieBio’s Bay Area incubator is about to debut its 15th cohort of biotech startups. We took special note of a few, which were making some major, bordering on ludicrous, claims…

YouTube TV’s ‘multiview’ feature is now available on Android phones and tablets
YouTube TV has announced that its multiview feature for watching four streams at once is now available on Android phones and tablets. The Android launch comes two months after YouTube…

Featured Article
Two Santa Cruz students uncover security bug that could let millions do their laundry for free
CSC ServiceWorks provides laundry machines to thousands of residential homes and universities, but the company ignored requests to fix a security bug.

OpenAI created a team to control ‘superintelligent’ AI — then let it wither, source says
OpenAI’s Superalignment team, responsible for developing ways to govern and steer “superintelligent” AI systems, was promised 20% of the company’s compute resources, according to a person from that team. But…

Harness the TechCrunch Effect: Host a Side Event at Disrupt 2024
TechCrunch Disrupt 2024 is just around the corner, and the buzz is palpable. But what if we told you there’s a chance for you to not just attend, but also…

Pitch Deck Teardown: Goodcarbon’s $5.5M seed deck
Decks are all about telling a compelling story and Goodcarbon does a good job on that front. But there’s important information missing too.

Slack under attack over sneaky AI training policy
Slack is making it difficult for its customers if they want the company to stop using its data for model training.

Healthcare company WebTPA discloses breach affecting 2.5 million people
A Texas-based company that provides health insurance and benefit plans disclosed a data breach affecting almost 2.5 million people, some of whom had their Social Security number stolen. WebTPA said…

Microsoft dodges UK antitrust scrutiny over its Mistral AI stake
Microsoft won’t be facing antitrust scrutiny in the U.K. over its recent investment into French AI startup Mistral AI.

Embedded finance is still trendy as accounting automation startup Ember partners with HSBC UK
Ember has partnered with HSBC in the U.K. so that the bank’s business customers can access Ember’s services from their online accounts.

Kudos lands $10M for an AI smart wallet that picks the best credit card for purchases
Kudos uses AI to figure out consumer spending habits so it can then provide more personalized financial advice, like maximizing rewards and utilizing credit effectively.

EU warns Microsoft it could be fined billions over missing GenAI risk info
The EU’s warning comes after Microsoft failed to respond to a legally binding request for information that focused on its generative AI tools.

A US Trustee wants troubled fintech Synapse to be liquidated via Chapter 7 bankruptcy, cites ‘gross mismanagement’
The prospects for troubled banking-as-a-service startup Synapse have gone from bad to worse this week after a United States Trustee filed an emergency motion on Wednesday. The trustee is asking…

Seraphim’s latest space accelerator welcomes nine companies
U.K.-based Seraphim Space is spinning up its 13th accelerator program, with nine participating companies working on a range of tech from propulsion to in-space manufacturing and space situational awareness. The…

OpenAI inks deal to train AI on Reddit data
OpenAI has reached a deal with Reddit to use the social news site’s data for training AI models. In a blog post on OpenAI’s press relations site, the company said…

X pushes more users to Communities
X users will now be able to discover posts from new Communities that are trending directly from an Explore tab within the section.

Mark Zuckerberg’s makeover: Midlife crisis or carefully crafted rebrand?
For Mark Zuckerberg’s 40th birthday, his wife got him a photoshoot. Zuckerberg gives the camera a sly smile as he sits amid a carefully crafted re-creation of his childhood bedroom.…

Strava taps AI to weed out leaderboard cheats, unveils ‘family’ plan, dark mode and more
Strava announced a slew of features, including AI to weed out leaderboard cheats, a new ‘family’ subscription plan, dark mode and more.

Astronauts fall over. Robotic limbs can help them back up.
We all fall down sometimes. Astronauts are no exception. You need to be in peak physical condition for space travel, but bulky space suits and lower gravity levels can be…

Microsoft’s custom Cobalt chips will come to Azure next week
Microsoft will launch its custom Cobalt 100 chips to customers as a public preview at its Build conference next week, TechCrunch has learned. In an analyst briefing ahead of Build,…
Tesla keeps cutting jobs and the feds probe Waymo
What a wild week for transportation news! It was a smorgasbord of news that seemed to touch every sector and theme in transportation.

Sony Music warns tech companies over ‘unauthorized’ use of its content to train AI
Sony Music Group has sent letters to more than 700 tech companies and music streaming services to warn them not to use its music to train AI without explicit permission.…

GrubMarket buys Butter to give its food distribution tech an AI boost
Winston Chi, Butter’s founder and CEO, told TechCrunch that “most parties, including our investors and us, are making money” from the exit.

Bolt founder Ryan Breslow wants to settle an investor lawsuit by returning $37 million worth of shares
The investor lawsuit is related to Bolt securing a $30 million personal loan to Ryan Breslow, which was later defaulted on.

With the end of Workplace, it’s fair to wonder if Meta was ever serious about the enterprise
Meta, the parent company of Facebook, launched an enterprise version of the prominent social network in 2015. It always seemed like a stretch for a company built on a consumer…

Meta Threads is testing pinned columns on the web, similar to the old TweetDeck
X, formerly Twitter, turned TweetDeck into X Pro and pushed it behind a paywall. But there is a new column-based social media tool in town, and it’s from Instagram Threads.…

Google expands hands-free and eyes-free interfaces on Android
As part of 2024’s Accessibility Awareness Day, Google is showing off some updates to Android that should be useful to folks with mobility or vision impairments. Project Gameface allows gamers…


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Yes, you can get a PhD in robotics, and one example of such a program is offered jointly by the College of Computing and the College of Engineering at Georgia Institute of Technology. How long is a PhD in robotics? A PhD in robotics typically takes about five to six years to complete. The program includes coursework, a research qualifier, and ...
The Robotics program supports Tech's mission to provide instruction in disciplines related to science, technology, and interdisciplinary areas. Program of Study. The main emphasis of the Ph.D. program is the successful completion of an original and independent research thesis. The degree requirements are designed around this goal.
Curriculum. The PhD in Robotics Engineering doctoral program is groundbreaking and internationally known for its outstanding faculty and advanced research projects. A small student-to-faculty ratio means students work side by side with world-class professors who are exploring everything from medical robotic devices and multi-robot systems to ...
Georgia Tech is one of the first institutions to offer an interdisciplinary Ph.D. program in robotics to students enrolled in a participating home school in the College of Computing or the College of Engineering. A fully integrated and multidisciplinary experience, the program educates a new generation of robotics researchers who are prepared ...
Georgia Tech is one of the first institutions to offer an interdisciplinary Ph.D. program in robotics to students enrolled in a participating home school in the College of Computing or the College of Engineering. A fully integrated and multidisciplinary experience, the program educates a new generation of robotics researchers who are prepared ...
Graduates of the CMU Robotics PhD program take a leading role in the research and development of future generations of integrated robotics technologies and systems.
The Robotics graduate program at Colorado School of Mines offers a core curriculum focused on robotic perception, cognition, action and interaction, with technical electives in computer science, mechanical engineering and electrical engineering. Ph.D. / Full-time / On Campus. Colorado School of Mines Golden, Colorado, United States. Ranked top 5%.
Students are responsible for ensuring that they understand and satisfy any home unit requirements as well as the Robotics program and Institute requirements. Ph.D. Robotics Degree Requirements - 36 semester hours with a letter grade. CS/AE/ECE/ME 7785, Introduction to Robotics Research.
PhD Program in Robotics Offered jointly by the College of Computing and the College of Engineering, the Ph.D. program in Robotics is the first truly multidisciplinary robotics degree of its kind in the world—and only the second robotics doctorate offered in the U.S. The program involves the schools of Interactive
Robotics (Ph.D.) Course Description and Catalog. Focus: educating a new breed of multidisciplinary researchers in robotics who will provide leadership in this rapidly evolving discipline and help meet the growing industrial and societal demand for advanced education and research in robotics.
The admission process begins by applying for graduate admission.The application requires that following items must be submitted: Two (2) Letters of Recommendation; Statement of Purpose: Submit online a 300- to 500-word statement of purpose describing your motivation and rationale for obtaining a PhD in the robotics and autonomous systems program at Arizona State University and how it relates ...
The Robotics program supports Tech's mission to provide instruction in disciplines related to science, technology, and interdisciplinary areas. Program of Study. The main emphasis of the Ph.D. program is the successful completion of an original and independent research thesis. The degree requirements are designed around this goal.
The mechatronics and automation concentration of the PhD program in robotics and autonomous systems provides an opportunity for in-depth independent research in a highly focused problem domain approved by the student's advisory committee. This program is intended primarily for those who desire to develop expertise in a particular and focused ...
Yes, you can get a PhD in Automation and Robotics Engineering online, even from accredited institutions. Online PhD programs are becoming more popular every year as it allows people to continue their education without having to leave their jobs or families. Online academic programs are also typically cheaper and faster to complete than on-site ...
A PhD in robotics focuses on training researchers in the field of automation and robotics engineering. Doctoral students are characterised by the application of the techniques of this field in solving new problems and technological challenges. Nowadays, the field of automation covers a wide spectrum, ranging from the automation of industrial ...
This page shows a selection of the available PhDs in United States. If you're interested in studying a Robotics degree in United States you can view all 7 PhDs. You can also read more about Robotics degrees in general, or about studying in United States. Many universities and colleges in United States offer English-taught PhD's degrees.
Our PhD in Robotics and Autonomous Systems will give you the knowledge, skills and expertise needed for a career in engineering, research or academia. You'll be intellectually challenged, develop research and management skills, and become an expert in your chosen field of study. It normally takes around three years to complete a full-time PhD.
Everything you need to know about studying a PhD in Robotics. part of Engineering & Technology. Robotics is defined as the field of Computer Science and Engineering that deals with the design, construction, operation, and application of robots. Robots are automated machines that can assist humans in a variety of settings, from manufacturing ...
The intent of the Robotics core is to ensure each program of study both specializes in robotics, and contains sufficient breadth. To that end, the four-course core comprises one introductory course, one introductory hands-on robotics course, one autonomy course, and one fundamental control/dynamics course: 1. ROB 514: Introduction to Robotics 2.
Master of Science (Thesis Option) 30 credit hours (5000-level courses and above) 4-6 thesis credit hours (of the 30 required for a PhD) Minimum GPA 3.00. 18 credit hours in ROBO courses. One core course required: Intro to Robotics. Candidacy: C or better in all 5000-level courses and above.
A PhD is a terminal degree, meaning it is the highest degree that you can earn. Almost without exception, people only earn one PhD. This degree is required for some jobs, mostly in academia, but is often just considered equivalent to years worked in industry. For some positions, hiring managers may even prefer to hire people without PhDs.
PhD Program in Robotics . Offered jointly by the College of Computing and the College of Engineering, the Ph.D. program in . Robotics is the first truly multidisciplinary robotics degree of its kind in the world—and only the . second robotics doctorate offered in the U.S. The program involves the schools of Aerospace
University of Michigan (U-M) graduate Oluwami Dosunmu-Ogunbi has made history! The Street Journal reports she has earned a Ph.D. in robotics, the first for a Black woman at the institution.
Oluwami (Wami) Dosunmu-Ogunbi is the first Black woman to get a PhD in robotics at the University of Michigan.The daughter of Nigerian immigrants set off on her educational career with no clear ...
Paolo Rocco is a Full Professor in automatic control and robotics with the Politecnico di Milano, Milan, Italy. He is also a Co-Founder of Smart Robots, a spin-off company of Politecnico di Milano. He has authored about 200 papers in the areas of robotics, motion control, and mechatronics.His current research interests include industrial robotics, with a particular focus on safe and productive ...
Brad Meltzer offers four tricks to guide graduates — then springs another one. Spring Commencement speaker Brad Meltzer told University of Michigan graduates to draw upon the magic in their lives as they enter the world and continue to grow and transform into the best versions of themselves. "Life will absolutely not be what you think it ...
An interdisciplinary branch of engineering, mechatronics involves mechanical, electrical, and computer engineering. Robotics is a subset of that, focusing on applied systems to design, build, and operate smart machines. "Think about how robots work or how motors work," Sheldon explained. "There are physical things that you have to put ...
Final admission decisions will be made by the Robotics Ph.D. Program Committee in coordination with the home units. They will be based on a combination of factors, including academic degrees and records, the statement of purpose, letters of recommendation, test scores, and relevant work experience. Also considered is the appropriateness of the ...
I just wanted you to know, I'm getting my Phd.'" ... in her childhood—Klassen still vividly remembers re-engineering an automated stroller for a doll to turn it into a robot—and was a major reason she pursued a master of divinity from Union Theological Seminary after graduating from Stanford University and teaching with AmeriCorps.
Festooned with cameras, the company's co-founders and PhD graduates, Alex Kendall and Amar Shah, tuned the deep-learning algorithms powering the car's autonomous systems until they'd got it ...