How to Write a Bibliography, With Examples

You spent the past six hours grinding out your latest paper, but finally, it’s finished. It’s late, you’re exhausted, and all you want to do is click “Submit Assignment” and then get some sleep.
Not so fast. If your paper doesn’t have a properly formatted bibliography, it’s not finished.
A bibliography is a list of all the sources you consulted while writing your paper. Every book, article, and even video you used to gather information for your paper needs to be cited in your bibliography so your instructor (and any others reading your work) can trace the facts, statistics, and insights back to their original sources.
Give your paper extra polish Grammarly helps you communicate confidently Write with Grammarly

What is the purpose of a bibliography?
A bibliography is the list of sources a work’s author used to create the work. It accompanies just about every type of academic writing , like essays , research papers , and reports . You might also find a brief, less formal bibliography at the end of a journalistic piece, presentation, or video when the author feels it’s necessary to cite their sources . In nearly all academic instances, a bibliography is required. Not including a bibliography (or including an incomplete, incorrect, or falsified bibliography) can be considered an act of plagiarism , which can lead to a failing grade, being dropped from your course or program, and even being suspended or expelled from your school.
A bibliography accomplishes a few things. These include:
- Showing your instructor that you conducted the necessary research for your assignment
- Crediting your sources’ authors for the research they conducted
- Making it easy for anybody who reads your work to find the sources you used and conduct their own research on the same or a similar topic
Additionally, future historians consulting your writing can use your bibliography to identify primary and secondary sources in your research field. Documenting the course information from its original source through later academic works can help researchers understand how that information has been cited and interpreted over time. It can also help them review the information in the face of competing—and possibly contradictory or revisionary—data.
In nearly all cases, a bibliography is found at the end of a book or paper.
What are the different kinds of bibliographies?
Different types of academic works call for different types of bibliographies. For example, your computer science professor might require you to submit an annotated bibliography along with your paper because this type of bibliography explains the why behind each source you chose to consult.
Analytical bibliography
An analytical bibliography documents a work’s journey from manuscript to published book or article. This type of bibliography includes the physical characteristics of each cited source, like each work’s number of pages, type of binding used, and illustrations.
Annotated bibliography
An annotated bibliography is a bibliography that includes annotations, which are short notes explaining why the author chose each of the sources. Generally a few sentences long, these notes might summarize or reflect on the source.
An annotated bibliography is not the same as a literature review . While a literature review discusses how you conducted your research and how your work fits into the overall body of established research in your field, an annotated bibliography simply explains how each source you used is relevant to your work.
Enumerative bibliography
An enumerative bibliography is the most basic type of bibliography. It’s a list of sources used to conduct research, often ordered according to specific characteristics, like alphabetically by authors’ last names or grouped according to topic or language.
Specific types of enumerative bibliographies used for research works include:
National bibliography
A national bibliography groups sources published in a specific region or nation. In many cases, these bibliographies also group works according to the time period during which they were published.
Personal bibliography
A personal bibliography lists multiple works by the same individual author or group of authors. Often, personal bibliographies include works that would be difficult to find elsewhere, like unpublished works.
Corporate bibliography
In a corporate bibliography, the sources are grouped according to their relation to a specific organization. The sources can be about an organization, published by that organization, or owned by that organization.
Subject bibliography
Subject bibliographies group works according to the subjects they cover. Generally, these bibliographies list primary and secondary sources, whereas other types of enumerative bibliographies, like personal bibliographies, might not.
Other types of bibliographies
In some cases, it makes sense to use a bibliography format other than those listed here. These include:
Single-author bibliography
This type of bibliography lists works by a single author. With certain assignments, like an essay comparing two of an author’s books, your bibliography is a single-author bibliography by default. In this case, you can choose how to order the sources, such as by publication date or alphabetically by title.
Selected bibliography
A selected bibliography is a bibliography that only lists some of the sources you consulted. Usually, these are the most important sources for your work. You might write a selected bibliography if you consulted a variety of minor sources that you didn’t end up citing directly in your work. A selected bibliography may also be an annotated bibliography.
How is a bibliography structured?
Although each style guide has its own formatting rules for bibliographies, all bibliographies follow a similar structure. Key points to keep in mind when you’re structuring a bibliography include:
- Every bibliography page has a header. Format this header according to the style guide you’re using.
- Every bibliography has a title, such as “Works Cited,” “References,” or simply “Bibliography.”
- Bibliographies are lists. List your sources alphabetically according to their authors’ last names or their titles—whichever is applicable according to the style guide you’re using. The exception is a single-author bibliography or one that groups sources according to a shared characteristic.
- Bibliographies are double-spaced.
- Bibliographies should be in legible fonts, typically the same font as the papers they accompany.
As noted above, different kinds of assignments require different kinds of bibliographies. For example, you might write an analytical bibliography for your art history paper because this type of bibliography gives you space to discuss how the construction methods used for your sources inform their content and vice-versa. If you aren’t sure which kind of bibliography to write, ask your instructor.
How do you write a bibliography?
The term “bibliography” is a catch-all for any list of sources cited at the end of an academic work. Certain style guides use different terminology to refer to bibliographies. For example, MLA format refers to a paper’s bibliography as its Works Cited page. APA refers to it as the References page. No matter which style guide you’re using, the process for writing a bibliography is generally the same. The primary difference between the different style guides is how the bibliography is formatted.
The first step in writing a bibliography is organizing all the relevant information about the sources you used in your research. Relevant information about a source can vary according to the type of media it is, the type of bibliography you’re writing, and your style guide. Determine which information you need to include about each source by consulting the style guide you’re using. If you aren’t sure what to include, or if you’re not sure which style guide to use, ask your instructor.
The next step is to format your sources according to the style guide you’re using. MLA , APA , and the Chicago Manual of Style are three of the most commonly used style guides in academic writing.
MLA Works Cited page
In MLA format , the bibliography is known as the Works Cited page. MLA is typically used for writing in the humanities, like English and History. Because of this, it includes guidelines for citing sources like plays, videos , and works of visual art —sources you’d find yourself consulting for these courses, but probably not in your science and business courses.
In MLA format, books are cited like this:
If the cited book was published prior to 1900, is from a publisher with offices in multiple countries, or is from a publisher that is largely unknown in the US, include the book’s city of publication. Otherwise, this can be left out.
Scholarly articles are cited in this format:
- Author(s). “Title of Article.” Title of Periodical, Day Month Year, pages.
APA References page
In APA format —the format typically used in psychology, nursing, business, and the social sciences—the bibliography page is titled References. This format includes citation instructions for technical papers and data-heavy research, the types of sources you’re likely to consult for academic writing in these fields.
In APA format, books are cited like this:
Digital object identifier (DOI).
(issue number) , article’s page range (i.e., 10-15). URL.
Chicago Manual of Style
The Chicago Manual of Style (CMoS) permits authors to format bibliographies in two different ways: the notes and bibliography system and the author-date system. The former is generally used in the humanities, whereas the latter is usually used in the sciences and social sciences.
Both systems include guidelines for citations on a paper’s body pages as well as a bibliographic list that follows the paper. This list is titled Bibliography.
In CMoS, books are cited like this:
publication.
number (year published): page numbers of the article (i.e., 10-15).
Bibliography FAQs
What is a bibliography.
A bibliography is the list of sources a work’s author used to create the work.
What are the different kinds of bibliographies?
There are many different kinds of bibliographies. These include:
- Enumerative bibliographies
- Annotated bibliographies
- Analytical bibliographies
How do you write a bibliography for different style guides?
Each style guide publishes its bibliography guidelines online. Locate the guidelines for the style guide you’re following ( Chicago Manual of Style , MLA , APA ), and using the examples provided, format and list the sources for your work.

How to Write a Bibliography for a Research Paper

Do not try to “wow” your instructor with a long bibliography when your instructor requests only a works cited page. It is tempting, after doing a lot of work to research a paper, to try to include summaries on each source as you write your paper so that your instructor appreciates how much work you did. That is a trap you want to avoid. MLA style, the one that is most commonly followed in high schools and university writing courses, dictates that you include only the works you actually cited in your paper—not all those that you used.
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code, assembling bibliographies and works cited.
- If your assignment calls for a bibliography, list all the sources you consulted in your research.
- If your assignment calls for a works cited or references page, include only the sources you quote, summarize, paraphrase, or mention in your paper.
- If your works cited page includes a source that you did not cite in your paper, delete it.
- All in-text citations that you used at the end of quotations, summaries, and paraphrases to credit others for their ideas,words, and work must be accompanied by a cited reference in the bibliography or works cited. These references must include specific information about the source so that your readers can identify precisely where the information came from.The citation entries on a works cited page typically include the author’s name, the name of the article, the name of the publication, the name of the publisher (for books), where it was published (for books), and when it was published.
The good news is that you do not have to memorize all the many ways the works cited entries should be written. Numerous helpful style guides are available to show you the information that should be included, in what order it should appear, and how to format it. The format often differs according to the style guide you are using. The Modern Language Association (MLA) follows a particular style that is a bit different from APA (American Psychological Association) style, and both are somewhat different from the Chicago Manual of Style (CMS). Always ask your teacher which style you should use.
A bibliography usually appears at the end of a paper on its own separate page. All bibliography entries—books, periodicals, Web sites, and nontext sources such radio broadcasts—are listed together in alphabetical order. Books and articles are alphabetized by the author’s last name.
Most teachers suggest that you follow a standard style for listing different types of sources. If your teacher asks you to use a different form, however, follow his or her instructions. Take pride in your bibliography. It represents some of the most important work you’ve done for your research paper—and using proper form shows that you are a serious and careful researcher.
Bibliography Entry for a Book
A bibliography entry for a book begins with the author’s name, which is written in this order: last name, comma, first name, period. After the author’s name comes the title of the book. If you are handwriting your bibliography, underline each title. If you are working on a computer, put the book title in italicized type. Be sure to capitalize the words in the title correctly, exactly as they are written in the book itself. Following the title is the city where the book was published, followed by a colon, the name of the publisher, a comma, the date published, and a period. Here is an example:
Format : Author’s last name, first name. Book Title. Place of publication: publisher, date of publication.
- A book with one author : Hartz, Paula. Abortion: A Doctor’s Perspective, a Woman’s Dilemma . New York: Donald I. Fine, Inc., 1992.
- A book with two or more authors : Landis, Jean M. and Rita J. Simon. Intelligence: Nature or Nurture? New York: HarperCollins, 1998.
Bibliography Entry for a Periodical
A bibliography entry for a periodical differs slightly in form from a bibliography entry for a book. For a magazine article, start with the author’s last name first, followed by a comma, then the first name and a period. Next, write the title of the article in quotation marks, and include a period (or other closing punctuation) inside the closing quotation mark. The title of the magazine is next, underlined or in italic type, depending on whether you are handwriting or using a computer, followed by a period. The date and year, followed by a colon and the pages on which the article appeared, come last. Here is an example:
Format: Author’s last name, first name. “Title of the Article.” Magazine. Month and year of publication: page numbers.
- Article in a monthly magazine : Crowley, J.E.,T.E. Levitan and R.P. Quinn.“Seven Deadly Half-Truths About Women.” Psychology Today March 1978: 94–106.
- Article in a weekly magazine : Schwartz, Felice N.“Management,Women, and the New Facts of Life.” Newsweek 20 July 2006: 21–22.
- Signed newspaper article : Ferraro, Susan. “In-law and Order: Finding Relative Calm.” The Daily News 30 June 1998: 73.
- Unsigned newspaper article : “Beanie Babies May Be a Rotten Nest Egg.” Chicago Tribune 21 June 2004: 12.
Bibliography Entry for a Web Site
For sources such as Web sites include the information a reader needs to find the source or to know where and when you found it. Always begin with the last name of the author, broadcaster, person you interviewed, and so on. Here is an example of a bibliography for a Web site:
Format : Author.“Document Title.” Publication or Web site title. Date of publication. Date of access.
Example : Dodman, Dr. Nicholas. “Dog-Human Communication.” Pet Place . 10 November 2006. 23 January 2014 < http://www.petplace.com/dogs/dog-human-communication-2/page1.aspx >
After completing the bibliography you can breathe a huge sigh of relief and pat yourself on the back. You probably plan to turn in your work in printed or handwritten form, but you also may be making an oral presentation. However you plan to present your paper, do your best to show it in its best light. You’ve put a great deal of work and thought into this assignment, so you want your paper to look and sound its best. You’ve completed your research paper!
Back to How To Write A Research Paper .
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write a Bibliography in APA Format
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
- APA Bibliography
- How to Create One
- Why You Need It
Sample Bibliography
An APA format bibliography lists all of the sources that might be used in a paper. A bibliography can be a great tool to help you keep track of information during the research and writing process. In some cases, your instructor may require you to include a bibliography as part of your assignment.
At a Glance
A well-written APA format bibliography can help you keep track of information and sources as you research and write your psychology paper. To create a bibliography, gather up all of the sources that you might use in your paper. Create an APA format reference for each source and then write a brief annotation. Your annotation should be a brief summary of what each reference is about. You can quickly refer to these annotations When writing your paper and determine which to include.
What Is an APA Format Bibliography?
An APA format bibliography is an alphabetical listing of all sources that might be used to write an academic paper, essay, article, or research paper—particularly work that is covering psychology or psychology-related topics. APA format is the official style of the American Psychological Association (APA). This format is used by many psychology professors, students, and researchers.
Even if it is not a required part of your assignment, writing a bibliography can help you keep track of your sources and make it much easier to create your final reference page in proper APA format.
Creating an APA Bibliography
A bibliography is similar in many ways to a reference section , but there are some important differences. While a reference section includes every source that was actually used in your paper, a bibliography may include sources that you considered using but may have dismissed because they were irrelevant or outdated.
Bibliographies can be a great way to keep track of information you might want to use in your paper and to organize the information that you find in different sources. The following are four steps you can follow to create your APA format bibliography.
Start on a New Page
Your working bibliography should be kept separate from the rest of your paper. Start it on a new page, with the title "Bibliography" centered at the top and in bold text. Some people use the title "References" instead, so it's best to check with your professor or instructor about which they prefer you to use.
Gather Your Sources
Compile all the sources you might possibly use in your paper. While you might not use all of these sources in your paper, having a complete list will make it easier later on when you prepare your reference section.
Gathering your sources can be particularly helpful when outlining and writing your paper.
By quickly glancing through your working bibliography, you will be able to get a better idea of which sources will be the most appropriate to support your thesis and main points.
Reference Each Source
Your references should be listed alphabetically by the author’s last name, and they should be double-spaced. The first line of each reference should be flush left, while each additional line of a single reference should be a few spaces to the right of the left margin, which is known as a hanging indent.
The format of each source is as follows for academic journals:
- Last name of first author (followed by their first initial)
- The year the source was published in parentheses
- The title of the source
- The journal that published the source (in italics)
- The volume number, if applicable (in italics)
- The issue number, if applicable
- Page numbers (in parentheses)
- The URL or "doi" in lowercase letters followed by a colon and the doi number, if applicable
The following examples are scholarly articles in academic journals, cited in APA format:
- Kulacaoglu, F., & Kose, S. (2018). Borderline personality disorder (BPD): In the midst of vulnerability, chaos, and awe. Brain sciences , 8 (11), 201. doi:10.3390/brainsci8110201
- Cattane, N., Rossi, R., & Lanfredi, M. (2017). Borderline personality disorder and childhood trauma: exploring the affected biological systems and mechanisms. BMC Psychiatry, 18 (221). doi:10.1186/s12888-017-1383-2
Visit the American Psychological Association's website for more information on citing other types of sources including online media, audiovisual media, and more.
Create an Annotation for Each Source
Normally a bibliography contains only references' information, but in some cases you might decide to create an annotated bibliography. An annotation is a summary or evaluation of the source.
An annotation is a brief description of approximately 150 words describing the information in the source, your evaluation of its credibility, and how it pertains to your topic. Writing one of these for each piece of research will make your writing process faster and easier.
This step helpful in determining which sources to ultimately use in your paper. Your instructor may also require it as part of the assignment so they can assess your thought process and understanding of your topic.
Reasons to Write a Bibliography
One of the biggest reasons to create an APA format bibliography is simply to make the research and writing process easier.
If you do not have a comprehensive list of all of your references, you might find yourself scrambling to figure out where you found certain bits of information that you included in your paper.
A bibliography is also an important tool that your readers can use to access your sources.
While writing an annotated bibliography might not be required for your assignment, it can be a very useful step. The process of writing an annotation helps you learn more about your topic, develop a deeper understanding of the subject, and become better at evaluating various sources of information.
The following is an example of an APA format bibliography by the website EasyBib:
There are many online resources that demonstrate different formats of bibliographies, including the American Psychological Association website . Purdue University's Online Writing Lab also has examples of formatting an APA format bibliography.
Check out this video on their YouTube channel which provides detailed instructions on formatting an APA style bibliography in Microsoft Word.
You can check out the Purdue site for more information on writing an annotated APA bibliography as well.
What This Means For You
If you are taking a psychology class, you may be asked to create a bibliography as part of the research paper writing process. Even if your instructor does not expressly require a bibliography, creating one can be a helpful way to help structure your research and make the writing process more manageable.
For psychology majors , it can be helpful to save any bibliographies you have written throughout your studies so that you can refer back to them later when studying for exams or writing papers for other psychology courses.
American Psychological Association. Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association . 7th Edition. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association; 2020.
Masic I. The importance of proper citation of references in biomedical articles. Acta Inform Med . 2013;21(3):148–155. doi:10.5455/aim.2013.21.148-155
American Psychological Association. How do you format a bibliography in APA Style?
Cornell University Library. How to prepare an annotated bibliography: The annotated bibliography .
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Citing sources
- What Is an Annotated Bibliography? | Examples & Format
What Is an Annotated Bibliography? | Examples & Format
Published on March 9, 2021 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on August 23, 2022.
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that includes a short descriptive text (an annotation) for each source. It may be assigned as part of the research process for a paper , or as an individual assignment to gather and read relevant sources on a topic.
Scribbr’s free Citation Generator allows you to easily create and manage your annotated bibliography in APA or MLA style. To generate a perfectly formatted annotated bibliography, select the source type, fill out the relevant fields, and add your annotation.
An example of an annotated source is shown below:

Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Annotated bibliography format: apa, mla, chicago, how to write an annotated bibliography, descriptive annotation example, evaluative annotation example, reflective annotation example, finding sources for your annotated bibliography, frequently asked questions about annotated bibliographies.
Make sure your annotated bibliography is formatted according to the guidelines of the style guide you’re working with. Three common styles are covered below:
In APA Style , both the reference entry and the annotation should be double-spaced and left-aligned.
The reference entry itself should have a hanging indent . The annotation follows on the next line, and the whole annotation should be indented to match the hanging indent. The first line of any additional paragraphs should be indented an additional time.

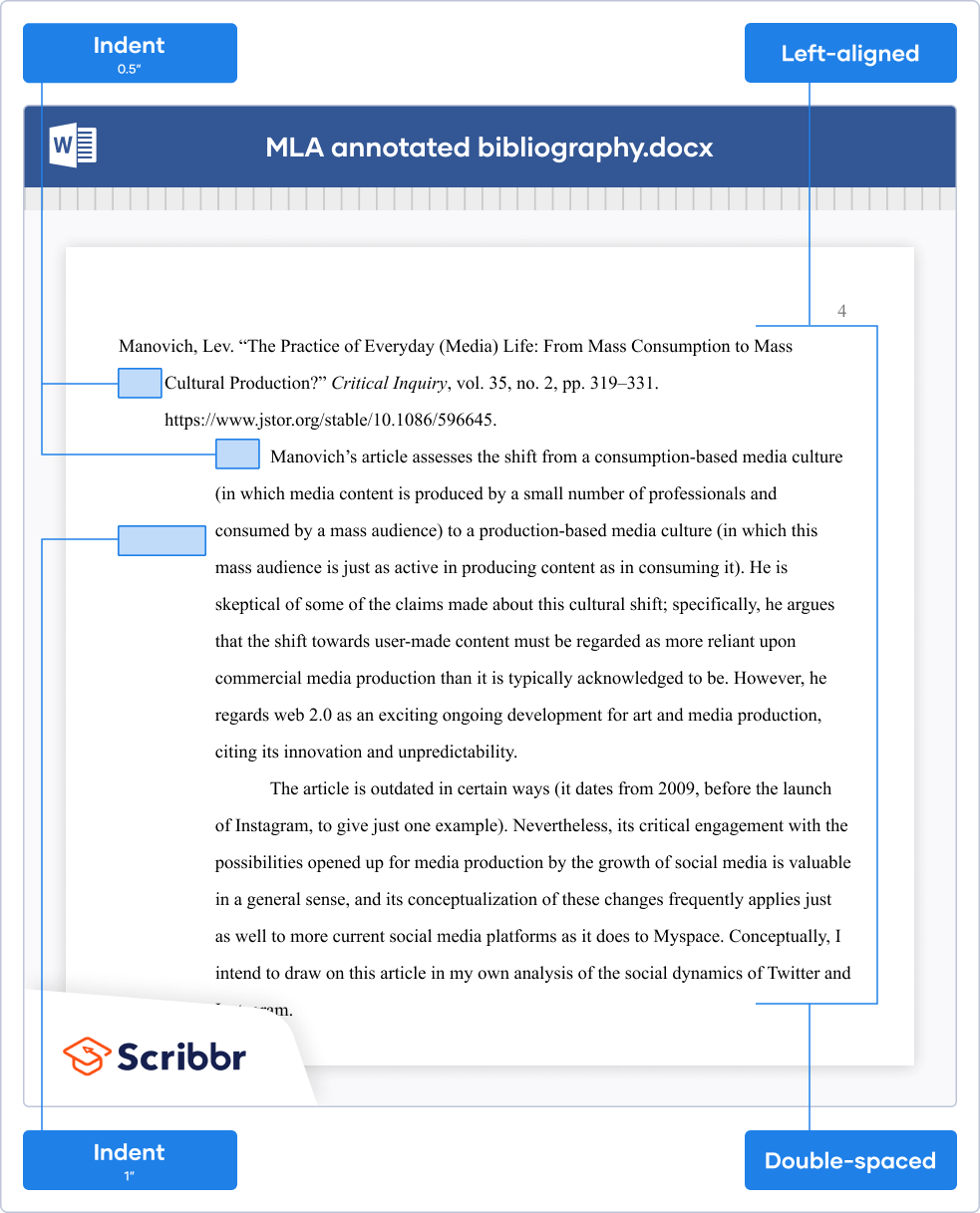
In an MLA style annotated bibliography , the Works Cited entry and the annotation are both double-spaced and left-aligned.
The Works Cited entry has a hanging indent. The annotation itself is indented 1 inch (twice as far as the hanging indent). If there are two or more paragraphs in the annotation, the first line of each paragraph is indented an additional half-inch, but not if there is only one paragraph.
Chicago style
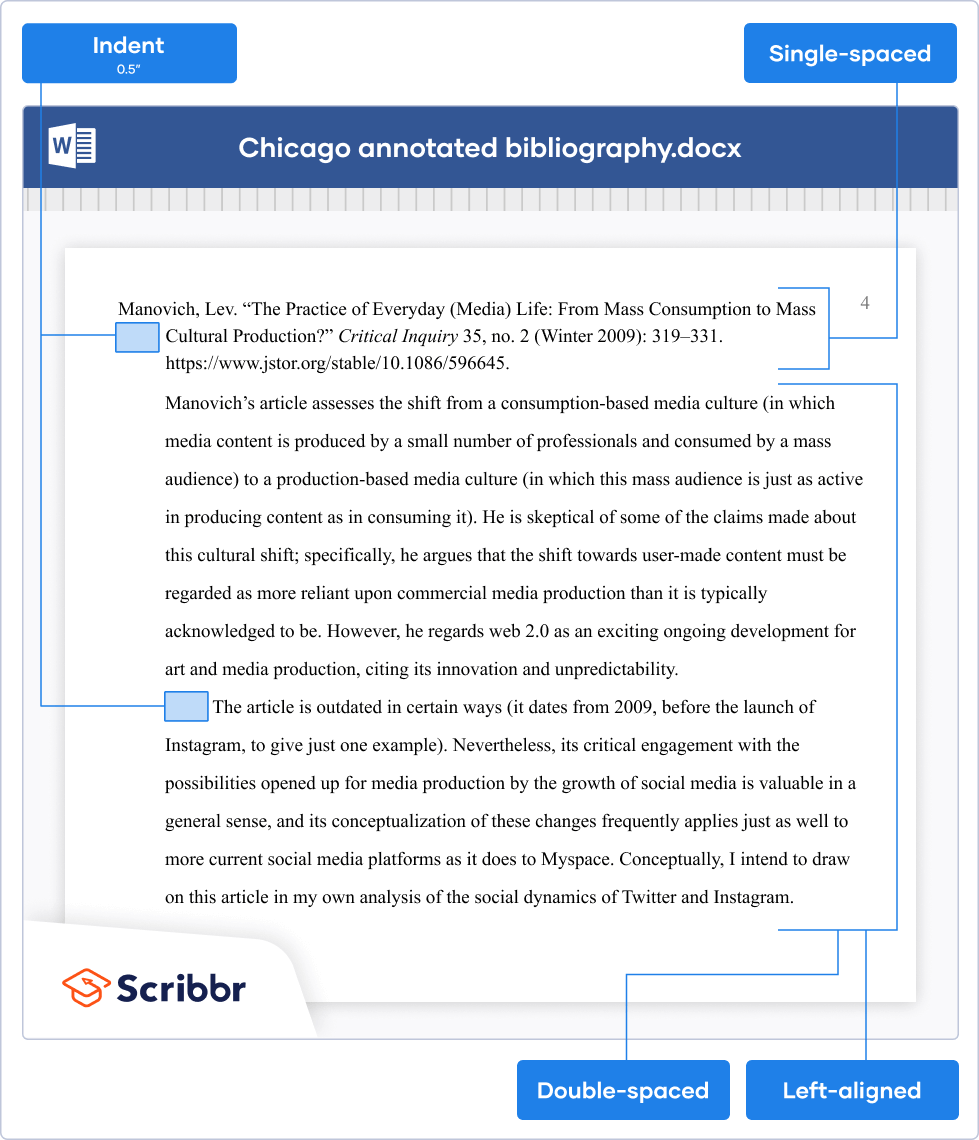
In a Chicago style annotated bibliography , the bibliography entry itself should be single-spaced and feature a hanging indent.
The annotation should be indented, double-spaced, and left-aligned. The first line of any additional paragraphs should be indented an additional time.
Scribbr Citation Checker New
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries

For each source, start by writing (or generating ) a full reference entry that gives the author, title, date, and other information. The annotated bibliography format varies based on the citation style you’re using.
The annotations themselves are usually between 50 and 200 words in length, typically formatted as a single paragraph. This can vary depending on the word count of the assignment, the relative length and importance of different sources, and the number of sources you include.
Consider the instructions you’ve been given or consult your instructor to determine what kind of annotations they’re looking for:
- Descriptive annotations : When the assignment is just about gathering and summarizing information, focus on the key arguments and methods of each source.
- Evaluative annotations : When the assignment is about evaluating the sources , you should also assess the validity and effectiveness of these arguments and methods.
- Reflective annotations : When the assignment is part of a larger research process, you need to consider the relevance and usefulness of the sources to your own research.
These specific terms won’t necessarily be used. The important thing is to understand the purpose of your assignment and pick the approach that matches it best. Interactive examples of the different styles of annotation are shown below.
A descriptive annotation summarizes the approach and arguments of a source in an objective way, without attempting to assess their validity.
In this way, it resembles an abstract , but you should never just copy text from a source’s abstract, as this would be considered plagiarism . You’ll naturally cover similar ground, but you should also consider whether the abstract omits any important points from the full text.
The interactive example shown below describes an article about the relationship between business regulations and CO 2 emissions.
Rieger, A. (2019). Doing business and increasing emissions? An exploratory analysis of the impact of business regulation on CO 2 emissions. Human Ecology Review , 25 (1), 69–86. https://www.jstor.org/stable/26964340
An evaluative annotation also describes the content of a source, but it goes on to evaluate elements like the validity of the source’s arguments and the appropriateness of its methods .
For example, the following annotation describes, and evaluates the effectiveness of, a book about the history of Western philosophy.
Kenny, A. (2010). A new history of Western philosophy: In four parts . Oxford University Press.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
A reflective annotation is similar to an evaluative one, but it focuses on the source’s usefulness or relevance to your own research.
Reflective annotations are often required when the point is to gather sources for a future research project, or to assess how they were used in a project you already completed.
The annotation below assesses the usefulness of a particular article for the author’s own research in the field of media studies.
Manovich, Lev. (2009). The practice of everyday (media) life: From mass consumption to mass cultural production? Critical Inquiry , 35 (2), 319–331. https://www.jstor.org/stable/10.1086/596645
Manovich’s article assesses the shift from a consumption-based media culture (in which media content is produced by a small number of professionals and consumed by a mass audience) to a production-based media culture (in which this mass audience is just as active in producing content as in consuming it). He is skeptical of some of the claims made about this cultural shift; specifically, he argues that the shift towards user-made content must be regarded as more reliant upon commercial media production than it is typically acknowledged to be. However, he regards web 2.0 as an exciting ongoing development for art and media production, citing its innovation and unpredictability.
The article is outdated in certain ways (it dates from 2009, before the launch of Instagram, to give just one example). Nevertheless, its critical engagement with the possibilities opened up for media production by the growth of social media is valuable in a general sense, and its conceptualization of these changes frequently applies just as well to more current social media platforms as it does to Myspace. Conceptually, I intend to draw on this article in my own analysis of the social dynamics of Twitter and Instagram.
Before you can write your annotations, you’ll need to find sources . If the annotated bibliography is part of the research process for a paper, your sources will be those you consult and cite as you prepare the paper. Otherwise, your assignment and your choice of topic will guide you in what kind of sources to look for.
Make sure that you’ve clearly defined your topic , and then consider what keywords are relevant to it, including variants of the terms. Use these keywords to search databases (e.g., Google Scholar ), using Boolean operators to refine your search.
Sources can include journal articles, books, and other source types , depending on the scope of the assignment. Read the abstracts or blurbs of the sources you find to see whether they’re relevant, and try exploring their bibliographies to discover more. If a particular source keeps showing up, it’s probably important.
Once you’ve selected an appropriate range of sources, read through them, taking notes that you can use to build up your annotations. You may even prefer to write your annotations as you go, while each source is fresh in your mind.
An annotated bibliography is an assignment where you collect sources on a specific topic and write an annotation for each source. An annotation is a short text that describes and sometimes evaluates the source.
Any credible sources on your topic can be included in an annotated bibliography . The exact sources you cover will vary depending on the assignment, but you should usually focus on collecting journal articles and scholarly books . When in doubt, utilize the CRAAP test !
Each annotation in an annotated bibliography is usually between 50 and 200 words long. Longer annotations may be divided into paragraphs .
The content of the annotation varies according to your assignment. An annotation can be descriptive, meaning it just describes the source objectively; evaluative, meaning it assesses its usefulness; or reflective, meaning it explains how the source will be used in your own research .
A source annotation in an annotated bibliography fulfills a similar purpose to an abstract : they’re both intended to summarize the approach and key points of a source.
However, an annotation may also evaluate the source , discussing the validity and effectiveness of its arguments. Even if your annotation is purely descriptive , you may have a different perspective on the source from the author and highlight different key points.
You should never just copy text from the abstract for your annotation, as doing so constitutes plagiarism .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2022, August 23). What Is an Annotated Bibliography? | Examples & Format. Scribbr. Retrieved April 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/citing-sources/annotated-bibliography/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, evaluating sources | methods & examples, how to find sources | scholarly articles, books, etc., hanging indent | word & google docs instructions, what is your plagiarism score.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Referencing
- Harvard Style Bibliography | Format & Examples
Harvard Style Bibliography | Format & Examples
Published on 1 May 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on 7 November 2022.
In Harvard style , the bibliography or reference list provides full references for the sources you used in your writing.
- A reference list consists of entries corresponding to your in-text citations .
- A bibliography sometimes also lists sources that you consulted for background research, but did not cite in your text.
The two terms are sometimes used interchangeably. If in doubt about which to include, check with your instructor or department.
The information you include in a reference varies depending on the type of source, but it usually includes the author, date, and title of the work, followed by details of where it was published. You can automatically generate accurate references using our free reference generator:
Harvard Reference Generator
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Formatting a harvard style bibliography, harvard reference examples, referencing sources with multiple authors, referencing sources with missing information, frequently asked questions about harvard bibliographies.
Sources are alphabetised by author last name. The heading ‘Reference list’ or ‘Bibliography’ appears at the top.
Each new source appears on a new line, and when an entry for a single source extends onto a second line, a hanging indent is used:

Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Reference list or bibliography entries always start with the author’s last name and initial, the publication date and the title of the source. The other information required varies depending on the source type. Formats and examples for the most common source types are given below.
- Entire book
- Book chapter
- Translated book
- Edition of a book
Journal articles
- Print journal
- Online-only journal with DOI
- Online-only journal without DOI
- General web page
- Online article or blog
- Social media post
Newspapers and magazines
- Newspaper article
- Magazine article
When a source has up to three authors, list all of them in the order their names appear on the source. If there are four or more, give only the first name followed by ‘ et al. ’:
Sometimes a source won’t list all the information you need for your reference. Here’s what to do when you don’t know the publication date or author of a source.
Some online sources, as well as historical documents, may lack a clear publication date. In these cases, you can replace the date in the reference list entry with the words ‘no date’. With online sources, you still include an access date at the end:
When a source doesn’t list an author, you can often list a corporate source as an author instead, as with ‘Scribbr’ in the above example. When that’s not possible, begin the entry with the title instead of the author:
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Though the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, there is a difference in meaning:
- A reference list only includes sources cited in the text – every entry corresponds to an in-text citation .
- A bibliography also includes other sources which were consulted during the research but not cited.
In Harvard referencing, up to three author names are included in an in-text citation or reference list entry. When there are four or more authors, include only the first, followed by ‘ et al. ’
In Harvard style referencing , to distinguish between two sources by the same author that were published in the same year, you add a different letter after the year for each source:
- (Smith, 2019a)
- (Smith, 2019b)
Add ‘a’ to the first one you cite, ‘b’ to the second, and so on. Do the same in your bibliography or reference list .
To create a hanging indent for your bibliography or reference list :
- Highlight all the entries
- Click on the arrow in the bottom-right corner of the ‘Paragraph’ tab in the top menu.
- In the pop-up window, under ‘Special’ in the ‘Indentation’ section, use the drop-down menu to select ‘Hanging’.
- Then close the window with ‘OK’.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2022, November 07). Harvard Style Bibliography | Format & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 9 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/referencing/harvard-bibliography/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, a quick guide to harvard referencing | citation examples, harvard in-text citation | a complete guide & examples, referencing books in harvard style | templates & examples, scribbr apa citation checker.
An innovative new tool that checks your APA citations with AI software. Say goodbye to inaccurate citations!


- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Common Assignments: Annotated Bibliographies
Basics of annotated bibliographies.
An annotated bibliography is a combination of the words "annotation" and "bibliography." An annotation is a set of notes, comments, or critiques. A bibliography is list of references that helps a reader identify sources of information. An annotated bibliography is a list of references that not only identifies the sources of information but also includes information such as a summary, a critique or analysis, and an application of those sources' information.
Review our resources on the following pages for more information about each component of an annotated bibliography. As always, read the instructions and any examples in your assignment carefully; some of what follows might not be required in your particular course.
Components of an Annotated Entry
Download the following sample to see the components of an annotated bibliography. Follow the links to more information on formatting, summary, critique/analysis, application, and example in the left sidebar menu. Note that citations are not necessary in the annotations since the notes are understood to be about the listed source.
- Annotated Bibliography Sample Document A sample of an annotated bibliography illustrating its various components. Updated to APA 7 guidelines.
Related Multimedia Resources
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Other Tips
- Next Page: Formatting
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
An annotated bibliography is a list of cited resources related to a particular topic or arranged thematically that include a brief descriptive or evaluative summary. The annotated bibliography can be arranged chronologically by date of publication or alphabetically by author, with citations to print and/or digital materials, such as, books, newspaper articles, journal articles, dissertations, government documents, pamphlets, web sites, etc., multimedia sources like films and audio recordings, or documents and materials preserved in archival collections.
Beatty, Luke and Cynthia Cochran. Writing the Annotated Bibliography: A Guide for Students and Researchers . New York: Routledge, 2020; Harner, James L. On Compiling an Annotated Bibliography . 2nd edition. New York: Modern Language Association, 2000.
Importance of a Good Annotated Bibliography
In lieu of writing a formal research paper or in preparation for a larger writing project, your professor may ask you to develop an annotated bibliography. An annotated bibliography may be assigned for a number of reasons, including :
- To show that you can identify and evaluate the literature underpinning a research problem;
- To demonstrate that you can identify and conduct an effective and thorough review of pertinent literature;
- To develop skills in discerning the most relevant research studies from those which have only superficial relevance to your topic;
- To explore how different types of sources contribute to understanding the research problem;
- To be thoroughly engaged with individual sources in order to strengthen your analytical skills; or,
- To share sources among your classmates so that, collectively, everyone in the class obtains a comprehensive understanding of research about a particular topic.
On a broader level, writing an annotated bibliography can lay the foundation for conducting a larger research project. It serves as a method to evaluate what research has been conducted and where your proposed study may fit within it. By critically analyzing and synthesizing the contents of a variety of sources, you can begin to evaluate what the key issues are in relation to the research problem and, by so doing, gain a better perspective about the deliberations taking place among scholars. As a result of this analysis, you are better prepared to develop your own point of view and contributions to the literature.
In summary, creating a good annotated bibliography...
- Encourages you to think critically about the content of the works you are using, their place within the broader field of study, and their relation to your own research, assumptions, and ideas;
- Gives you practical experience conducting a thorough review of the literature concerning a research problem;
- Provides evidence that you have read and understood your sources;
- Establishes validity for the research you have done and of you as a researcher;
- Gives you the opportunity to consider and include key digital, multimedia, or archival materials among your review of the literature;
- Situates your study and underlying research problem in a continuing conversation among scholars;
- Provides an opportunity for others to determine whether a source will be helpful for their research; and,
- Could help researchers determine whether they are interested in a topic by providing background information and an idea of the kind of scholarly investigations that have been conducted in a particular area of study.
In summary, writing an annotated bibliography helps you develop skills related to critically reading and identifying the key points of a research study and to effectively synthesize the content in a way that helps the reader determine its validity and usefulness in relation to the research problem or topic of investigation.
NOTE: Do not confuse annotating source materials in the social sciences with annotating source materials in the arts and humanities. Rather than encompassing forms of synopsis and critical analysis, an annotation assignment in arts and humanities courses refers to the systematic interpretation of literary texts, art works, musical scores, performances, and other forms of creative human communication for the purpose of clarifying and encouraging analytical thinking about what the author(s)/creator(s) have written or created. They are assigned to encourage students to actively engage with the text or creative object.
Annotated Bibliographies. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Annotated Bibliographies. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Annotated Bibliography. The Waldin Writing Center. Waldin University; Hartley, James. Academic Writing and Publishing: A Practical Guide . (New York: Routledge, 2008), p. 127-128; Writing an Annotated Bibliography. Assignment Structures and Samples Research and Learning Online, Monash University; Kalir, Remi H. and Antero Garcia. Annotation . Essential Knowledge Series. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 2021.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Types
- Descriptive : This annotation describes the source without summarizing the actual argument, hypothesis, or message in the content. Like an abstract , it describes what the source addresses, what issues are being investigated, and any special features, such as appendices or bibliographies, that are used to supplement the main text. What it does not include is any evaluation or criticism of the content. This type of annotation seeks to answer the question: Does this source cover or address the topic I am researching? Collectively, this type of annotated bibliography synthesizes prior research about a topic or serves as a review of the literature before conducting a broader research study.
- Informative/Summative : This type of annotation summarizes what the content, message, or argument of the source is. It generally contains the hypothesis, methodology, and conclusion or findings, but like the descriptive type, you are not offering your own evaluative comments about such content. This type of annotation seeks to answer these types of questions: What are the author's main arguments? What are the key findings? What conclusions or recommended actions did the author state? Collectively, this type of annotated bibliography summarizes the way in which scholars have studied and documented outcomes about a topic.
- Evaluative/Critical/Analytical : This annotation includes your own evaluative statements about the content of a source. It is the most common type of annotation your professor will ask you to write. Your critique may focus on describing a study's strengths and weaknesses or it may describe the applicability of the conclusions to the research problem you are studying. This type of annotation seeks to answer these types of questions: Is the reasoning sound? Is the methodology sound? Does this source address all the relevant issues? How does this source compare to other sources on this topic? Collectively, this type of annotated bibliography offers a detailed analysis and critical assessment of the research literature about a topic.
NOTE: There are a variety of strategies you can use to critically evaluate a source based on its content, purpose, and format. A description of these strategies can be found here .
II. Choosing Sources for Your Bibliography
There are two good strategies to begin identifying possible sources for your bibliography--one that looks back into the literature and one that projects forward based on tracking sources cited by researchers.
- The first strategy is to identify several recently published [within the past few years] scholarly books using the USC Libraries catalog or journal articles found by searching a comprehensive, multidisciplinary database like ProQuest Multiple . Review the list of references to sources cited by the author(s). Review these citations to identify prior research published about your topic. For a complete list of scholarly databases GO HERE .
- The second strategy is to identify one or more books, book chapters, journal articles, or research reports on your topic and paste the title of the item into Google Scholar [e.g., from Negotiation Journal , entering the title of the article, " Civic Fusion: Moving from Certainty through Not Knowing to Curiosity " ]. If it is a short title or it uses a lot of common words, place quotation marks around the title so Google Scholar searches the source as a phrase rather than a combination of individual words. Below the citation may be a "Cited by" reference link followed by a number [e.g., Cited by 45]. This number refers to the number of times a source has subsequently been cited by other authors in other sources after the item you found was published.
Your method for selecting which sources to annotate depends on the purpose of the assignment and the research problem you are investigating . For example, if the course is on international social movements and the research problem you choose to study is to compare cultural factors that led to protests in Egypt with the factors that led to protests against the government of the Philippines in the 1980's, you should consider including non-U.S., historical, and, if possible, foreign language sources in your bibliography.
NOTE: Appropriate sources to include can be anything that you believe has value in understanding the research problem . Be creative in thinking about possible sources, including non-textual items, such as, films, maps, photographs, and audio recordings, or archival documents and primary source materials, such as, diaries, government documents, collections of personal correspondence, meeting minutes, or official memorandums. If you want to include these types of sources in your annotated bibliography, consult with a librarian if you're not sure where to locate them.
III. Strategies to Define the Scope of Your Bibliography
It is important that the scope of sources cited and summarized in your bibliography are well-defined and sufficiently narrow in coverage to ensure that you're not overwhelmed by the number of potential items to consider including. Many of the general strategies used to narrow a topic for a research paper are the same that be applied to framing the scope of sources to include in an annotated bibliography.
- Aspect -- choose one lens through which to view the research problem, or look at just one facet of your topic [e.g., rather than annotating a bibliography of sources about the role of food in religious rituals, create a bibliography on the role of food in Hindu ceremonies].
- Time -- the shorter the time period to be covered, the more narrow the focus [e.g., rather than political scandals of the 20th century, cite literature on political scandals during the 1980s].
- Comparative -- a list of resources that focus on comparing two or more issues related to the broader research topic can be used to narrow the scope of your bibliography [e.g., rather than college student activism during the 20th century, cite literature that compares student activism in the 1930s and the 1960s]
- Geography -- the smaller the area of analysis, the fewer items there are to consider including in your bibliography [e.g., rather than cite sources about trade relations in West Africa, include only sources that examine, as a case study, trade relations between Niger and Cameroon].
- Type -- focus your bibliography on a specific type or class of people, places, or things [e.g., rather than health care provision in Japan, cite research on health care provided to the elderly in Japan].
- Source -- your bibliography includes specific types of materials [e.g., only books, only scholarly journal articles, only films, only archival materials, etc.]. However, be sure to describe why only one type of source is appropriate.
- Combination -- use two or more of the above strategies to focus your bibliography very narrowly or to broaden coverage of a very specific research problem [e.g., cite literature only about political scandals during the 1980s that took place in Great Britain].
IV. Assessing the Relevance and Value of Sources All the items included in your bibliography should reflect the source's contribution to understanding the research problem . In order to determine how you will use the source or define its contribution, you will need to critically evaluate the quality of the central argument within the source or, in the case of including non-textual items, determine how the source contributes to understanding the research problem [e.g., if the bibliography lists sources about outreach strategies to homeless populations, a non-textual source would be a film that profiles the life of a homeless person]. Specific elements to assess a research study include an item’s overall value in relation to other sources on the topic, its limitations, its effectiveness in defining the research problem, the methodology used, the quality of the evidence, and the strength of the author’s conclusions and/or recommendations. With this in mind, determining whether a source should be included in your bibliography depends on how you think about and answer the following questions related to its content:
- Are you interested in the way the author(s) frame the research questions or in the way the author goes about investigating the questions [the method]?
- Does the research findings make new connections or promote new ways of understanding the problem?
- Are you interested in the way the author(s) use a theoretical framework or a key concept?
- Does the source refer to and analyze a particular body of evidence that you want to highlight?
- How are the author's conclusions relevant to your overall investigation of the topic?
V. Format and Content
The format of an annotated bibliography can differ depending on its purpose and the nature of the assignment. Contents may be listed alphabetically by author, arranged chronologically by publication date, or arranged under headings that list different types of sources [i.e., books, articles, government documents, research reports, etc.]. If the bibliography includes a lot of sources, items may also be subdivided thematically, by time periods of coverage or publication, or by source type. If you are unsure, ask your professor for specific guidelines in terms of length, focus, and the type of annotation you are to write. Note that most professors assign annotated bibliographies that only need to be arranged alphabetically by author.
Introduction Your bibliography should include an introduction that describes the research problem or topic being covered, including any limits placed on items to be included [e.g., only material published in the last ten years], explains the method used to identify possible sources [such as databases you searched or methods used to identify sources], the rationale for selecting the sources, and, if appropriate, an explanation stating why specific types of some sources were deliberately excluded. The introduction's length depends, in general, on the complexity of the topic and the variety of sources included.
Citation This first part of your entry contains the bibliographic information written in a standard documentation style , such as, MLA, Chicago, or APA. Ask your professor what style is most appropriate, and be consistent! If your professor does not have a preferred citation style, choose the type you are most familiar with or that is used predominantly within your major or area of study.
Annotation The second part of your entry should summarize, in paragraph form, the content of the source. What you say about the source is dictated by the type of annotation you are asked to write [see above]. In most cases, however, your annotation should describe the content and provide critical commentary that evaluates the source and its relationship to the topic.
In general, the annotation should include one to three sentences about the item in the following order : (1) an introduction of the item; (2) a brief description of what the study was intended to achieve and the research methods used to gather information; ( 3) the scope of study [i.e., limits and boundaries of the research related to sample size, area of concern, targeted groups examined, or extent of focus on the problem]; (4) a statement about the study's usefulness in relation to your research and the topic; (5) a note concerning any limitations found in the study; (6) a summary of any recommendations or further research offered by the author(s); and, (7) a critical statement that elucidates how the source clarifies your topic or pertains to the research problem.
Things to think critically about when writing the annotation include:
- Does the source offer a good introduction on the issue?
- Does the source effectively address the issue?
- Would novices find the work accessible or is it intended for an audience already familiar with the topic?
- What limitations does the source have [reading level, timeliness, reliability, etc.]?
- Are any special features, such as, appendices or non-textual elements effectively presented?
- What is your overall reaction to the source?
- If it's a website or online resource, is it up-to-date, well-organized, and easy to read, use, and navigate?
Length An annotation can vary in length from a few sentences to more than a page, single-spaced. However, they are normally about 300 words--the length of a standard paragraph. The length also depends on the purpose of the annotated bibliography [critical assessments are generally lengthier than descriptive annotations] and the type of source [e.g., books generally require a more detailed annotation than a magazine article]. If you are just writing summaries of your sources, the annotations may not be very long. However, if you are writing an extensive analysis of each source, you'll need to devote more space.
Annotated Bibliographies. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Annotated Bibliographies. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Annotated Bibliography. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Annotated Bibliography. Writing Center. Walden University; Annotated Bibliography. Writing Skills, Student Support and Development, University of New South Wales; Engle, Michael et al. How to Prepare an Annotated Bibliography. Olin Reference, Research and Learning Services. Cornell University Library; Guidelines for Preparing an Annotated Bibliography. Writing Center at Campus Library. University of Washington, Bothell; Harner, James L. On Compiling an Annotated Bibliography . 2nd edition. New York: Modern Language Association, 2000; How to Write an Annotated Bibliography. Information and Library Services. University of Maryland; Knott, Deborah. Writing an Annotated Bibliography. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Norton, Donna. Top 32 Effective Tips for Writing an Annotated Bibliography Top-notch study tips for A+ students blog; Writing from Sources: Writing an Annotated Bibliography. The Reading/Writing Center. Hunter College.
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article >>
- Last Updated: Mar 6, 2024 1:00 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments

How to Write a Research Paper: Annotated Bibliography
- Anatomy of a Research Paper
- Developing a Research Focus
- Background Research Tips
- Searching Tips
- Scholarly Journals vs. Popular Journals
- Thesis Statement
- Annotated Bibliography
- Citing Sources
- Evaluating Sources
- Literature Review
- Academic Integrity
- Scholarship as Conversation
- Understanding Fake News
- Data, Information, Knowledge
What is an Annotated Bibliography?
UMary Writing Center

Check out the resources available from the Writing Center .
Write an Annotated Bibliography
What is an annotated bibliography?
It is a list of citations for various books, articles, and other sources on a topic.
An annotation is a short summary and/or critical evaluation of a source.
Annotated bibliographies answer the question: "What would be the most relevant, most useful, or most up-to-date sources for this topic?"
Annotated bibliographies can be part of a larger research project, or can be a stand-alone report in itself.
Annotation versus abstracts
An abstract is a paragraph at the beginning of the paper that discusses the main point of the original work. They typically do not include evaluation comments.
Annotations can either be descriptive or evaluative. The annotated bibliography looks like a works cited page but includes an annotation after each source cited.
Types of Annotations:
Descriptive Annotations: Focuses on description. Describes the source by answering the following questions.
Who wrote the document?
What does the document discuss?
When and where was the document written?
Why was the document produced?
How was it provided to the public?
Evaluative Annotations: Focuses on description and evaluation. Includes a summary and critically assess the work for accuracy, relevance, and quality.
Evaluative annotations help you learn about your topic, develop a thesis statement, decide if a specific source will be useful for your assignment, and determine if there is enough valid information available to complete your project.
What does the annotation include?
Depending on your assignment and style guide, annotations may include some or all of the following information.
- Should be no more than 150 words or 4 to 6 sentences long.
- What is the main focus or purpose of the work?
- Who is the intended audience?
- How useful or relevant was the article to your topic?
- Was there any unique features that useful to you?
- What is the background and credibility of the author?
- What are any conclusions or observations that your reached about the article?
Which citation style to use?
There are many styles manuals with specific instructions on how to format your annotated bibliography. This largely depends on what your instructor prefers or your subject discipline. Check out our citation guides for more information.
Additional Information
Why doesn't APA have an official APA-approved format for annotated bibliographies?
Always consult your instructor about the format of an annotated bibliography for your class assignments. These guides provide you with examples of various styles for annotated bibliographies and they may not be in the format required by your instructor.
Citation Examples and Annotations
Book Citation with Descriptive Annotation
Liroff, R. A., & G. G. Davis. (1981). Protecting open space: Land use control in the Adirondack Park. Cambridge, MA: Ballinger.
This book describes the implementation of regional planning and land use regulation in the Adirondack Park in upstate New York. The authors provide program evaluations of the Adirondack Park Agencys regulatory and local planning assistance programs.
Journal Article Citation with Evaluative Annotation
Gottlieb, P. D. (1995). The “golden egg” as a natural resource: Toward a normative theory of growth management. Society and Natural Resources, 8, (5): 49-56.
This article explains the dilemma faced by North American suburbs, which demand both preservation of local amenities (to protect quality of life) and physical development (to expand the tax base). Growth management has been proposed as a policy solution to this dilemma. An analogy is made between this approach and resource economics. The author concludes that the growth management debate raises legitimate issues of sustainability and efficiency.
Examples were taken from http://lib.calpoly.edu/support/how-to/write-an-annotated-bibliography/#samples
Book Citation
Lee, Seok-hoon, Yong-pil Kim, Nigel Hemmington, and Deok-kyun Yun. “Competitive Service Quality Improvement (CSQI): A Case Study in the Fast-Food Industry.” Food Service Technology 4 (2004): 75-84.
In this highly technical paper, three industrial engineering professors in Korea and one services management professor in the UK discuss the mathematical limitations of the popular SERVQUAL scales. Significantly, they also aim to measure service quality in the fast-food industry, a neglected area of study. Unfortunately, the paper’s sophisticated analytical methods make it inaccessible to all but the most expert of researchers.
Battle, Ken. “Child Poverty: The Evolution and Impact of Child Benefits.” A Question of Commitment: Children's Rights in Canada . Ed. Katherine Covell and R.Brian Howe. Waterloo, ON: Wilfrid Laurier University Press. 2007. 21-44.
Ken Battle draws on a close study of government documents, as well as his own research as an extensively-published policy analyst, to explain Canadian child benefit programs. He outlines some fundamental assumptions supporting the belief that all society members should contribute to the upbringing of children. His comparison of child poverty rates in a number of countries is a useful wake-up to anyone assuming Canadian society is doing a good job of protecting children. Battle pays particular attention to the National Child Benefit (NCB), arguing that it did not deserve to be criticized by politicians and journalists. He outlines the NCB’s development, costs, and benefits, and laments that the Conservative government scaled it back in favour of the inferior Universal Child Care Benefit (UCCB). However, he relies too heavily on his own work; he is the sole or primary author of almost half the sources in his bibliography. He could make this work stronger by drawing from others' perspectives and analyses. However, Battle does offer a valuable source for this essay, because the chapter provides a concise overview of government-funded assistance currently available to parents. This offers context for analyzing the scope and financial reality of child poverty in Canada.
Journal Article Example
Kerr, Don and Roderic Beaujot. “Child Poverty and Family Structure in Canada, 1981-1997.” Journal of Comparative Family Studies 34.3 (2003): 321-335.
Sociology professors Kerr and Beaujot analyze the demographics of impoverished families. Drawing on data from Canada’s annual Survey of Consumer Finances, the authors consider whether each family had one or two parents, the age of single parents, and the number of children in each household. They analyze child poverty rates in light of both these demographic factors and larger economic issues. Kerr and Beaujot use this data to argue that.
Examples were taken from http://libguides.enc.edu/writing_basics/ annotatedbib/mla
Check out these resources for more information about Annotated Bibliographies.
- Purdue Owl- Annotated Bibliographies
- University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill- Annotated Bibliographies
- << Previous: Thesis Statement
- Next: Citing Sources >>
- Last Updated: Apr 4, 2024 5:51 PM
- URL: https://libguide.umary.edu/researchpaper

Writing an Annotated Bibliography
Learn how to write and format an annotated bibliography in APA Style (7th ed.).
Conducting research and documenting your findings is an essential part of the academic writing process. There are times when you will need (or be required) to conduct initial research prior to deciding on a thesis or focus for your writing. An annotated bibliography is a helpful tool to help you track and assess your sources.
Similar to formatting a paper, an annotated bibliography is formatted with double spacing and has a title page. An annotated bibliography does not typically include a list of references, since the annotated bibliography itself is a list of references, only each entry also provides information about the source.
Components of an Annotated Bibliography
An annotated bibliography includes a reference entry and a short annotation (paragraph) for each source. How annotations are written depends on the purpose of the research. There are two main components for each source included in an annotated bibliography:
- Bibliographic Information : This includes the same information you would provide in a reference list, formatted according to a reference entry for the particular type of source it is.
- Annotation : This is a short paragraph about the source that oftentimes summarizes the source and evaluates the usefulness of the source for your research paper or project, but what you include in the paragraph will largely depend on your particular assignment requirements.
Purposes of Writing an Annotated Bibliography
Writing an annotated bibliography is an effective way to document the research process and better prepare for a first draft. By requiring an annotated bibliography, your professor is setting you up for success. Some of the purposes and benefits of writing an annotated bibliography include the following:
- Formulate a thesis : Conducting research is a prewriting activity that can help narrow the focus of a topic that you are researching. Writing annotations for each source can help you understand the breadth and depth of a subject and determine your focus.
- Review the literature : An annotated bibliography can help you analyze the available literature on a subject. This is especially helpful for relatively new or persuasive topics where it is important to read about multiple sides of an issue.
- Illustrate the direction of your research : An employer or professor may want a preview of your research prior to the final draft of your paper. An annotated bibliography is a way to show your current research and its usefulness.
- Help other researchers : When other researchers find your paper particularly engaging, they often will examine your reference entries. However, an annotated bibliography provides more information about a source, such as a summary, which allows researchers to make an informed decision about whether to locate that source. With a references list, the reader has to guess whether a source will be useful and relevant.
Ways to Annotate Sources
There are several ways to write annotations depending on the purpose or the requirements of the assignment or research. Common approaches to writing annotations include the following:
- Summarize the source : Summarizing the source means to state briefly the main ideas of the source in relation to the current research. For instance, a medical book may have multiple chapters, but the only part to summarize for this source is the information that pertains to the research for the current paper’s topic. Please note: A summary must be written in your own words.
- Evaluate the source : To evaluate a source means you determine the strengths and weaknesses of the piece in relation to a particular research topic. When evaluating a source, the reliability and validity of the source are also determined. Reliability refers to the source’s credibility. Is it biased? Is the article from a website that is also selling a product related to the subject of the article? Is there a hidden agenda in the source? Validity indicates the accuracy or correctness of the information. Is the information gathered from experts? Is it just the opinion of the author? Is the author an authority on the topic at hand? What are their professional or academic credentials?
- Reflect on the usefulness of the source : How does this source fit in with the current research project? Is this a source you can use in your paper? Does it help define a problem or present an argument that would add depth and detail to your research? Is it better suited as a starting point to find other sources (i.e., is it useful only for background information)?
- Combination : Any combination of the above approaches to writing an annotation may be required. You may choose to write a separate short paragraph for each approach, or combine them into one annotation. As always, it is essential that you are careful to restate things in your own words to avoid plagiarizing an authors’ original words or ideas.
Sample Annotated Bibliography
Note. When formatting an Annotated Bibliography on a Word document, the bibliographic references have hanging indents .
Baker, B. (2003, November 27). Version control helps keep rework to a minimum. *EDN, 48*(26), 227-232. https://doi.org/10.9999/1.111111
This is a short article geared mostly toward digital developers who either are programming more than 10,000 lines of code or are programming within teams. It also emphasizes the importance of a VCS, but more so in the development environment. For this project, the only thing I might use this for is the simple statement that while a VCS is great for any work environment, without the discipline to use it regularly, they are worthless.
Huber, T. (2005, May). *JEDI version control system*. SourceForge. https://jedivcs.sourceforge.net
This site includes detailed instructions for operating an open source VCS. It is written for a technical audience that must have some background on this particular system. What is interesting about this site is the idea of open source. Maybe there are other version control systems available via the Internet through shareware sites. This particular site will probably not be used in writing the final project, but it is a source that can lead to further research on this idea of freeware for a VCS.
McVittie, L. (2007). Version control, with integrity. *Network Computing, 12*(21), 34-45. https://doi.org/10.9999/2.222222
This is an informative article with an overview of the details inside a VCS—branching, configuration, repository, access management, and more. What makes this article valuable though is the overview of several version control systems on the market (at least in 2001). After reading through the overview of several products, if one fits what my company is looking for, I can begin searching for that product and further information on the Internet. This article may or may not be used in the actual writing of the final proposal, but it will be useful information for further research on the project.
Share this:
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
Follow Blog via Email
Enter your email address to follow this blog and receive email notifications of new posts.
Email Address
- RSS - Posts
- RSS - Comments
- COLLEGE WRITING
- USING SOURCES & APA STYLE
- EFFECTIVE WRITING PODCASTS
- LEARNING FOR SUCCESS
- PLAGIARISM INFORMATION
- FACULTY RESOURCES
- Student Webinar Calendar
- Academic Success Center
- Writing Center
- About the ASC Tutors
- DIVERSITY TRAINING
- PG Peer Tutors
- PG Student Access
Subscribe to Blog via Email
Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
- College Writing
- Using Sources & APA Style
- Learning for Success
- Effective Writing Podcasts
- Plagiarism Information
- Faculty Resources
- Tutor Training
Twitter feed
Annotated Bibliographies

What Is An Annotated Bibliography?
What is an annotated bibliography.
An annotated bibliography is a list of citations (references) to books, articles, and documents followed by a brief summary, analysis or evaluation, usually between 100-300 words, of the sources that are cited in the paper. This summary provides a description of the contents of the source and may also include evaluative comments, such as the relevance, accuracy and quality of the source. These summaries are known as annotations.
- Annotated bibliographies are completed before a paper is written
- They can be stand-along assignments
- They can be used as a reference tool as a person works on their paper
Annotations vs. Abstracts
Abstracts are the descriptive summaries of article contents found at the beginning of scholarly journal articles that are written by the article author(s) or editor. Their purpose is to inform a reader about the topic, methodology, results and conclusion of the research of the article's author(s). The summaries are provided so that a researcher can determine whether or not the article may have information of interest to them. Abstracts do not serve an evaluative purpose.
Annotations found in bibliographies are evaluations of sources cited in a paper. They describe a work, but also critique the source by examining the author’s point of view, the strengths and weakness of the research or article hypothesis or how well the author presented their research or findings.
How to write an annotated bibliography
The creation of an annotated bibliography is a three-step process. It starts with finding and evaluating sources for your paper. Next is choosing the type or category of annotation, then writing the annotation for each different source. The final step is to choose a citation style for the bibliography.
Types of Annotated Bibliographies
Types of Annotations
Annotations come in different types, the one to use depends on the instructor’s assignment. Annotations can be descriptive, a summary, or an evaluation or a combination of descriptive and evaluation.
Descriptive/Summarizing Annotations
There are two kinds of descriptive or summarizing annotations, informative or indicative, depending on what is most important for a reader to learn about a source. Descriptive/summarizing annotations provide a brief overview or summary of the source. This can include a description of the contents and a statement of the main argument or position of the article as well as a summary of the main points. It may also describe why the source would be useful for the paper’s topic or question.
Indicative annotations provide a quick overview of the source, the kinds of questions/topics/issues or main points that are addressed by the source, but do not include information from the argument or position itself.
Informative annotations, like indicative annotations, provide a brief summary of the source. In addition, an informative annotation identifies the hypothesis, results, and conclusions presented by the source. When appropriate, they describe the author’s methodology or approach to the topic under discussion. However, they do not provide information about the sources usefulness to the paper or contains analytical or critical information about the source’s quality.
Evaluative Annotations (also known as critical or analytical)
Evaluative annotations go beyond just summarizing the source and listing out it’s key points, but also analyzes the content. It looks at the strengths and weaknesses of the article’s argument, the reliability of the presented information as well as any biases of the author. It talks about how the source may be useful to a particular field of study or the person’s research project.
Combination Annotations
Combination annotations “combine” aspects from indicative/informative and evaluative annotations and are the most common category of annotated bibliography. Combination annotations include one to two sentences summarizing or describing content, in addition to one or more sentences providing an critical evaluation.
Writing Style for Annotations
Annotations typically follow three specific formats depending on how long they are.
- Phrases – Short phrases providing the information in a quick, concise manner.
- Sentences – Complete sentences with proper punctuation and grammar, but are short and concise.
- Paragraphs – Longer annotations break the information out into different paragraphs. This format is very effective for combination annotations.
To sum it up:
An annotation may include the following information:
- A brief summary or overview of the source content
- The source’s strengths and weaknesses in presenting the argument or position
- Its conclusions
- Why the source is relevant in to field of study of the paper
- Its relationships to other studies in the field
- An evaluation of the research methodology (if applicable)
- Information about the author’s background and potential biases
- Conclusions about the usefulness of the source for the paper
Critically Analyzing Articles
In order to write an annotation for a paper source, you need to first read and then critically analyze it:
- Try to identify the topic of the source -- what is it about and is it clearly stated.
- See if you can identify the purpose of the author(s) in doing the research or writing about the topic. Is it to survey and summarize research on a topic? Is the author(s) presenting an argument based on previous research, or refuting previously published research?
- Identify the research methods used and try to identify whether they appear to be suitable or not for the stated purpose of the research.
- Was the research reported in a consistent or clear manner? Or, was the author's argument/position presented in a consistent or convincing manner? Did the author(s) fail to acknowledge and explain any limitations?
- Was the logic of the research/argument claims properly supported with convincing evidence/analysis/data? Did you spot any fallacies?
- Check whether the author(s) refers to other research and if similar studies have been done.
- If illustrations or charts are used, are they effective in presenting information?
- Analyze the sources that were used by the author(s). Did the author(s) miss any important studies they should have considered?
- Your opinion of the source -- do you agree with or are convinced of the findings?
- Your estimation of the source’s contribution to knowledge and its implications or applications to the field of study.
Worksheet for Taking Notes for Critical Analysis of Sources/Articles
Additional Resources:
Hofmann, B., Magelssen, M. In pursuit of goodness in bioethics: analysis of an exemplary article. BMC Med Ethics 19, 60 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-018-0299-9
Jansen, M., & Ellerton, P. (2018). How to read an ethics paper. Journal of Medical Ethics, 44(12), 810-813. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/medethics-2018-104997
Research & Learning Services, Olin Library, Cornell University Library Critically Analyzing Information Sources: Critical Appraisal and Analysis
Formatting An Annotated Bibliography
How do I format my annotated bibliography?
An annotated bibliography entry consists of two components: the Citation and the Annotation.
The citation should be formatted in the bibliographic style that your instructor has requested for the paper. Some common citation styles include APA, MLA, and Chicago. For more information on citation styles, see Writing Guides, Style Manuals and the Publication Process in the Biological & Health Sciences .
Many databases (e.g., PubMed, Academic Search Premier, Library Search on library homepage, and Google Scholar) offer the option of creating your references in various citation styles.
Look for the "cite" link -- see examples for the following resources:
University of Minnesota Library Search

Google Scholar

Sample Annotated Bibliography Entries
An example of an Evaluative Annotation , APA style (7th ed). (sample from University Libraries, University of Nevada ).
APA does not have specific formatting rules for annotations, just for the citation and bibliography.
Maak, T. (2007). Responsible leadership, stakeholder engagement, and the emergence of social capital. Journal of Business Ethics, 74, 329-343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-007-9510-5
This article focuses on the role of social capital in responsible leadership. It looks at both the social networks that a leader builds within an organization, and the links that a leader creates with external stakeholders. Maak’s main aim with this article seems to be to persuade people of the importance of continued research into the abilities that a leader requires and how they can be acquired. The focus on the world of multinational business means that for readers outside this world many of the conclusions seem rather obvious (be part of the solution not part of the problem). In spite of this, the article provides useful background information on the topic of responsible leadership and definitions of social capital which are relevant to an analysis of a public servant.
An example of an Evaluative Annotation , MLA Style (10th ed), (sample from Columbia College, Vancouver, Canada )
MLA style requires double-spacing (not shown here) and paragraph indentations.
London, Herbert. “Five Myths of the Television Age.” Television Quarterly, vol. 10, no. 1, Mar. 1982, pp. 81-69.
Herbert London, the Dean of Journalism at New York University and author of several books and articles, explains how television contradicts five commonly believed ideas. He uses specific examples of events seen on television, such as the assassination of John Kennedy, to illustrate his points. His examples have been selected to contradict such truisms as: “seeing is believing”; “a picture is worth a thousand words”; and “satisfaction is its own reward.” London uses logical arguments to support his ideas which are his personal opinion. He does not refer to any previous works on the topic. London’s style and vocabulary would make the article of interest to any reader. The article clearly illustrates London’s points, but does not explore their implications leaving the reader with many unanswered questions.
Additional Resources
University Libraries Tutorial -- Tutorial: What are citations? Completing this tutorial you will:
- Understand what citations are
- Recognize why they are important
- Create and use citations in your papers and other scholarly work
University of Minnesota Resources
Beatty, L., & Cochran, C. (2020). Writing the annotated bibliography : A guide for students & researchers . New York, NY: Routledge. [ebook]
Efron, S., Ravid, R., & ProQuest. (2019). Writing the literature review : A practical guide . New York: The Guilford Press. [ebook -- see Chapter 6 on Evaluating Research Articles]
Center for Writing: Student Writing Support
- Critical reading strategies
- Common Writing Projects (includes resources for literature reviews & analyzing research articles)
Resources from Other Libraries
Annotated Bibliographies (The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill)
Writing An Annotated Bibliography (University of Toronto)
Annotated Bibliographies (Purdue Writing Lab, Purdue University)
Annotated Bibliography (UNSW Sydney)
What is an annotated bibliography? (Santiago Canyon College Library): Oct 17, 2017. 3:47 min.
Writing an annotated bibliography (EasyBib.com) Oct 22, 2020. 4:53 min.
Creating an annotated bibliography (Laurier University Library, Waterloo, Ontario)/ Apr 3, 2019, 3:32 min.
How to create an annotated bibliography: MLA (JamesTheDLC) Oct 23, 2019. 3:03 min.
Citing Sources
Introduction
Citations are brief notations in the body of a research paper that point to a source in the bibliography or references cited section.
If your paper quotes, paraphrases, summarizes the work of someone else, you need to use citations.
Citation style guides such as APA, Chicago and MLA provide detailed instructions on how citations and bibliographies should be formatted.

Health Sciences Research Toolkit
Resources, tips, and guidelines to help you through the research process., finding information.
Library Research Checklist Helpful hints for starting a library research project.
Search Strategy Checklist and Tips Helpful tips on how to develop a literature search strategy.
Boolean Operators: A Cheat Sheet Boolean logic (named after mathematician George Boole) is a system of logic to designed to yield optimal search results. The Boolean operators, AND, OR, and NOT, help you construct a logical search. Boolean operators act on sets -- groups of records containing a particular word or concept.
Literature Searching Overview and tips on how to conduct a literature search.
Health Statistics and Data Sources Health related statistics and data sources are increasingly available on the Internet. They can be found already neatly packaged, or as raw data sets. The most reliable data comes from governmental sources or health-care professional organizations.
Evaluating Information
Primary, Secondary and Tertiary Sources in the Health Sciences Understand what are considered primary, secondary and tertiary sources.
Scholarly vs Popular Journals/Magazines How to determine what are scholarly journals vs trade or popular magazines.
Identifying Peer-Reviewed Journals A “peer-reviewed” or “refereed” journal is one in which the articles it contains have been examined by people with credentials in the article’s field of study before it is published.
Evaluating Web Resources When searching for information on the Internet, it is important to be aware of the quality of the information being presented to you. Keep in mind that anyone can host a web site. To be sure that the information you are looking at is credible and of value.
Conducting Research Through An Anti-Racism Lens This guide is for students, staff, and faculty who are incorporating an anti-racist lens at all stages of the research life cycle.
Understanding Research Study Designs Covers case studies, randomized control trials, systematic reviews and meta-analysis.
Qualitative Studies Overview of what is a qualitative study and how to recognize, find and critically appraise.
Writing and Publishing
Citing Sources Citations are brief notations in the body of a research paper that point to a source in the bibliography or references cited section.
Structure of a Research Paper Reports of research studies usually follow the IMRAD format. IMRAD (Introduction, Methods, Results, [and] Discussion) is a mnemonic for the major components of a scientific paper. These elements are included in the overall structure of a research paper.
Top Reasons for Non-Acceptance of Scientific Articles Avoid these mistakes when preparing an article for publication.
Annotated Bibliographies Guide on how to create an annotated bibliography.
Writing guides, Style Manuals and the Publication Process in the Biological and Health Sciences Style manuals, citation guides as well as information on public access policies, copyright and plagiarism.
News alert: UC Berkeley has announced its next university librarian
Secondary menu
- Log in to your Library account
- Hours and Maps
- Connect from Off Campus
- UC Berkeley Home
Search form
Effective research assignments: home, communicate your expectations.
- Assess the quality of the sources your students cite as part of their overall grades, and explain clearly in your rubric how that evaluation will be made.
- Spell out your expectations regarding sources. Instead of asking for scholarly sources, for example, you could ask your students to "cite at least two peer-reviewed journal articles and two primary sources".
- Explain terminology and provide background regarding scholarly publishing. What’s peer-review? What are some differences between scholarly books and journal articles? When should one consult popular news sources? What’s a primary source?
- Clearly communicate which style manual is required.
- Include a policy on plagiarism in the assignment and discuss the purposes of proper attribution. Discuss examples: does paraphrasing another author’s ideas require a citation?
- Provide examples of topics that are appropriate in scope for the assignment at hand, and provide feedback to individual students as they begin to develop and refine their topics.
Design and test your assignment An effective research assignment targets specific skills, for example, the ability to trace a scholarly argument through the literature or the ability to organize consulted resources into a bibliography.
- Test the assignment yourself. Can you find the kinds of sources required? Are you required to evaluate the sources you find?
- Ask students for feedback on the assignment. Are they having problems finding relevant materials? Do they understand your expectations?
- If the assignment is particularly demanding, consider dividing a single research project into multiple assignments (outline, draft, final draft), each one focusing on a different aspect of the research process.
Ideas for alternative research assignments
- Assign an annotated bibliography in which students identify primary and secondary sources, popular and scholarly publications, and detect and comment on forms of bias.
- Ask for students to document the search tools they use (library catalog, article databases, Google, etc.) for a research paper and to reflect on the kinds of information they find in each.
- Provide a resource list or a single source from which students’ research should begin. Discuss the utility of known sources for identifying keywords, key concepts, and other citations to inform further searching.
- Assign students to prepare a guide for introducing their classmates to the essential literature on a given topic.
- Have students compile a glossary of important terms specific to a given topic in your discipline.
- Require students to edit an anthology of important scholarship on a specific topic and write an introduction explaining the development of the field over time.
Avoid these common mistakes
- Since many scholarly sources are available online, it can be confusing for students when “Internet” or “Web” sources are forbidden. It’s helpful to describe why certain sources (such as Wikipedia) may not be allowed.
- Make sure the resources required by the assignment are available to your students in the library or in library databases. You can also place hard-to-find required sources on course reserve .
- Last Updated: May 4, 2022 10:41 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.berkeley.edu/effective-research-assignments
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Writing Evaluative Annotated Bibliographies
Dawn Atkinson
Chapter Overview
This chapter aims to help you understand what an annotated bibliography is and how this type of document can be used when planning assignments, conducting research, and evaluating sources. An annotated bibliography generally takes one of two forms: descriptive annotated bibliographies reference and briefly describe sources, while evaluative (or critical ) annotated bibliographies reference, succinctly summarize, and evaluate resources. Regardless of form, an annotated bibliography may be incorporated into a longer text, such as a formal report, or be produced as a stand-alone piece to document research work—for example, to accompany an in-depth assignment like a researched argument essay. Either way, the sources listed on an annotated bibliography should center on a topic or focus; if the annotated bibliography documents research efforts related to an associated assignment, the focus will reflect the author’s thesis, research questions (questions that a study seeks to answer), or research objectives.
The remainder of this chapter addresses evaluative annotated bibliographies.
What, specifically, is an evaluative annotated bibliography?
An evaluative annotated bibliography focuses on an overarching topic by listing pertinent references and by providing sentences that discuss and assess the resources identified in those references. Place the reference for a source at the beginning of an annotated bibliography entry, and then craft sentences and paragraphs about the source that do some or all of the following in accordance with the specifications for the assignment.
- Summarize the source’s main argument, main point, central themes, or key takeaways.
- Evaluate the source; in other words, assess the source based on criteria. For example, what is your view of the source’s usefulness or relevance (in terms of research about a topic), accuracy, trustworthiness, timeliness, level of objectivity, or quality, and why do you hold that view? What methods did the author(s) of the source use to collect data, are they sound, and how did you draw that conclusion? How does the source compare with other publications listed on the annotated bibliography that address the same topic? You will need to read all the sources on your annotated bibliography before you can answer this last question.
- Comment on how the source corresponds with your research aim. How does it fit with, support, or differ from your viewpoint? How has it expanded your thinking on a topic? How might you use the source when writing an associated assignment?
An annotation may also include information about an author’s credentials, the intended audience for a source, and the purpose of a text. Note that in technical and academic genres, authors oftentimes foreground the purposes of their works by indicating them early on, to help readers understand the overall direction of the writing. The purpose of a scholarly journal article, for instance, will typically be stated in its abstract , which is a summary of the article located after the publication’s title but before its introduction.
Why might you be asked to consider author credentials and date of publication when compiling sources for an annotated bibliography?
What does an evaluative annotated bibliography look like?
When constructing an annotated bibliography, follow your instructor’s directions about what information to include and how to format the document, and structure its references according to the style conventions specified. References in the following annotated bibliography entries adhere to APA style; the annotated bibliography as a whole also follows APA formatting conventions. The entries, which are adapted from McLaughlin (2020) as cited in Excelsior Online Writing Lab (2020, “Sample Annotated Bibliography”), feature combinations of the annotated bibliography information listed previously in this chapter and center on the topic of the transferability of writing skills , or applying knowledge and skills about writing gained in one context to another context—a practice that may advance a writer’s knowledge and skills. If you are asked to produce an annotated bibliography for a class, help readers navigate its contents by being consistent about the type of information you supply in each of its entries. In accordance with APA style, the references in the following sample are alphabetized by first author’s last name.
Boone, S., Biggs Chaney, S., Compton, J., Donahue, C., & Gocsik, K. (2012). Imagining a writing and rhetoric program based on principles of knowledge “transfer”: Dartmouth’s Institute for Writing and Rhetoric. Composition Forum, 26 . http://compositionforum.com/issue/26/dartmouth.php
In this article, Boone et al. (2012) overview the writing program at Dartmouth College’s Institute for Writing and Rhetoric to discuss an example of what a program based on writing transfer research looks like. The authors trace the history of the program’s development, explain current curriculum and organization, and look at future directions for the program. Beginning with the idea that skills and knowledge do not all transfer in the same way, program developers at Dartmouth set out to explore what kind of knowledge writing is and how this knowledge is transferred. By developing curriculum and sequences of courses that foster reflection and connections to future courses and by encouraging faculty development, Dartmouth has established a thoughtfully constructed writing program that serves as a model for other such programs. The authors explore the state of research on the program and goals based on the results of their research.
This piece serves as a useful guide composed by writing program administrators and writing researchers who are interested in seeing how current studies of writing transfer can be applied to an operating program. The authors offer practical advice, include sample syllabi and curriculum, and honestly reflect on successes and struggles of the program. This article provides much-needed information for those interested in developing a writing program that aligns with transfer research.
Moore, J. (2012). Mapping the questions: The state of writing-related transfer research . Composition Forum, 26 . http://compositionforum.com/issue/26/map-questions-transfer-research.php
Moore (2012) reviews the literature on writing skill transfer in this article as a starting point for who those who are interested in the research area and are already conversant in the language of rhetoric and composition studies. The author begins by discussing the history of research on writing skill transfer, describing issues related to common definitions and multi-institutional studies. She also explores the goals and methods of recent investigations and, ultimately, calls for explorations of new areas pertinent to writing transfer research. In doing the latter, she raises important questions about how students’ involvement in non-writing courses and non-academic activities may influence what they do when writing.
Moore’s article provides a helpful overview of studies in the field of writing skill transfer and establishes a jumping-off point for new investigations in the area. I can use information from the article in my term paper introduction to establish context for the reader before exploring different dimensions of writing skill transfer in the body of the piece.
Wardle, E. (2007). Understanding ‘transfer’ from FYC: Preliminary results of a longitudinal study. Writing Program Administration, 31 (1-2), 65-85. http://associationdatabase.co/archives/31n1-2/31n1-2wardle.pdf
In her report on a longitudinal study conducted at the University of Dayton, Wardle (2007) explores the transfer of writing skills from first-year college composition courses. She begins by explaining that research is limited when it comes to transfer of writing skills, even though transfer is seen as a key function of first-year writing courses. The research that does exist indicates that the skills do not transfer well. With this in mind, Wardle established a curriculum designed to support writing transfer and followed students for two years after they had completed first-year composition. Her research indicates that the skills from first-year writing did not transfer well, not because students were unable to make the transfer but because the writing assignments they encountered, along with a variety of other issues, made them feel there was no need to transfer the skills.
This longitudinal study is a foundational piece for writing program directors and serves as a call for more research on writing skill transfer, particularly as it relates to first-year college writing courses. Consequently, lessons gleaned from this study continue to inform writing teachers, program directors, and researchers. In the article, Wardle cites her work with colleague Doug Downs. Together, Wardle and Downs are known as leaders in writing transfer research, which again speaks to the article’s contribution as a trustworthy and influential piece of scholarship.
While the above sample focuses exclusively on the topic of writing skill transfer, an annotated bibliography that focuses on multiple topics related to a central theme may organize these under specific and informative headings to help readers distinguish one topic area from another. Additionally, if you are asked to produce an annotated bibliography as a stand-alone document, you may be required to provide an introduction to help set the context for the rest of the piece and to explain its purpose.
What are evaluative annotated bibliographies used for?
Because evaluative annotated bibliographies summarize, evaluate, and consider the relevance of sources, they can be used to narrow a research focus, to weigh up research in an area, and to document research findings. To illustrate, maybe you have been asked to compose an evaluative annotated bibliography on the way to producing a researched argument essay. Although you know which topic you want to write about in your essay, you are less clear about what the research says regarding this topic. After reading a book chapter and several journal, magazine, and newspaper articles on the topic, you begin drafting your annotated bibliography and notice that the sources discuss similar and opposing viewpoints and support these with various pieces of evidence. Although you were fairly certain of your perspective on the issue before you began the annotated bibliography assignment, you acknowledge that your view has expanded as a result of reading, writing about, and considering how the sources relate to your researched argument paper. Furthermore, by evaluating the sources for accuracy, quality, and relevance, you are also able to determine which ones best underpin your claims, as well as opposing claims. Thus, you are able to develop a focused thesis statement and supporting topic sentences for your essay that acknowledge the complexities of the topic. Furthermore, your annotated bibliography documents your research work for readers, communicating which sources you investigated for purposes of composing your researched argument and your evaluations of these sources.
Activity: Produce an Evaluative Annotated Bibliography Entry
Read Michael Bunn’s (2011) essay “How to Read Like a Writer,” which can be found at https://wac.colostate.edu/docs/books/writingspaces2/bunn–how-to-read.pdf . Bunn teaches in the University of Southern California’s Writing Program. After reading, reflect on the essay and its pertinence to your own reading and writing life by answering the four discussion questions on page 85 of the text. Be prepared to talk about your answers in class.
Once you have read, reflected on, and discussed the essay, produce an annotated bibliography entry for the source by following these steps.
Step 1: Write a complete, accurate APA reference list entry for the source.
Step 2 : Answer the following questions.
- What qualifications does the author have? Google him to discover additional information about his credentials beyond that already supplied.
- Who is the intended audience for the source?
- What the purpose of the source?
- How do the audience and purpose influence how information is presented in the source?
- What argument does the author make?
- Is the argument convincing? Why or why not?
- How does the source contribute to your own ideas about reading and writing or relate to other sources you have read about reading and writing?
Step 3: Use the notes you have made to draft an evaluative annotated bibliography entry for the Bunn (2011) text. Refer to the information and examples provided in this chapter for guidance.
Homework: Produce an Evaluative Annotated Bibliography
Identify a topic of inquiry you can explore via means of an annotated bibliography. Your instructor may assign you a topic or ask you to select one. Research the topic by locating and reading sources about it; a librarian can help you identify a focused list of sources. Afterwards, compose an evaluative annotated bibliography that references, summarizes, and evaluates the sources. Your instructor may also ask you to identify author credentials and the intended audience and purpose for each source. In addition, you may be asked to discuss how the sources relate to a larger research aim. Since the evaluative annotated bibliography is a stand-alone assignment, supply an introduction to help set the context for the rest of the piece and to explain its purpose.
After drafting your evaluative annotated bibliography, your instructor may ask you to assess it in relation to the rubric criteria outlined in Rinto (2013, p. 10) in order to refine its content. The rubric is provided here in adapted format for your reference.
When refining your annotated bibliography, use the following handout, produced by the Writing and Communication Centre, University of Waterloo (n.d.), to ensure you have used the words that and which correctly.
Which vs That: Restrictive and Non-Restrictive Clauses
Restrictive and Non-Restrictive Clauses
Which and that both introduce clauses (groups of words) that provide more information but are not grammatically necessary to the sentence.
e.g., The daily special, which was poached salmon , cost a lot. e.g., The dish that the sous-chef prepared turned out to be better than the daily special.
Using Restrictive Clauses: That
Use that when the information in the clause is necessary to the meaning of the sentence. It’s called a restrictive clause because it limits or affects the purpose of the sentence.
e.g., Suitcases that weigh more than 23kg must be checked.
that weigh more than 23 kg is necessary to the purpose of the sentence. If you removed this restrictive clause, it would imply that all suitcases must be checked, which isn’t what the author intends.
e.g., Drinks that have caffeine make it hard to fall asleep.
that have caffeine is also restrictive. If you take this part out, it suggests that all drinks make it hard to fall asleep.
Some writers will use which for a restrictive clause instead of that . This is technically fine, but if you are having any confusion about the distinctions between restrictive and non-restrictive clauses, it is better to maintain a clear distinction between that and which , for clarity’s sake.
Using Non-Restrictive Clauses: Which
Use which when the information in the clause is not necessary to the meaning of the sentence. It might be helpful or interesting, but if you took it out, the sentence would still make sense.
e.g., The suitcase, which was stuffed with dirty clothes , didn’t fit in the overhead bin.
If which was removed: e.g., The suitcase didn’t fit in the overhead bin.
e.g., Coffee and tea, which both have caffeine , are Canada’s favourite morning drinks.
If which was removed: e.g., Coffee and tea are Canada’s favourite morning drinks.
Note that the non-restrictive which clause is set off by commas.
Use that without commas for a restrictive (necessary) clause. That is required more often than which . Use which with commas for a non-restrictive (not necessary) clause.
Write in that (for restrictive clauses) or which (for non-restrictive clauses).
- The spoon __________ fell on the floor needed to be washed.
- The book __________ she wanted was on the top shelf.
- They used Post-It notes __________ come in various colours to organize the pages.
- For the hike I need shoes __________ are sturdy.
- For the hike I need sturdy shoes __________ are expensive.
- The first skyscraper we saw __________ was the biggest one on that street had 67 floors.
- The only elevator __________ went all the way to the top was out of service.
- The cord __________ charges this computer is missing.
- He provided us with a whole box of samples __________ we didn’t really need so we could make a decision.
Bunn, M. (2011). How to read like a writer. In C. Lowe, & P. Zemliansky (Eds.), Writing spaces: Readings on writing (Vol. 2, pp. 71-86). Parlor Press. License: CC-BY 4.0. https://wac.colostate.edu/docs/books/writingspaces2/bunn–how-to-read.pdf
Excelsior Online Writing Lab. (2020). Annotated bibliographies . License: CC-BY 4.0. https://owl.excelsior.edu/research/annotated-bibliographies/
Rinto, E.E. (2013). Developing and applying an information literacy rubric to student annotated bibliographies. Evidence Based Library and Information Practice, 8 (3), 5-18. License: CC-BY-NC-SA 4.0 . https://doi.org/10.18438/B8559F
Writing Centre, University of Waterloo. (n.d.). Which vs that: Restrictive and non-restrictive clauses . License: CC-BY-SA 4.0 . https://uwaterloo.ca/writing-and-communication-centre/sites/ca.writing-and-communication-centre/files/uploads/files/which_vs_that.pdf
Mindful Technical Writing Copyright © 2020 by Dawn Atkinson is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
31 Bibliography
Annotated bibliography.
A bibliography is an alphabetized list of sources showing the author, date, and publication information for each source.
An annotation is like a note; it’s a brief paragraph that explains what the writer learned from the source.
Annotated bibliographies combine bibliographies and brief notes about the sources.
Writers often create annotated bibliographies as a part of a research project, as a means of recording their thoughts and deciding which sources to actually use to support the purpose of their research. Some writers include annotated bibliographies at the end of a research paper as a way of offering their insights about the source’s usability to their readers.
Instructors in college often assign annotated bibliographies as a means of helping students think through their source’s quality and appropriateness to their research question or topic. (23)
Formatting the Annotated Bibliography
The citations (bibliographic information – title, date, author, publisher, etc.) in the annotated bibliography are formatted using the particular style manual (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.) that your discipline requires.
Annotations are written in paragraph form, usually 3-7 sentences (or 80-200 words). Depending on your assignment your annotations will generally include the following:
- Summary: Summarize the information given in the source. Note the intended audience. What are the main arguments? What is the point of this book or article? What topics are covered? If someone asked what this article/book is about, what would you say?
- Evaluate/Assess: Is this source credible? Who wrote it? What are their credentials? Who is the publisher? Is it a useful source? How does it compare with other sources in your bibliography? Is the information reliable? Is this source biased or objective? What is the goal of this source?
- Reflect/React: Once you’ve summarized and assessed a source, you need to ask how it fits into your research. State your reaction and any additional questions you have about the information in your source. Was this source helpful to you? How does it help you shape your argument? How can you use this source in your research project? Has it changed how you think about your topic? Compare each source to other sources in your annotated bibliography in terms of its usefulness and thoroughness in helping answer your research question. (24)
Annotated Bibliography Examples
In the following examples, the bold font indicates the reflection component of the annotation that is sometimes required in an assignment.
APA style 6 th edition for the journal citation:
Waite, L. J., Goldschneider, F. K., & Witsberger, C. (1986). Nonfamily living and the erosion of traditional family orientations among young adults. American Sociological Review , 51, 541-554.
The authors, researchers at the Rand Corporation and Brown University, use data from the National Longitudinal Surveys of Young Women and Young Men to test their hypothesis that nonfamily living by young adults alters their attitudes, values, plans, and expectations, moving them away from their belief in traditional sex roles. They find their hypothesis strongly supported in young females, while the effects were fewer in studies of young males. Increasing the time away from parents before marrying increased individualism, self-sufficiency, and changes in attitudes about families. In contrast, an earlier study by Williams cited below shows no significant gender differences in sex role attitudes as a result of nonfamily living. (25)
MLA 8 style for a website citation:
Anderson, L.V. “Can You Libel Someone on Twitter?” Slate.com, The Slate Group, A Graham Holdings. Company, 26 Nov. 2012, http://www.slate.com/articles/technology/explainer/2012/11/libel_on_twitter_you_can_be_sued_for_libel_for_what_you_write_on_facebook.html . Accessed 2 Apr. 2018.
This article provides an overview of defamation law in the United States compared to the United Kingdom, in layman’s terms. It also explains how defamation law applies to social media platforms and individuals who use social media. Libelous comments posted on social media can be subject to lawsuit, depending on the content of the statement, and whether the person is a public or private figure. The article is found on the website, Slate.com, which is a web-based daily magazine that focuses on general interest topics. While the writer’s credentials are unavailable, she does thank Sandra S. Baron, Executive Director of the Media Law Resource Center and Jeff Hermes, director of the Digital Media Law Project for providing information. She also links to the United States laws that she cites. I would use the article to compare United States law to United Kingdom law and for background information. (1)
Information creation is a process. Scholars produce information in the forms of peer-reviewed journal articles, books, and conference presentations, to name a few. As a student researcher, you will be expected to create research projects such as essays, reports, visual presentations, and annotated bibliographies. Most scholarly writing makes an argument—whether it is to persuade your readers that your claim is true or to act on it. In order to create a sound argument, you must gather sources that will argue and counter-argue your claims.
When creating an argument, the researcher typically organizes their report or presentation with the claim/thesis at the beginning, which answers their research question. Then they provide reasons and supporting evidence to validate their claim. They acknowledge and respond to counter-arguments by citing sources that disagree with them, and refuting or conceding those counter-claims. Their conclusion restates their thesis and discusses why their research is important to the scholarly conversation, as well as potential areas for further research.
A Roman numeral outline is one way to organize your argument before you begin writing. It helps to identify sources for each section of your outline, so you know if you need further research to support your argument.
An annotated bibliography is one way to present research, and can be used as a cumulative assignment, or a precursor to your actual research paper. A good annotated bibliography will provide a variety of sources that met all your research needs—background, evidence, argument, and method. In other words, you should be able to take your annotated bibliography and write a complete research report based on those sources. (1)
Introduction to College Research Copyright © by Lumen Learning is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
FREE Poetry Worksheet Bundle! Perfect for National Poetry Month.
How To Write a Bibliography (Three Styles, Plus Examples)
Give credit where credit is due.

Writing a research paper involves a lot of work. Students need to consult a variety of sources to gather reliable information and ensure their points are well supported. Research papers include a bibliography, which can be a little tricky for students. Learn how to write a bibliography in multiple styles and find basic examples below.
IMPORTANT: Each style guide has its own very specific rules, and they often conflict with one another. Additionally, each type of reference material has many possible formats, depending on a variety of factors. The overviews shown here are meant to guide students in writing basic bibliographies, but this information is by no means complete. Students should always refer directly to the preferred style guide to ensure they’re using the most up-to-date formats and styles.
What is a bibliography?
When you’re researching a paper, you’ll likely consult a wide variety of sources. You may quote some of these directly in your work, summarize some of the points they make, or simply use them to further the knowledge you need to write your paper. Since these ideas are not your own, it’s vital to give credit to the authors who originally wrote them. This list of sources, organized alphabetically, is called a bibliography.
A bibliography should include all the materials you consulted in your research, even if you don’t quote directly from them in your paper. These resources could include (but aren’t limited to):
- Books and e-books
- Periodicals like magazines or newspapers
- Online articles or websites
- Primary source documents like letters or official records
Bibliography vs. References
These two terms are sometimes used interchangeably, but they actually have different meanings. As noted above, a bibliography includes all the materials you used while researching your paper, whether or not you quote from them or refer to them directly in your writing.
A list of references only includes the materials you cite throughout your work. You might use direct quotes or summarize the information for the reader. Either way, you must ensure you give credit to the original author or document. This section can be titled “List of Works Cited” or simply “References.”
Your teacher may specify whether you should include a bibliography or a reference list. If they don’t, consider choosing a bibliography, to show all the works you used in researching your paper. This can help the reader see that your points are well supported, and allow them to do further reading on their own if they’re interested.
Bibliography vs. Citations
Citations refer to direct quotations from a text, woven into your own writing. There are a variety of ways to write citations, including footnotes and endnotes. These are generally shorter than the entries in a reference list or bibliography. Learn more about writing citations here.
What does a bibliography entry include?
Depending on the reference material, bibliography entries include a variety of information intended to help a reader locate the material if they want to refer to it themselves. These entries are listed in alphabetical order, and may include:
- Author/s or creator/s
- Publication date
- Volume and issue numbers
- Publisher and publication city
- Website URL
These entries don’t generally need to include specific page numbers or locations within the work (except for print magazine or journal articles). That type of information is usually only needed in a footnote or endnote citation.
What are the different bibliography styles?
In most cases, writers use one of three major style guides: APA (American Psychological Association), MLA (Modern Language Association), or The Chicago Manual of Style . There are many others as well, but these three are the most common choices for K–12 students.
Many teachers will state their preference for one style guide over another. If they don’t, you can choose your own preferred style. However, you should also use that guide for your entire paper, following their recommendations for punctuation, grammar, and more. This will ensure you are consistent throughout.
Below, you’ll learn how to write a simple bibliography using each of the three major style guides. We’ve included details for books and e-books, periodicals, and electronic sources like websites and videos. If the reference material type you need to include isn’t shown here, refer directly to the style guide you’re using.
APA Style Bibliography and Examples
Source: Verywell Mind
Technically, APA style calls for a list of references instead of a bibliography. If your teacher requires you to use the APA style guide , you can limit your reference list only to items you cite throughout your work.
How To Write a Bibliography (References) Using APA Style
Here are some general notes on writing an APA reference list:
- Title your bibliography section “References” and center the title on the top line of the page.
- Do not center your references; they should be left-aligned. For longer items, subsequent lines should use a hanging indent of 1/2 inch.
- Include all types of resources in the same list.
- Alphabetize your list by author or creator, last name first.
- Do not spell out the author/creator’s first or middle name; only use their initials.
- If there are multiple authors/creators, use an ampersand (&) before the final author/creator.
- Place the date in parentheses.
- Capitalize only the first word of the title and subtitle, unless the word would otherwise be capitalized (proper names, etc.).
- Italicize the titles of books, periodicals, or videos.
- For websites, include the full site information, including the http:// or https:// at the beginning.
Books and E-Books APA Bibliography Examples
For books, APA reference list entries use this format (only include the publisher’s website for e-books).
Last Name, First Initial. Middle Initial. (Publication date). Title with only first word capitalized . Publisher. Publisher’s website
- Wynn, S. (2020). City of London at war 1939–45 . Pen & Sword Military. https://www.pen-and-sword.co.uk/City-of-London-at-War-193945-Paperback/p/17299
Periodical APA Bibliography Examples
For journal or magazine articles, use this format. If you viewed the article online, include the URL at the end of the citation.
Last Name, First Initial. Middle Initial. (Publication date). Title of article. Magazine or Journal Title (Volume number) Issue number, page numbers. URL
- Bell, A. (2009). Landscapes of fear: Wartime London, 1939–1945. Journal of British Studies (48) 1, 153–175. https://www.jstor.org/stable/25482966
Here’s the format for newspapers. For print editions, include the page number/s. For online articles, include the full URL.
Last Name, First Initial. Middle Initial. (Year, Month Date) Title of article. Newspaper title. Page number/s. URL
- Blakemore, E. (2022, November 12) Researchers track down two copies of fossil destroyed by the Nazis. The Washington Post. https://www.washingtonpost.com/science/2022/11/12/ichthyosaur-fossil-images-discovered/
Electronic APA Bibliography Examples
For articles with a specific author on a website, use this format.
Last Name, First Initial. Middle Initial. (Year, Month Date). Title . Site name. URL
- Wukovits, J. (2023, January 30). A World War II survivor recalls the London Blitz . British Heritage . https://britishheritage.com/history/world-war-ii-survivor-london-blitz
When an online article doesn’t include a specific author or date, list it like this:
Title . (Year, Month Date). Site name. Retrieved Month Date, Year, from URL
- Growing up in the Second World War . (n.d.). Imperial War Museums. Retrieved May 12, 2023, from https://www.iwm.org.uk/history/growing-up-in-the-second-world-war
When you need to list a YouTube video, use the name of the account that uploaded the video, and format it like this:
Name of Account. (Upload year, month day). Title [Video]. YouTube. URL
- War Stories. (2023, January 15). How did London survive the Blitz during WW2? | Cities at war: London | War stories [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/uwY6JlCvbxc
For more information on writing APA bibliographies, see the APA Style Guide website.
APA Bibliography (Reference List) Example Pages

Source: Simply Psychology
More APA example pages:
- Western Australia Library Services APA References Example Page
- Ancilla College APA References Page Example
- Scribbr APA References Page Example
MLA Style Bibliography Examples

Source: PressBooks
MLA style calls for a Works Cited section, which includes all materials quoted or referred to in your paper. You may also include a Works Consulted section, including other reference sources you reviewed but didn’t directly cite. Together, these constitute a bibliography. If your teacher requests an MLA Style Guide bibliography, ask if you should include Works Consulted as well as Works Cited.
How To Write a Bibliography (Works Cited and Works Consulted) in MLA Style
For both MLA Works Cited and Works Consulted sections, use these general guidelines:
- Start your Works Cited list on a new page. If you include a Works Consulted list, start that on its own new page after the Works Cited section.
- Center the title (Works Cited or Works Consulted) in the middle of the line at the top of the page.
- Align the start of each source to the left margin, and use a hanging indent (1/2 inch) for the following lines of each source.
- Alphabetize your sources using the first word of the citation, usually the author’s last name.
- Include the author’s full name as listed, last name first.
- Capitalize titles using the standard MLA format.
- Leave off the http:// or https:// at the beginning of a URL.
Books and E-Books MLA Bibliography Examples
For books, MLA reference list entries use this format. Add the URL at the end for e-books.
Last Name, First Name Middle Name. Title . Publisher, Date. URL
- Wynn, Stephen. City of London at War 1939–45 . Pen & Sword Military, 2020. www.pen-and-sword.co.uk/City-of-London-at-War-193945-Paperback/p/17299
Periodical MLA Bibliography Examples
Here’s the style format for magazines, journals, and newspapers. For online articles, add the URL at the end of the listing.
For magazines and journals:
Last Name, First Name. “Title: Subtitle.” Name of Journal , volume number, issue number, Date of Publication, First Page Number–Last Page Number.
- Bell, Amy. “Landscapes of Fear: Wartime London, 1939–1945.” Journal of British Studies , vol. 48, no. 1, pp. 153–175. www.jstor.org/stable/25482966
When citing newspapers, include the page number/s for print editions or the URL for online articles.
Last Name, First Name. “Title of article.” Newspaper title. Page number/s. Year, month day. Page number or URL
- Blakemore, Erin. “Researchers Track Down Two Copies of Fossil Destroyed by the Nazis.” The Washington Post. 2022, Nov. 12. www.washingtonpost.com/science/2022/11/12/ichthyosaur-fossil-images-discovered/
Electronic MLA Bibliography Examples
Last Name, First Name. Year. “Title.” Month Day, Year published. URL
- Wukovits, John. 2023. “A World War II Survivor Recalls the London Blitz.” January 30, 2023. https://britishheritage.com/history/world-war-ii-survivor-london-blitz
Website. n.d. “Title.” Accessed Day Month Year. URL.
- Imperial War Museum. n.d. “Growing Up in the Second World War.” Accessed May 9, 2023. https://www.iwm.org.uk/history/growing-up-in-the-second-world-war.
Here’s how to list YouTube and other online videos.
Creator, if available. “Title of Video.” Website. Uploaded by Username, Day Month Year. URL.
- “How did London survive the Blitz during WW2? | Cities at war: London | War stories.” YouTube . Uploaded by War Stories, 15 Jan. 2023. youtu.be/uwY6JlCvbxc.
For more information on writing MLA style bibliographies, see the MLA Style website.
MLA Bibliography (Works Cited) Example Pages

Source: The Visual Communication Guy
More MLA example pages:
- Writing Commons Sample Works Cited Page
- Scribbr MLA Works Cited Sample Page
- Montana State University MLA Works Cited Page
Chicago Manual of Style Bibliography Examples
The Chicago Manual of Style (sometimes called “Turabian”) actually has two options for citing reference material : Notes and Bibliography and Author-Date. Regardless of which you use, you’ll need a complete detailed list of reference items at the end of your paper. The examples below demonstrate how to write that list.
How To Write a Bibliography Using The Chicago Manual of Style

Source: South Texas College
Here are some general notes on writing a Chicago -style bibliography:
- You may title it “Bibliography” or “References.” Center this title at the top of the page and add two blank lines before the first entry.
- Left-align each entry, with a hanging half-inch indent for subsequent lines of each entry.
- Single-space each entry, with a blank line between entries.
- Include the “http://” or “https://” at the beginning of URLs.
Books and E-Books Chicago Manual of Style Bibliography Examples
For books, Chicago -style reference list entries use this format. (For print books, leave off the information about how the book was accessed.)
Last Name, First Name Middle Name. Title . City of Publication: Publisher, Date. How e-book was accessed.
- Wynn, Stephen. City of London at War 1939–45 . Yorkshire: Pen & Sword Military, 2020. Kindle edition.
Periodical Chicago Manual of Style Bibliography Examples
For journal and magazine articles, use this format.
Last Name, First Name. Year of Publication. “Title: Subtitle.” Name of Journal , Volume Number, issue number, First Page Number–Last Page Number. URL.
- Bell, Amy. 2009. “Landscapes of Fear: Wartime London, 1939–1945.” Journal of British Studies, 48 no. 1, 153–175. https://www.jstor.org/stable/25482966.
When citing newspapers, include the URL for online articles.
Last Name, First Name. Year of Publication. “Title: Subtitle.” Name of Newspaper , Month day, year. URL.
- Blakemore, Erin. 2022. “Researchers Track Down Two Copies of Fossil Destroyed by the Nazis.” The Washington Post , November 12, 2022. https://www.washingtonpost.com/science/2022/11/12/ichthyosaur-fossil-images-discovered/.
Electronic Chicago Manual of Style Bibliography Examples
Last Name, First Name Middle Name. “Title.” Site Name . Year, Month Day. URL.
- Wukovits, John. “A World War II Survivor Recalls the London Blitz.” British Heritage. 2023, Jan. 30. britishheritage.com/history/world-war-ii-survivor-london-blitz.
“Title.” Site Name . URL. Accessed Day Month Year.
- “Growing Up in the Second World War.” Imperial War Museums . www.iwm.org.uk/history/growing-up-in-the-second-world-war. Accessed May 9, 2023.
Creator or Username. “Title of Video.” Website video, length. Month Day, Year. URL.
- War Stories. “How Did London Survive the Blitz During WW2? | Cities at War: London | War Stories.” YouTube video, 51:25. January 15, 2023. https://youtu.be/uwY6JlCvbxc.
For more information on writing Chicago -style bibliographies, see the Chicago Manual of Style website.
Chicago Manual of Style Bibliography Example Pages

Source: Chicago Manual of Style
More Chicago example pages:
- Scribbr Chicago Style Bibliography Example
- Purdue Online Writing Lab CMOS Bibliography Page
- Bibcitation Sample Chicago Bibliography
Now that you know how to write a bibliography, take a look at the Best Websites for Teaching & Learning Writing .
Plus, get all the latest teaching tips and ideas when you sign up for our free newsletters .

You Might Also Like

How To Use Sentence Stems (Plus 60+ Examples for Every Subject)
Sentence stems help students ... Continue Reading
Copyright © 2023. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
WRT 254 - Advanced Professional Communication - PimaOnline: APA Annotated Bibliography
- Multimodal Resources
- Find Background Information
- Find Articles
- APA Annotated Bibliography
- Write & Cite This link opens in a new window
What is an Annotated Bibliography? Why do I have to do one?
An annotated bibliography is composed of an APA citation of a source followed by notes and commentary about that source. The word “annotate” means “to make critical or explanatory notes” and the word “bibliography” means “a list of sources”--so, an annotated bibliography is a list of sources combined with notes about each source.
Creating an annotated bibliography helps you to become a better researcher and focus your research topic. By starting the research process early (before your extended proposals are due), you can make sure that you've picked a topic that will yield enough information to write your proposal. You'll also read the articles you find and write about them, which ensures that you've found information that is relevant to your topic. Annotated bibliographies are great preparation for major research assignments!
Formatting an Annotated Bibliography
Formatting your annotated bibliography is the same as formatting an APA reference list. You use the same author-date style and place the elements in the same order. Here’s a quick rundown of the guidelines:
- Right-aligned page number
- Running header (Optional)
- One-inch margins
- Double spaced
- The title “Annotated Bibliography” centered
- Hanging indent for second and subsequent lines of the citation
- Annotated Bibliography Template You may use this template as a model for creating your annotated bibliography. Go to "File" and then "Make a Copy" to copy a version you can edit.
APA Annotated Bibliography Example

- View larger image here Image from Bibliography.com's "APA Annotated Bibliograpy Guide with Examples"
APA Format Annotated Bibliography
Organizing an annotated bibliography.
An annotated bibliography is organized in the same manner as the reference list. Alphabetize using the letter by letter system by the author’s last name.
Creating an APA Citation
After your APA annotated bibliography is formatted, you create a citation for each entry. The composition of your citation varies based on the type of source you are using. For example, a book citation in APA is different than a journal citation. Therefore, when creating your citation, use the format APA has designated for that specific source

How to Write an Annotation
The first step to creating your APA annotations is reading the source and making notes about the relevant information it contains. Once you've read the source, create your annotation using the guidelines below: • 2 to 4 sentences to summarize the main idea(s) of the source. - What are the main arguments? - What is the point of this book/article? - What topics are covered? • 1 or 2 sentences to assess and evaluate the source. - How does it compare with other sources in your bibliography? - Is this information reliable? current? - Is the author credible? have the background to write on this topic? - Is the source objective or biased? • 1 or 2 sentences to reflect on the source. - Was this source helpful to you? Why? - How can you use this source for your research project? - Has it changed how you think about your topic?
The length of your bibliographic entry depends on your instructor’s guidelines but typically is about 100-300 words.
- << Previous: Find Articles
- Next: Write & Cite >>
- Last Updated: Apr 8, 2024 2:54 PM
- URL: https://libguides.pima.edu/WRT254
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Annotated Bibliography Samples

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
This handout provides information about annotated bibliographies in MLA, APA, and CMS.
Below you will find sample annotations from annotated bibliographies, each with a different research project. Remember that the annotations you include in your own bibliography should reflect your research project and/or the guidelines of your assignment.
As mentioned elsewhere in this resource, depending on the purpose of your bibliography, some annotations may summarize, some may assess or evaluate a source, and some may reflect on the source’s possible uses for the project at hand. Some annotations may address all three of these steps. Consider the purpose of your annotated bibliography and/or your instructor’s directions when deciding how much information to include in your annotations.
Please keep in mind that all your text, including the write-up beneath the citation, must be indented so that the author's last name is the only text that is flush left.
Sample MLA Annotation
Lamott, Anne. Bird by Bird: Some Instructions on Writing and Life . Anchor Books, 1995.
Lamott's book offers honest advice on the nature of a writing life, complete with its insecurities and failures. Taking a humorous approach to the realities of being a writer, the chapters in Lamott's book are wry and anecdotal and offer advice on everything from plot development to jealousy, from perfectionism to struggling with one's own internal critic.
In the process, Lamott includes writing exercises designed to be both productive and fun. Lamott offers sane advice for those struggling with the anxieties of writing, but her main project seems to be offering the reader a reality check regarding writing, publishing, and struggling with one's own imperfect humanity in the process. Rather than a practical handbook to producing and/or publishing, this text is indispensable because of its honest perspective, its down-to-earth humor, and its encouraging approach.
Chapters in this text could easily be included in the curriculum for a writing class. Several of the chapters in Part 1 address the writing process and would serve to generate discussion on students' own drafting and revising processes. Some of the writing exercises would also be appropriate for generating classroom writing exercises. Students should find Lamott's style both engaging and enjoyable.
In the sample annotation above, the writer includes three paragraphs: a summary, an evaluation of the text, and a reflection on its applicability to his/her own research, respectively.
For information on formatting MLA citations, see our MLA 9th Edition (2021) Formatting and Style Guide .
Sample APA Annotation
Ehrenreich, B. (2001). Nickel and dimed: On (not) getting by in America . Henry Holt and Company.
In this book of nonfiction based on the journalist's experiential research, Ehrenreich attempts to ascertain whether it is currently possible for an individual to live on a minimum-wage in America. Taking jobs as a waitress, a maid in a cleaning service, and a Walmart sales employee, the author summarizes and reflects on her work, her relationships with fellow workers, and her financial struggles in each situation.
An experienced journalist, Ehrenreich is aware of the limitations of her experiment and the ethical implications of her experiential research tactics and reflects on these issues in the text. The author is forthcoming about her methods and supplements her experiences with scholarly research on her places of employment, the economy, and the rising cost of living in America. Ehrenreich’s project is timely, descriptive, and well-researched.
The annotation above both summarizes and assesses the book in the citation. The first paragraph provides a brief summary of the author's project in the book, covering the main points of the work. The second paragraph points out the project’s strengths and evaluates its methods and presentation. This particular annotation does not reflect on the source’s potential importance or usefulness for this person’s own research.
For information on formatting APA citations, see our APA Formatting and Style Guide .
Sample Chicago Manual of Style Annotation
Davidson, Hilda Ellis. Roles of the Northern Goddess . London: Routledge, 1998.
Davidson's book provides a thorough examination of the major roles filled by the numerous pagan goddesses of Northern Europe in everyday life, including their roles in hunting, agriculture, domestic arts like weaving, the household, and death. The author discusses relevant archaeological evidence, patterns of symbol and ritual, and previous research. The book includes a number of black and white photographs of relevant artifacts.
This annotation includes only one paragraph, a summary of the book. It provides a concise description of the project and the book's project and its major features.
For information on formatting Chicago Style citations, see our Chicago Manual of Style resources.

- California State University, Northridge
HIST 301: The Historian’s Craft: Reading, Research and Writing History
- Annotated Bibliography
- Finding Articles
- Using Newspapers
- Historiographical Essay Assignments
- Research Prospectus Assignments
- What is a Primary Source?
- Colonial Period/Revolutionary War Sources
- California History Digital Resources
- Online Archive Resources
- Primary Source Voices
- U.S. History Government Document Sources
- Tips for Finding Books
- Search Strategies
- Search Tips
- Citing Your Sources
- Ask A Librarian
Creating Annotated Bibliographies
An annotated bibliography is a list of sources (books, articles, websites, etc.) with short paragraph about each source. An annotated bibliography is sometimes a useful step before drafting a research paper, or it can stand alone as an overview of the research available on a topic.
Each source in the annotated bibliography has a citation - the information a reader needs to find the original source, in a consistent format to make that easier. These consistent formats are called citation styles. NOTE: For History majors and historians the citation style format of choice is The Chicago Manual of Style or Turabian . The other most common citation styles are MLA (Modern Language Association) for humanities, and APA (American Psychological Association) for social sciences.
Annotations are about 4 to 6 sentences long (roughly 150 words), and address:
- Main focus or purpose of the work
- Usefulness or relevance to your research topic
- Special features of the work that were unique or helpful
- Background and credibility of the author
- Conclusions or observations reached by the author
- Conclusions or observations reached by you
Annotations versus Abstracts
Many scholarly articles start with an abstract, which is the author's summary of the article to help you decide whether you should read the entire article. This abstract is not the same thing as an annotation. The annotation needs to be in your own words, to explain the relevance of the source to your particular assignment or research question.
Compiling an Annotated Bibliography in Chicago Style (Red Deer Library & More)
Visit this helpful guide to learn more about how to approach building your annotated bibliography. The authors of this guide point out that, "An annotated bibliography is the same as a “regular” bibliography (also known as a Works Cited or References list), with the addition of annotations (short paragraphs about each source). Two types of annotated bibliographies are the most common:
- Descriptive: annotations describe the content of a source
- Evaluative: annotations describe AND critically evaluate the source"
Red Deer Library
- https://rdc.libguides.com/chicago/annotated
- They also have posted formatting assistance from this link .
UCLA History Department (REVISED) Annotated Bibliography Assistance These guidelines may help you write an annotated bibliography for a history class. Your professor might provide specific guidelines that provide more detail than the information here. Always follow your professor’s instructions.
Annotated Bibliography video
- << Previous: Citing Your Sources
- Next: Ask A Librarian >>
- Last Updated: Jan 11, 2024 11:42 AM
- URL: https://libguides.csun.edu/hist301
Document Reader
Report ADA Problems with Library Services and Resources

Research Instruction
- Classroom Activities
- Assignment Design
Let's chat!

An Evolving Resource
These lists will be constantly in flux as I come across new ideas and/or links break. If you have activities and assignments related to research and information literacy and are willing to share them, please let me know! I'd love to add them to this list.
Assignment Design Ideas
Jump to: Alternative research assignment ideas
Think twice about source type/search tool requirements
Often, these requirements ("Only use scholarly articles," "Don't use Google," "You must have 1 print book") seem arbitrary to students. Absent context, these requirements can cause students undue stress and anxiety--especially if they have trouble identifying source types in the first place.
- Ask yourself, "What am I actually trying to get students to learn about research by requiring the use of [specific types of sources]?"
- Discuss how and why different kinds of information are produced
- Discuss what kinds of sources are considered authoritative in your field, and why
- Take it a step further and consider what voices might be left out if students were only allowed to use one type of source (such as scholarly articles)
- Library search tools (the catalog, databases) contain many different types of sources
- Include discussion about the differences between library search tools and search engines like Google
Annotated bibliography assignments
Annotated bibliographies are great for scaffolding research projects. They help students practice source evaluation and summary.
- Hunter College: Annotated Bibliography Activities Includes tips for getting students to think more critically about their sources and some ideas for slight variations on annotated bibs.
Provide an initial set of sources
This can help students get a sense of what kinds of information (what types of sources, what perspectives) exist for a topic.
- For sources with bibliographies, discuss how to use a source to find more like it
- When everyone's looked at the same set of sources, it's easier to have students work in groups or practice synthesizing/evaluating as a whole class--before they have to do it on their own in a research assignment
Require an initial bibliography of more sources than they'll actually use
Scaffold the process of choosing and using sources by having students initially gather more resources than they're required to cite in the final version of their project. Then have them choose the sources they'll actually use from this larger list.
- This helps with "satisficing" -- when students use the first few sources they encounter that they consider "good enough" and stop there
- This also gives you the opportunity to provide feedback on sources and citations, and gives students one more opportunity to practice citations
- Due first: working bibliography of 10 sources
- Due next: annotated bibliography of 5-7 sources that will actually be cited in the final project
- Your students will use better sources, and you'll get better projects
Alternative research assignments
Students often appreciate more creative format options for research projects. If you're sick of grading research papers, imagine how sick your students are of writing them... Try:
- Curation assignments--assignments that focus on storytelling, creating personal learning environments, or designing exhibits
- Search process assignments--have students write (and/or present) a reflection on the process of searching for and evaluating information on a topic
- Multimodal or audiovisual assignments--have students create podcasts, documentaries, websites, or something that combines mediums
- Non-disposable assignments--assignments with a lifespan beyond the due date (community partnerships, materials that are shared/used campus-wide, public writing like Wikipedia editing assignments)
- Grant proposals are also a fun option
- History of scholarship assignments--students trace the scholarly conversation on a particular topic back to a certain date or as far back as they can get, then write or present on how scholarship on the topic has changed over time
- Alternative Information Literacy Assignment Ideas An extensive list of assignment ideas complied by librarians Faith Rusk and Daphna Atias (U of DC at the time the list was created).
More Links & Inspiration
- CORA: Community of Online Research Assignments An open repository of reusable and adaptable lesson plans and assignments related to research.
- << Previous: Classroom Activities
- Last Updated: Aug 25, 2023 1:26 PM
- URL: https://libguides.uj.edu/instruction
- CSN Libraries
- Library Guides
- Course Guides
ENG 102 - Anderson
- Annotated Bibliography / Research Paper
- Useful Databases at CSN Libraries
- Citing in MLA
What is an Annotated Bibliogrphy?
An annotated bibliography is a list of citations followed by a brief (usually about 150 words) evaluative paragraph called an annotation. Essentially, it is a works cited or reference list with additional information about each source. Make sure to follow the citation format your instructor requires! (MLA, APA, Chicago, etc.)
Your annotation can include a sentences answering the following questions:
- Summarize : Some annotations merely summarize the source. What are the main arguments? What is the point of this book or article? What topics are covered? If someone asked what this article/book is about, what would you say? The length of your annotations will determine how detailed your summary is.
- Assess : After summarizing a source, it may be helpful to evaluate it. Is it a useful source? How does it compare with other sources in your bibliography? Is the information reliable? Is this source biased or objective? What is the goal of this source?
- Reflect : Once you've summarized and assessed a source, you need to ask how it fits into your research. Was this source helpful to you? How does it help you shape your argument? How can you use this source in your research project? Has it changed how you think about your topic?
This information was adapted from Purdue Owl. To learn more about annotated bibliographies, visit the Purdue Owl Annotated Bibliography Guide .
Sample Annotated Citation
- Sample MLA Annotated Citation
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Useful Databases at CSN Libraries >>
- Last Updated: Apr 8, 2024 9:05 AM
- URL: https://libguides.csn.edu/anderson

CPS Online Library Research Guide (UNH Manchester Library): Developing Effective Library Research Assignments
- Home & Table of Contents
- Different Types of Information
- The Savvy Information Consumer
- Primary & Secondary Sources
- Periodical Literature
- Peer Review
- Research Glossary
- Business Research Databases
- Understanding the Assignment
- Preliminary Considerations
- 7 Steps to Completing a Research Assignment
- Define the Topic
- Find & Evaluate Your Sources
- Research Integrity & Citing Your Sources
- Searching for Information
- Evaluating Information
- How to Read an Academic Journal Article This link opens in a new window
- Evaluating Social Media Sources
- Writing Your Research Paper
- Create a Literature Review
- Summarize an Article
- How to Write an Abstract
- How to Write a Book Review
- How to Do an Annotated Bibliography
- Finding Professional Organizations
- Find Key Journals in Your Field of Study
- Find Peer-Reviewed Articles
- Write a Research Paper Proposal
- Research a Company This link opens in a new window
- Citing Your Sources
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- NHCUC Libraries
- Other Types of Research
- Academic Libraries in NH
- Government Documents
- Using Google for Academic Research
- Information Literacy
- Developing Effective Library Research Assignments
- Using Permalinks
- Primary Source Websites
Introductory Library Research Assignments
Develop introductory assignments that allow students to practice basic research skills:.
- locate, summarize, analyze sources
- develop an annotated bibliographies
- create a research log or journal
- edit "Wikipedia" articles
- examine coverage of a controversial topic in several sources
- brainstorm key terms to use in order to find information on a given topic
- compare internet and database searches on a precise search topic; compare the findings
Spend some class time discussing the research process
- how information is structured
- what resources are appropriate at different stages and complexity of a research assignment.
Use a series of small assignments independent of the final project that are designed to familiarize students with wide variety of information resources, practice using the GSC library resources, and articulate their own best research practices.
Characteristics of an Effective Course-Related Research Assignment
- Has a specific, understood purpose.
- Relates to some aspect of course subject matter or learning objectives.
- Leads to increased understanding of a subject or the process of locating information related to a subject.
- Makes students aware of the variety of information sources and formats available (e.g., print, electronic, video, etc).It
- Teaches students to select and evaluate quality information sources appropriate to their topics.
- Reinforces habits of ethical scholarship.
Schedule an in-class or online workshop with the GSC Librarian
Effective library research assignments, some guidance on library research assignments.
Make sure you check with the GSC Librarian before you assign a research project. This allows time for the Librarian to plan how best to link the student with appropriate and available resources.
- If the assignment requires the use of specific sources, give the students a list of them and make arrangements with the GSC Librarian to guarantee that students will have the support and guidance they need.
- If it involves the use of complex sources or unfamiliar research strategies, your students will need to be oriented to these- schedule a customized library instruction session with the GSC Librarian.
- If students have difficulty understanding what they are supposed to do, they will have trouble doing it. Give assignments in writing (rather than orally). Use correct and unambiguous terminology. Students tend to interpret research assignments literally and are easily confused by terms that they don't understand or a librarian cannot interpret definitively.
- Examples of common research assignment problems are: Some instructors differentiate between magazines and journals, while others use the terms interchangeably. It is very helpful to use the terms academic journal or periodical. This is consistent with the terminology used in the student's Research Guide .
- It is very helpful for you to also know how to use the GSC Discovery Service and how they might access additional databases at other NHCUC libraries.
- Do your students know what the phrases "peer-reviewed journal" and "primary vs. secondary sources" mean in your discipline? Use full and current titles of journals; avoid abbreviations and superseded titles.
- Check your assignments regularly so that you are not asking your students to use outdated modes of access. Contact the GSC Librarian for assistance as needed .
- Reasonable Time Frame - Do the assignment yourself to see how long it takes before you decide how long students need to do it, allowing for their limited perspective and inexperience and for movement of materials.
- Pitfalls to Avoid : Assuming most students know the language of research . Do not assume that your students know what an annotated bibliography is, the difference between APA or MLA format, or other terms that you might be very familiar with. The Research Glossary is helpful as well as full explanations and examples as needed. Assuming most students know the basics Do not assume that your students have had prior experience using an academic library, a prior orientation to a library, or that their general orientation is relevant to your assignment. Requiring resources not available .
- A scavenger hunt is one of the least effective research assignments you can give. It lacks a clear purpose, does not teach students to do meaningful library research, and may be frustrating. Librarians rather than students frequently end up locating the answers. If, in spite of these warnings, you wish nonetheless to use a scavenger hunt, Contact the GSC Librarian for assistance in building a meaningful, workable assignment.
Help Your Students Avoid Plagiarism
Most plagiarism at GSC is the result of the student not understanding the proper use of resources and how to correctly cite the sources they use. The Librarian in partnership with other faculty will work with students and provide resources for students to develop research skills aimed at avoiding these problems.
Here are a few suggestions:
- Spend some time explaining what constitutes plagiarism in its various forms.
- Teach students how to paraphrase and how to cite sources.
- Give students a set of topics from which to choose and change topics frequently.
- Do not allow last-minute topic changes.
- Require students to submit annotated bibliographies, research notes, outlines, or drafts.
- Require precise formatting for papers according to teh correct manual of style for your discipline.
- Give pop quiz on paper contents.
- Require an oral report in addition to paper.
- Assign narrowly focused topics, rather than broad, general ones.
- Use very current topics to lessen chance of papers being available on the internet.
- Structure the writing assignment as a series of steps with checkpoints.
- Check the working bibliography early in the assignment.
- Require all resources to be current, no earlier than the last 5 years.
Adapted from: Ann Lathrop and Kathleen Foss, Student Cheating and Plagiarism in the Internet Era . Bernard Whitley, Jr. and Patricia Keith-Spiegel, Academic Dishonesty .
Contact the Library
Library Login Information Email: [email protected]
Phone: (603)822-LIBR (5427)
Chat: get assistance after-hours.
Library Chat Hours: Monday-Friday from midnight-9am & 5pm-midnight. All day Saturdays and Sundays.
- << Previous: Information Literacy
- Next: Using Permalinks >>
- Last Updated: Apr 9, 2024 2:30 PM
- URL: https://libraryguides.unh.edu/CPSonlineLibraryResearch
Action Research Case Study Proposal - Part 1 Data and Annotated Bibliography Assignment
Liberty University *
Linguistics
Apr 3, 2024
Uploaded by MinisterThunderLark31 on coursehero.com
- Access to all documents
- Unlimited textbook solutions
- 24/7 expert homework help

ENGL 1102 Worozbyt Spring 2024 : Assignment
- Library Catalog
- MLA Citation Help
- Tutoring at Decatur
Literature Research Assignment
Research Essay Topics
Compose in MLA format a research essay of at least 1000 words, using a minimum of four secondary sources. (The OED is a primary, not a secondary, source, but you are encouraged to use it.) Source material must be drawn from books and articles located in Galileo databases or the GSU library. Use secondary critical resources to support and complexify your arguments and points. The task is textual analysis, that and that alone. The supplemental lectures I have been posting are pretty good examples of what I am looking for. This is a research project, but I am most interested in seeing you display your own skill at critical thinking and analysis. Sources not found in Galileo or the GSU library will not count toward the research requirement, and you are discouraged from using them. That said, Wikipedia entries often have links at the bottom to legitimate, academic sources. Feel free to use Wikipedia as a launching point for research, even though Wikipedia entries themselves cannot be used, as they are not vetted. Do not summarize plots or provide biographies of the author. This essay is not to be about the author; it is to be about the text.
The Caveats:
You are obliged to familiarize yourself with proper MLA formatting and citation. This information is found in my Course Content, online at OWL, on Youtube, or simply by Googling “MLA citation.” By now I expect professionally clean and error-free copy, with no typos or mechanical errors. Papers not following these guidelines will be penalized accordingly. By now you have had a full semester of training in proper citation and format. Failure to format the body of your essay in MLA results a penalty up to twenty points, depending on severity. Failure to provide sufficient, relevant source material results in a fifteen-point penalty per missing source. Failure to properly acknowledge the use of secondary material constitutes plagiarism, whether intentional or not, and will result in no credit given, since I cannot distinguish between what writing is yours and what is not.. Make sure you quote and cite, both internally and in your works cited page.
Tennesse Williams, The Glass Menagerie:
1. Discuss the play’s presentation (and subversion) of traditional family and gender roles. How does the assumption and subsequent disruption of those roles define and control Laura’s destiny? How does having a brother for a father and a sister for a mother determine the outcome of Laura’s seduction by Jim?
2. Why does Williams’ reject conventional “realistic” stage drama? Analyze the stage directions and locate at least two echoes within the range of Tom’s dialogue and action. Are the lyrical and poetical qualities of the stage directions in (literary)/dramatic conflict with Tom’s desire to create a unified self, a “character” who characters, through writing poetry? Explain.
3. Consider the use of names and the function of naming in the play. How do names advance and complicate the major arguments and themes in The Glass Menagerie. Remember that a title is a “name” as well, and that to be a caller, gentleman or otherwise, is to be a namer. Needless to say, you should name the major arguments and themes.
4. Explore Williams’ concept of the stage as defined by the text of the play. How does our author manipulate the space and time of the stage? The first questions to wrestle with are: What is a stage? Where is the stage? When is the stage? Then: how does the playwright accomplish his redefinition of the conventional boundaries? Be specific, analyzing selected text passages.
5. Analyze the similarities and differences in the text of Williams’ play and the film of it you watched. This should not be simply a compare/contrast essay, but a thorough investigation of the way the two different media (reading and watching) are anticipated and dealt with by the play itself. The Production Notes and the corresponding echoes in the play would be a good place to start.
Alice Walker, Everyday Use:
1. “Everyday Use” presents us with the clash between personal and cultural history. Walker manages in this short work to interweave them and to produce a dialectic (a “conversation,” if you will) between the seemingly competing histories. Track this interweaving and explain how the story resolves the apparent contradictions between the two.
2. Consider Dee and Maggie as expressions of two sides to the mother’s character. Investigate and discuss how Walker creates these characters and how she makes them come so vibrantly alive in this story. Do not neglect in your analysis to discuss the significance of the mother’s dream.
3. Landscape and objects play a big role in this story. Discuss the idea of “inside” and “outside” in the story, paying careful and close attention to the way objects are depicted and used in the story to generate and facilitate the story’s major themes and ideas
Final Items:
Be generous with quotations, and never paraphrase the text or your secondary source material. Also, make absolutely sure you reproduce the text exactly as it appears in the original. When you change the words you change the meaning; when you change the meaning your argument fails. Likewise, it is always better to overquote than underquote. Analysis based on a brief, out of context phrase is much weaker than analysis of an entire paragraph or sentence.
Whether you choose Williams’ or Walker’s text to research, make sure you do the research before you start to write. Reading articles by vetted, published critics will help you deepen and organize your thoughts. Writing an essay and then going hunting for quotes that suit your wants will always lead to a poor research essay
- << Previous: Welcome!
- Next: Library Catalog >>
- Last Updated: Apr 10, 2024 3:31 PM
- URL: https://research.library.gsu.edu/ENGL1102WorozbytSpring2024
- Study Guides
- Homework Questions
Assignment 1Annotated Bibliography Upload

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Specific types of enumerative bibliographies used for research works include: National bibliography. A national bibliography groups sources published in a specific region or nation. In many cases, these bibliographies also group works according to the time period during which they were published. ... With certain assignments, like an essay ...
Bibliography Entry for a Book. A bibliography entry for a book begins with the author's name, which is written in this order: last name, comma, first name, period. After the author's name comes the title of the book. If you are handwriting your bibliography, underline each title. If you are working on a computer, put the book title in ...
An APA format bibliography lists all of the sources that might be used in a paper. A bibliography can be a great tool to help you keep track of information during the research and writing process. In some cases, your instructor may require you to include a bibliography as part of your assignment.
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that includes a short descriptive text (an annotation) for each source. It may be assigned as part of the research process for a paper, or as an individual assignment to gather and read relevant sources on a topic. Scribbr's free Citation Generator allows you to easily create and manage ...
Formatting a Harvard style bibliography. Sources are alphabetised by author last name. The heading 'Reference list' or 'Bibliography' appears at the top. Each new source appears on a new line, and when an entry for a single source extends onto a second line, a hanging indent is used: Harvard bibliography example.
An annotated bibliography is a combination of the words "annotation" and "bibliography." An annotation is a set of notes, comments, or critiques. A bibliography is list of references that helps a reader identify sources of information. An annotated bibliography is a list of references that not only identifies the sources of information but also ...
Your method for selecting which sources to annotate depends on the purpose of the assignment and the research problem you are investigating. For example, if the course is on international social movements and the research problem you choose to study is to compare cultural factors that led to protests in Egypt with the factors that led to ...
The reference list is an alphabetical list of all the sources that you cited in the text of your assignment. A bibliography is a separate list, presented in the same format as a reference list, however, it includes all the sources you consulted in the preparation of your assignment, not just those you cited.
Annotated bibliographies can be part of a larger research project, or can be a stand-alone report in itself. Annotation versus abstracts. An abstract is a paragraph at the beginning of the paper that discusses the main point of the original work. They typically do not include evaluation comments. Annotations can either be descriptive or evaluative.
Learn how to write and format an annotated bibliography in APA Style (7th ed.). Conducting research and documenting your findings is an essential part of the academic writing process. ... There are several ways to write annotations depending on the purpose or the requirements of the assignment or research. Common approaches to writing ...
An annotated bibliography is a list of citations (references) to books, articles, and documents followed by a brief summary, analysis or evaluation, usually between 100-300 words, of the sources that are cited in the paper. This summary provides a description of the contents of the source and may also include evaluative comments, such as the ...
An effective research assignment targets specific skills, for example, the ability to trace a scholarly argument through the literature or the ability to organize consulted resources into a bibliography. ... Ideas for alternative research assignments. Assign an annotated bibliography in which students identify primary and secondary sources ...
A bibliography usually just includes the bibliographic information (i.e., the author, title, publisher, etc.). An annotation is a summary and/or evaluation. Therefore, an annotated bibliography includes a summary and/or evaluation of each of the sources. Depending on your project or the assignment, your annotations may do one or more of the ...
Either way, the sources listed on an annotated bibliography should center on a topic or focus; if the annotated bibliography documents research efforts related to an associated assignment, the focus will reflect the author's thesis, research questions (questions that a study seeks to answer), or research objectives.
An annotated bibliography is one way to present research, and can be used as a cumulative assignment, or a precursor to your actual research paper. A good annotated bibliography will provide a variety of sources that met all your research needs—background, evidence, argument, and method. In other words, you should be able to take your ...
An annotated bibliography is a list of sources (books, articles, websites, etc.) with short paragraph about each source. An annotated bibliography is sometimes a useful step before drafting a research paper, or it can stand alone as an overview of the research available on a topic. Each source in the annotated bibliography has a citation - the ...
The purpose is to: An annotated bibliography is sometimes given as an assessment task at the beginning of a research project, or, as an assessment task in the lead up to an essay, to encourage you to survey and reflect on what has already been discovered about your topic. However, it might also be given as a stand-alone assignment to develop ...
Research Proposal and Annotated Bibliography Most research essays involve two particular documents that help guide, manage, and report on the on-going research process. ... Annotated bibliographies are thus a common assignment in courses that use research writing, even in alternate forms, such as the common high-school assignment of "note ...
Here are some general notes on writing an APA reference list: Title your bibliography section "References" and center the title on the top line of the page. Do not center your references; they should be left-aligned. For longer items, subsequent lines should use a hanging indent of 1/2 inch.
The word "annotate" means "to make critical or explanatory notes" and the word "bibliography" means "a list of sources"--so, an annotated bibliography is a list of sources combined with notes about each source. Creating an annotated bibliography helps you to become a better researcher and focus your research topic.
Remember that the annotations you include in your own bibliography should reflect your research project and/or the guidelines of your assignment. As mentioned elsewhere in this resource, depending on the purpose of your bibliography, some annotations may summarize, some may assess or evaluate a source, and some may reflect on the source's ...
The annotation needs to be in your own words, to explain the relevance of the source to your particular assignment or research question. Compiling an Annotated Bibliography in Chicago Style (Red Deer Library & More) ... "An annotated bibliography is the same as a "regular" bibliography (also known as a Works Cited or References list), ...
Curation assignments--assignments that focus on storytelling, creating personal learning environments, or designing exhibits. Search process assignments--have students write (and/or present) a reflection on the process of searching for and evaluating information on a topic. Multimodal or audiovisual assignments--have students create podcasts ...
An annotated bibliography includes a summary and evaluation of each source. These annotations are written in paragraph form and for the purposes of this class should include the following information: 1. an explanation of the main purpose of the source. 2. a short summary of key findings or arguments of the source.
An annotated bibliography is a list of citations followed by a brief (usually about 150 words) evaluative paragraph called an annotation. Essentially, it is a works cited or reference list with additional information about each source. Make sure to follow the citation format your instructor requires!
Use a series of small assignments independent of the final project that are designed to familiarize students with wide variety of information resources, practice using the GSC library resources, and articulate their own best research practices. Characteristics of an Effective Course-Related Research Assignment. Has a specific, understood purpose.
The purpose of this assignment is to demonstrate progress in compiling research and to indicate a methodology for organizing research sources. Include the following in your annotated bibliography. For each source: Cite the source in current APA Style. The citations should be organized in alphabetical order by the author as in an APA Reference list.
Action Research Case Study: Proposal - Part 1: Data and Annotated Bibliography Assignment Required Items Responses Volunteer Teacher Annette Rowe Kindergarten Teacher All Subjects Oakwood-Windsor Elementary School Classroom Experience: 6 Years Reviewed Data Formative Data: ESGI ESGI is a resource to analyze and interpret data, personalize instruction, communicate progress to parents and ...
Literature Research Assignment . Research Essay Topics . The Task: Compose in MLA format a research essay of at least 1000 words, using a minimum of four secondary sources. (The OED is a primary, not a secondary, source, but you are encouraged to use it.) Source material must be drawn from books and articles located in Galileo databases or the ...
Intro to Annotated Bibliography 5 plays in promoting and cultivating positive interpersonal relationships at work and in the forging of continuing service relationships. Paragraph Annotation: Liao, H. & Chuang, A. (2007) Liao and Chuang (2007) investigated the effects of transformational leadership on service employees and service organizational climate in a field-based, three-level ...