

What Is Creative Writing? (Ultimate Guide + 20 Examples)
Creative writing begins with a blank page and the courage to fill it with the stories only you can tell.
I face this intimidating blank page daily–and I have for the better part of 20+ years.
In this guide, you’ll learn all the ins and outs of creative writing with tons of examples.
What Is Creative Writing (Long Description)?
Creative Writing is the art of using words to express ideas and emotions in imaginative ways. It encompasses various forms including novels, poetry, and plays, focusing on narrative craft, character development, and the use of literary tropes.

Table of Contents
Let’s expand on that definition a bit.
Creative writing is an art form that transcends traditional literature boundaries.
It includes professional, journalistic, academic, and technical writing. This type of writing emphasizes narrative craft, character development, and literary tropes. It also explores poetry and poetics traditions.
In essence, creative writing lets you express ideas and emotions uniquely and imaginatively.
It’s about the freedom to invent worlds, characters, and stories. These creations evoke a spectrum of emotions in readers.
Creative writing covers fiction, poetry, and everything in between.
It allows writers to express inner thoughts and feelings. Often, it reflects human experiences through a fabricated lens.
Types of Creative Writing
There are many types of creative writing that we need to explain.
Some of the most common types:
- Short stories
- Screenplays
- Flash fiction
- Creative Nonfiction
Short Stories (The Brief Escape)
Short stories are like narrative treasures.
They are compact but impactful, telling a full story within a limited word count. These tales often focus on a single character or a crucial moment.
Short stories are known for their brevity.
They deliver emotion and insight in a concise yet powerful package. This format is ideal for exploring diverse genres, themes, and characters. It leaves a lasting impression on readers.
Example: Emma discovers an old photo of her smiling grandmother. It’s a rarity. Through flashbacks, Emma learns about her grandmother’s wartime love story. She comes to understand her grandmother’s resilience and the value of joy.
Novels (The Long Journey)
Novels are extensive explorations of character, plot, and setting.
They span thousands of words, giving writers the space to create entire worlds. Novels can weave complex stories across various themes and timelines.
The length of a novel allows for deep narrative and character development.
Readers get an immersive experience.
Example: Across the Divide tells of two siblings separated in childhood. They grow up in different cultures. Their reunion highlights the strength of family bonds, despite distance and differences.
Poetry (The Soul’s Language)
Poetry expresses ideas and emotions through rhythm, sound, and word beauty.
It distills emotions and thoughts into verses. Poetry often uses metaphors, similes, and figurative language to reach the reader’s heart and mind.
Poetry ranges from structured forms, like sonnets, to free verse.
The latter breaks away from traditional formats for more expressive thought.
Example: Whispers of Dawn is a poem collection capturing morning’s quiet moments. “First Light” personifies dawn as a painter. It brings colors of hope and renewal to the world.
Plays (The Dramatic Dialogue)
Plays are meant for performance. They bring characters and conflicts to life through dialogue and action.
This format uniquely explores human relationships and societal issues.
Playwrights face the challenge of conveying setting, emotion, and plot through dialogue and directions.
Example: Echoes of Tomorrow is set in a dystopian future. Memories can be bought and sold. It follows siblings on a quest to retrieve their stolen memories. They learn the cost of living in a world where the past has a price.
Screenplays (Cinema’s Blueprint)
Screenplays outline narratives for films and TV shows.
They require an understanding of visual storytelling, pacing, and dialogue. Screenplays must fit film production constraints.
Example: The Last Light is a screenplay for a sci-fi film. Humanity’s survivors on a dying Earth seek a new planet. The story focuses on spacecraft Argo’s crew as they face mission challenges and internal dynamics.
Memoirs (The Personal Journey)
Memoirs provide insight into an author’s life, focusing on personal experiences and emotional journeys.
They differ from autobiographies by concentrating on specific themes or events.
Memoirs invite readers into the author’s world.
They share lessons learned and hardships overcome.
Example: Under the Mango Tree is a memoir by Maria Gomez. It shares her childhood memories in rural Colombia. The mango tree in their yard symbolizes home, growth, and nostalgia. Maria reflects on her journey to a new life in America.
Flash Fiction (The Quick Twist)
Flash fiction tells stories in under 1,000 words.
It’s about crafting compelling narratives concisely. Each word in flash fiction must count, often leading to a twist.
This format captures life’s vivid moments, delivering quick, impactful insights.
Example: The Last Message features an astronaut’s final Earth message as her spacecraft drifts away. In 500 words, it explores isolation, hope, and the desire to connect against all odds.
Creative Nonfiction (The Factual Tale)
Creative nonfiction combines factual accuracy with creative storytelling.
This genre covers real events, people, and places with a twist. It uses descriptive language and narrative arcs to make true stories engaging.
Creative nonfiction includes biographies, essays, and travelogues.
Example: Echoes of Everest follows the author’s Mount Everest climb. It mixes factual details with personal reflections and the history of past climbers. The narrative captures the climb’s beauty and challenges, offering an immersive experience.
Fantasy (The World Beyond)
Fantasy transports readers to magical and mythical worlds.
It explores themes like good vs. evil and heroism in unreal settings. Fantasy requires careful world-building to create believable yet fantastic realms.
Example: The Crystal of Azmar tells of a young girl destined to save her world from darkness. She learns she’s the last sorceress in a forgotten lineage. Her journey involves mastering powers, forming alliances, and uncovering ancient kingdom myths.
Science Fiction (The Future Imagined)
Science fiction delves into futuristic and scientific themes.
It questions the impact of advancements on society and individuals.
Science fiction ranges from speculative to hard sci-fi, focusing on plausible futures.
Example: When the Stars Whisper is set in a future where humanity communicates with distant galaxies. It centers on a scientist who finds an alien message. This discovery prompts a deep look at humanity’s universe role and interstellar communication.
Watch this great video that explores the question, “What is creative writing?” and “How to get started?”:
What Are the 5 Cs of Creative Writing?
The 5 Cs of creative writing are fundamental pillars.
They guide writers to produce compelling and impactful work. These principles—Clarity, Coherence, Conciseness, Creativity, and Consistency—help craft stories that engage and entertain.
They also resonate deeply with readers. Let’s explore each of these critical components.
Clarity makes your writing understandable and accessible.
It involves choosing the right words and constructing clear sentences. Your narrative should be easy to follow.
In creative writing, clarity means conveying complex ideas in a digestible and enjoyable way.
Coherence ensures your writing flows logically.
It’s crucial for maintaining the reader’s interest. Characters should develop believably, and plots should progress logically. This makes the narrative feel cohesive.
Conciseness
Conciseness is about expressing ideas succinctly.
It’s being economical with words and avoiding redundancy. This principle helps maintain pace and tension, engaging readers throughout the story.
Creativity is the heart of creative writing.
It allows writers to invent new worlds and create memorable characters. Creativity involves originality and imagination. It’s seeing the world in unique ways and sharing that vision.
Consistency
Consistency maintains a uniform tone, style, and voice.
It means being faithful to the world you’ve created. Characters should act true to their development. This builds trust with readers, making your story immersive and believable.
Is Creative Writing Easy?
Creative writing is both rewarding and challenging.
Crafting stories from your imagination involves more than just words on a page. It requires discipline and a deep understanding of language and narrative structure.
Exploring complex characters and themes is also key.
Refining and revising your work is crucial for developing your voice.
The ease of creative writing varies. Some find the freedom of expression liberating.
Others struggle with writer’s block or plot development challenges. However, practice and feedback make creative writing more fulfilling.
What Does a Creative Writer Do?
A creative writer weaves narratives that entertain, enlighten, and inspire.
Writers explore both the world they create and the emotions they wish to evoke. Their tasks are diverse, involving more than just writing.
Creative writers develop ideas, research, and plan their stories.
They create characters and outline plots with attention to detail. Drafting and revising their work is a significant part of their process. They strive for the 5 Cs of compelling writing.
Writers engage with the literary community, seeking feedback and participating in workshops.
They may navigate the publishing world with agents and editors.
Creative writers are storytellers, craftsmen, and artists. They bring narratives to life, enriching our lives and expanding our imaginations.
How to Get Started With Creative Writing?
Embarking on a creative writing journey can feel like standing at the edge of a vast and mysterious forest.
The path is not always clear, but the adventure is calling.
Here’s how to take your first steps into the world of creative writing:
- Find a time of day when your mind is most alert and creative.
- Create a comfortable writing space free from distractions.
- Use prompts to spark your imagination. They can be as simple as a word, a phrase, or an image.
- Try writing for 15-20 minutes on a prompt without editing yourself. Let the ideas flow freely.
- Reading is fuel for your writing. Explore various genres and styles.
- Pay attention to how your favorite authors construct their sentences, develop characters, and build their worlds.
- Don’t pressure yourself to write a novel right away. Begin with short stories or poems.
- Small projects can help you hone your skills and boost your confidence.
- Look for writing groups in your area or online. These communities offer support, feedback, and motivation.
- Participating in workshops or classes can also provide valuable insights into your writing.
- Understand that your first draft is just the beginning. Revising your work is where the real magic happens.
- Be open to feedback and willing to rework your pieces.
- Carry a notebook or digital recorder to jot down ideas, observations, and snippets of conversations.
- These notes can be gold mines for future writing projects.
Final Thoughts: What Is Creative Writing?
Creative writing is an invitation to explore the unknown, to give voice to the silenced, and to celebrate the human spirit in all its forms.
Check out these creative writing tools (that I highly recommend):
Read This Next:
- What Is a Prompt in Writing? (Ultimate Guide + 200 Examples)
- What Is A Personal Account In Writing? (47 Examples)
- How To Write A Fantasy Short Story (Ultimate Guide + Examples)
- How To Write A Fantasy Romance Novel [21 Tips + Examples)

What is Creative Writing? A Key Piece of the Writer’s Toolbox
Not all writing is the same and there’s a type of writing that has the ability to transport, teach, and inspire others like no other.
Creative writing stands out due to its unique approach and focus on imagination. Here’s how to get started and grow as you explore the broad and beautiful world of creative writing!
What is Creative Writing?
Creative writing is a form of writing that extends beyond the bounds of regular professional, journalistic, academic, or technical forms of literature. It is characterized by its emphasis on narrative craft, character development, and the use of literary tropes or poetic techniques to express ideas in an original and imaginative way.
Creative writing can take on various forms such as:
- short stories
- screenplays
It’s a way for writers to express their thoughts, feelings, and ideas in a creative, often symbolic, way . It’s about using the power of words to transport readers into a world created by the writer.
5 Key Characteristics of Creative Writing
Creative writing is marked by several defining characteristics, each working to create a distinct form of expression:
1. Imagination and Creativity: Creative writing is all about harnessing your creativity and imagination to create an engaging and compelling piece of work. It allows writers to explore different scenarios, characters, and worlds that may not exist in reality.
2. Emotional Engagement: Creative writing often evokes strong emotions in the reader. It aims to make the reader feel something — whether it’s happiness, sorrow, excitement, or fear.
3. Originality: Creative writing values originality. It’s about presenting familiar things in new ways or exploring ideas that are less conventional.
4. Use of Literary Devices: Creative writing frequently employs literary devices such as metaphors, similes, personification, and others to enrich the text and convey meanings in a more subtle, layered manner.
5. Focus on Aesthetics: The beauty of language and the way words flow together is important in creative writing. The aim is to create a piece that’s not just interesting to read, but also beautiful to hear when read aloud.
Remember, creative writing is not just about producing a work of art. It’s also a means of self-expression and a way to share your perspective with the world. Whether you’re considering it as a hobby or contemplating a career in it, understanding the nature and characteristics of creative writing can help you hone your skills and create more engaging pieces .
For more insights into creative writing, check out our articles on creative writing jobs and what you can do with a creative writing degree and is a degree in creative writing worth it .
Styles of Creative Writing
To fully understand creative writing , you must be aware of the various styles involved. Creative writing explores a multitude of genres, each with its own unique characteristics and techniques.
Poetry is a form of creative writing that uses expressive language to evoke emotions and ideas. Poets often employ rhythm, rhyme, and other poetic devices to create pieces that are deeply personal and impactful. Poems can vary greatly in length, style, and subject matter, making this a versatile and dynamic form of creative writing.
Short Stories
Short stories are another common style of creative writing. These are brief narratives that typically revolve around a single event or idea. Despite their length, short stories can provide a powerful punch, using precise language and tight narrative structures to convey a complete story in a limited space.
Novels represent a longer form of narrative creative writing. They usually involve complex plots, multiple characters, and various themes. Writing a novel requires a significant investment of time and effort; however, the result can be a rich and immersive reading experience.
Screenplays
Screenplays are written works intended for the screen, be it television, film, or online platforms. They require a specific format, incorporating dialogue and visual descriptions to guide the production process. Screenwriters must also consider the practical aspects of filmmaking, making this an intricate and specialized form of creative writing.
If you’re interested in this style, understanding creative writing jobs and what you can do with a creative writing degree can provide useful insights.
Writing for the theater is another specialized form of creative writing. Plays, like screenplays, combine dialogue and action, but they also require an understanding of the unique dynamics of the theatrical stage. Playwrights must think about the live audience and the physical space of the theater when crafting their works.
Each of these styles offers unique opportunities for creativity and expression. Whether you’re drawn to the concise power of poetry, the detailed storytelling of novels, or the visual language of screenplays and plays, there’s a form of creative writing that will suit your artistic voice. The key is to explore, experiment, and find the style that resonates with you.
For those looking to spark their creativity, our article on creative writing prompts offers a wealth of ideas to get you started.
Importance of Creative Writing
Understanding what is creative writing involves recognizing its value and significance. Engaging in creative writing can provide numerous benefits – let’s take a closer look.
Developing Creativity and Imagination
Creative writing serves as a fertile ground for nurturing creativity and imagination. It encourages you to think outside the box, explore different perspectives, and create unique and original content. This leads to improved problem-solving skills and a broader worldview , both of which can be beneficial in various aspects of life.
Through creative writing, one can build entire worlds, create characters, and weave complex narratives, all of which are products of a creative mind and vivid imagination. This can be especially beneficial for those seeking creative writing jobs and what you can do with a creative writing degree .
Enhancing Communication Skills
Creative writing can also play a crucial role in honing communication skills. It demands clarity, precision, and a strong command of language. This helps to improve your vocabulary, grammar, and syntax, making it easier to express thoughts and ideas effectively .
Moreover, creative writing encourages empathy as you often need to portray a variety of characters from different backgrounds and perspectives. This leads to a better understanding of people and improved interpersonal communication skills.
Exploring Emotions and Ideas
One of the most profound aspects of creative writing is its ability to provide a safe space for exploring emotions and ideas. It serves as an outlet for thoughts and feelings , allowing you to express yourself in ways that might not be possible in everyday conversation.
Writing can be therapeutic, helping you process complex emotions, navigate difficult life events, and gain insight into your own experiences and perceptions. It can also be a means of self-discovery , helping you to understand yourself and the world around you better.
So, whether you’re a seasoned writer or just starting out, the benefits of creative writing are vast and varied. For those interested in developing their creative writing skills, check out our articles on creative writing prompts and how to teach creative writing . If you’re considering a career in this field, you might find our article on is a degree in creative writing worth it helpful.
4 Steps to Start Creative Writing
Creative writing can seem daunting to beginners, but with the right approach, anyone can start their journey into this creative field. Here are some steps to help you start creative writing .
1. Finding Inspiration
The first step in creative writing is finding inspiration . Inspiration can come from anywhere and anything. Observe the world around you, listen to conversations, explore different cultures, and delve into various topics of interest.
Reading widely can also be a significant source of inspiration. Read different types of books, articles, and blogs. Discover what resonates with you and sparks your imagination.
For structured creative prompts, visit our list of creative writing prompts to get your creative juices flowing.
Editor’s Note : When something excites or interests you, stop and take note – it could be the inspiration for your next creative writing piece.
2. Planning Your Piece
Once you have an idea, the next step is to plan your piece . Start by outlining:
- the main points
Remember, this can serve as a roadmap to guide your writing process. A plan doesn’t have to be rigid. It’s a flexible guideline that can be adjusted as you delve deeper into your writing. The primary purpose is to provide direction and prevent writer’s block.
3. Writing Your First Draft
After planning your piece, you can start writing your first draft . This is where you give life to your ideas and breathe life into your characters.
Don’t worry about making it perfect in the first go. The first draft is about getting your ideas down on paper . You can always refine and polish your work later. And if you don’t have a great place to write that first draft, consider a journal for writing .
4. Editing and Revising Your Work
The final step in the creative writing process is editing and revising your work . This is where you fine-tune your piece, correct grammatical errors, and improve sentence structure and flow.
Editing is also an opportunity to enhance your storytelling . You can add more descriptive details, develop your characters further, and make sure your plot is engaging and coherent.
Remember, writing is a craft that improves with practice . Don’t be discouraged if your first few pieces don’t meet your expectations. Keep writing, keep learning, and most importantly, enjoy the creative process.
For more insights on creative writing, check out our articles on how to teach creative writing or creative writing activities for kids.
Tips to Improve Creative Writing Skills
Understanding what is creative writing is the first step. But how can one improve their creative writing skills? Here are some tips that can help.
Read Widely
Reading is a vital part of becoming a better writer. By immersing oneself in a variety of genres, styles, and authors, one can gain a richer understanding of language and storytelling techniques . Different authors have unique voices and methods of telling stories, which can serve as inspiration for your own work. So, read widely and frequently!
Practice Regularly
Like any skill, creative writing improves with practice. Consistently writing — whether it be daily, weekly, or monthly — helps develop your writing style and voice . Using creative writing prompts can be a fun way to stimulate your imagination and get the words flowing.
Attend Writing Workshops and Courses
Formal education such as workshops and courses can offer structured learning and expert guidance. These can provide invaluable insights into the world of creative writing, from understanding plot development to character creation. If you’re wondering is a degree in creative writing worth it, these classes can also give you a taste of what studying creative writing at a higher level might look like .
Joining Writing Groups and Communities
Being part of a writing community can provide motivation, constructive feedback, and a sense of camaraderie. These groups often hold regular meetings where members share their work and give each other feedback. Plus, it’s a great way to connect with others who share your passion for writing.
Seeking Feedback on Your Work
Feedback is a crucial part of improving as a writer. It offers a fresh perspective on your work, highlighting areas of strength and opportunities for improvement. Whether it’s from a writing group, a mentor, or even friends and family, constructive criticism can help refine your writing .
Start Creative Writing Today!
Remember, becoming a proficient writer takes time and patience. So, don’t be discouraged by initial challenges. Keep writing, keep learning, and most importantly, keep enjoying the process. Who knows, your passion for creative writing might even lead to creative writing jobs and what you can do with a creative writing degree .
Happy writing!
Brooks Manley

Creative Primer is a resource on all things journaling, creativity, and productivity. We’ll help you produce better ideas, get more done, and live a more effective life.
My name is Brooks. I do a ton of journaling, like to think I’m a creative (jury’s out), and spend a lot of time thinking about productivity. I hope these resources and product recommendations serve you well. Reach out if you ever want to chat or let me know about a journal I need to check out!
Here’s my favorite journal for 2024:

Gratitude Journal Prompts Mindfulness Journal Prompts Journal Prompts for Anxiety Reflective Journal Prompts Healing Journal Prompts Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Journal Prompts Mental Health Journal Prompts ASMR Journal Prompts Manifestation Journal Prompts Self-Care Journal Prompts Morning Journal Prompts Evening Journal Prompts Self-Improvement Journal Prompts Creative Writing Journal Prompts Dream Journal Prompts Relationship Journal Prompts "What If" Journal Prompts New Year Journal Prompts Shadow Work Journal Prompts Journal Prompts for Overcoming Fear Journal Prompts for Dealing with Loss Journal Prompts for Discerning and Decision Making Travel Journal Prompts Fun Journal Prompts
Inspiring Ink: Expert Tips on How to Teach Creative Writing
You may also like, how to start and keep a sleep journal: a guide to sleep diaries.
Your Guide to Using a Happiness Journal
Analog vs digital journaling should you go with paper or an app, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Productivity
- Favorite Journals

What is Creative Writing?
by Melissa Donovan | Dec 7, 2023 | Creative Writing | 20 comments

What is creative writing?
Today’s post is an excerpt from the book Ready, Set, Write: A Guide to Creative Writing . This is the entirety of the first chapter, “What is Creative Writing?” Enjoy!
Creative writing can be difficult to define.
Certainly, fiction and poetry are forms of creative writing, but what about journal writing, articles and essays, memoirs and biographies? What about textbooks and copywriting? Technical writing? Blog posts?
Where do we draw the line between what is creative writing and other types of writing?
Have you ever read the terms and conditions on a website? Ever browsed through an instruction manual? Surely, you’ve suffered through a boring textbook. While these types of writing might require some level of creativity, they are not usually considered creative writing.
It’s easy to glance at a poem and know that it’s a piece of creative writing, and it’s easy to flip through a legal document and know that it’s not.
So what is creative writing?
If a historical textbook is not creative writing, then wouldn’t that exclude other nonfiction works like memoirs and biographies from the creative writing category?
Not necessarily.
While nonfiction indicates that the writing is rooted in fact, it can be written with emphasis on language and craftsmanship and therefore creative. Creative nonfiction is a broad genre that includes memoirs and biographies, personal essays, travel and food writing, and literary journalism.
Ultimately, we each get to decide what is art and what is creative writing. Most of us will know creative writing when we experience it, either as a writer or as a reader.
In the big scheme of things, it may not be that important to go around labeling what is and isn’t creative writing, but it’s certainly worthy of a few brief moments of consideration. You can determine what creative writing is for yourself, but others might see things differently.
Do you differentiate between creative writing and other types of writing? Do you feel that copywriting (ads, commercials, etc.) can be classified as creative writing even though its purpose is strictly commercial? If most textbooks are not considered creative writing, does that mean a textbook can never be written creatively? Is writing creative because of how the writer approaches the project, or how the reader receives it?
What is creative writing to you? Share your thoughts by leaving a comment, and keep writing.
Don’t forget to pick up a copy of Ready, Set, Write.

20 Comments
The act of creation, the literal source of the term creative, is an unbounded event that accepts a poorly whittled twig as company to the Mona Lisa. We have weakened that magnanimous gesture by listening to critics and marketers. That is the world, we are told, deal with it. Is it really?
The curse of the moniker “expert” is the finite limitations of experience. An expert can, truly, only judge a thing based on his personal experience. In many fields that is sufficient for a normalized event. You know a balanced perspective, what makes a pleasing composition, what pleases the ear, the pallet and the psyche. When something arises that does not fit the normal patterns, what then? Can you really use normal criteria to weigh it’s value? Experts do, of course, what choice do they have?
I have issue with kind and gracious critiques given so liberally to work the expert didn’t understand; but because the artist was renowned, and popular, it must be so. I read drivel, knowing it has been proclaimed a masterpiece, and laugh to myself. I study paintings that were little more than bovine scratching, and marvel at how highly prized it is, while brilliant groundbreaking work all around is ignored.
Creative writing – creative anything, is literally everything. Marketable work, is the term you are searching for. That has little to do with artistic merit, though some remarkable work does find it’s way to the light.
Caliban, thanks for sharing your thoughts. I believe that a true expert will know when faced with work that is beyond their experience or expertise and will act accordingly. I know nothing about football, so if someone asked me to critique a football player’s performance on the field, I would politely decline.
Having said that, everyone seems to have an opinion. Some may hold more weight than others. For example, I care more about what a well-read person thinks of my work than someone who rarely or never reads any kind of literature. I too have read drivel that has been declared a masterpiece and it’s frustrating to me. It’s difficult to understand, for example, why a shoddy writer is putting out two novels a year and consistently appearing on the bestseller list and receiving rave reviews. Yet it happens all the time (and no, I’m not naming any names!).
You’re right, creative writing or creative anything is literally everything. However, that is subjective. Me? I don’t consider legal, medical, or scientific writing to be creative. I worked as a technical writer and there was nothing creative about it, although it did require considerable skill in terms of language and grammar.
Really great questions here. Creative writing is such a broad category that so many things can fall under it. I personally think that when I’m at work, writing work documents like memos, press releases, contracts, etc., I’m not being creative. When I’m writing on my blog, in my journal, or a story/novel, I’m using my creative writing skills. Now, if only I could get a job where I can use my creative writing all the time…. 😉
Wouldn’t it be exciting to make a full-time living with creative writing? Successful novelists and freelance writers are able to do that, as are screenwriters. Where there’s a will, there’s a way.
Good stuff.
I think it’s words that make you think, feel, or act. It’s evocative. It’s clever in action. It’s looking at something a new way. I think the most evocative writing can win over the most evocative painting. Of course, it depends on whose eye the apple is in. It’s subjective and some of the most beautiful art is precisely divisive.
Ooh…evocative writing versus evocative painting. That would be quite a fight!
Interesting question! When somebody says “Creative writing,” I DO tend to think FICTION before anything else. Because that’s something that comes entirely from your own head. Whereas with non-fiction, you’re writing to a purpose or from a set of facts.
But the actual act of writing? Creative, either way.
Well, when it’s being done right. Because, of course, you can write a quick promotion on auto-pilot and have it be … fine. Routine. Run-of-the-mill. But the good ones? That give you that glow of satisfaction? Pure creativity, all the way!
I tend to immediately think fiction and poetry whenever people start talking about creative writing, but it turns out there’s a whole genre of nonfiction that is creative (and it has tons of sub-genres). For example, the memoir is quite popular right now. I guess it all has to do with how creative or literary your work is.
Really interesting question, the differentiation between what is creative writing and what is not is extremely subjective.
In some ways I think that all writing is somewhat creative as it has emerged from the mind and the writer has had to think about what they are going to produce and how they are going to do it.
I can appreciate that novels and poems are more likely to be considered creative and perhaps even more worthy to be described as such.
I agree with you – we can bring creativity into just about anything we do (including any type of writing), but some forms of art require a little more creativity than others.
Anything that doesn’t make me ‘want’ to read it, is in my mind, non creative as in business manuals, contracts,academic materials, etc. But, written stuff that contains a story line, causes me to reflect, chuckle and ‘want’ to read more of the same would be the creative side of writing for me. Most times, I don’t think about the difference, I just naturally ‘feel’ it:)
Yes, it’s hard to think of the dry writing (business, manuals, contracts) as creative. I do believe there are exceptions, but they are few and far between.
I agree with everyone in terms of the question itself being worthy of contemplation. I think there’s a difference between noise and music, so I will say there is a distinction between creative writing and other types of writing, just as there is art and non-art.
To use the music analogy again, I think technical documents are like playing perfect scales. Kudos to those who have the skill to do that really well, but it’s not a creative act until someone rearranges those notes into something unique and pleasant.
Thanks for getting me thinking this evening. Give us more to contemplate.
Sarah, this is an excellent analogy. I wish I’d thought of it myself. Your examples of noise vs. music and technical documents being similar to playing scales are spot-on! Thanks so much for adding your ideas to this discussion.
Completely stunned and baffled! I am dangling in between the two worlds of what is and isn’t on creative writing arena. Does that mean any writing can be said creative and also not, depending how we passive the pieces of works we may come across?
I think it’s just a judgment call. Each of us gets to decide.
I’m eighty-five years old and have only started writing in the past year or so. My writings have consisted of stories from my own life. My idea of creativity is to make those past experiences interesting. I’ve always been an avid reader of both fact and fiction. I relied heavily on self-help books while struggling with depression during my earlier years. Self-help books aren’t fiction, but I’ve found them to be creatively written.
Creative writing might also be described as, “making myself look pretty darn good” while telling tales of my past.
One of the great things about writing is that we can start it at any time in life. I have always found writing to be calming and therapeutic and a useful tool for self-expression. Thanks for sharing your experiences with writing, Richard.
Creative writing, literally focoses on the imaginative and true skillful arts of bring thoughts into words and actions. Thereby, imbues in readers the ability to critique on the applied skills levelled up by the writer in his or her works of art.
The purpose of creative writings varies. Some works are meant to entertain; others are meant to inform or inspire. While readers can certainly critique, that is actually not the common purpose from an author’s perspective. And most readers don’t get too deep into critiques. Most readers want to be entertained or learn something.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

Subscribe and get The Writer’s Creed graphic e-booklet, plus a weekly digest with the latest articles on writing, as well as special offers and exclusive content.

Recent Posts
- Writing While Inspired
- Thoughts on Becoming a Writer
- How to Write a Book
- Writing Resources: No Plot? No Problem!
- Character-Driven Fiction Writing Prompts
Write on, shine on!
Pin It on Pinterest
VIDEO COURSE
Finish your draft in our 3-month master class. Sign up now to watch a free lesson!
Learn How to Write a Novel
Finish your draft in our 3-month master class. Enroll now for daily lessons, weekly critique, and live events. Your first lesson is free!

Guides • Perfecting your Craft
Last updated on Feb 14, 2023
10 Types of Creative Writing (with Examples You’ll Love)
A lot falls under the term ‘creative writing’: poetry, short fiction, plays, novels, personal essays, and songs, to name just a few. By virtue of the creativity that characterizes it, creative writing is an extremely versatile art. So instead of defining what creative writing is , it may be easier to understand what it does by looking at examples that demonstrate the sheer range of styles and genres under its vast umbrella.
To that end, we’ve collected a non-exhaustive list of works across multiple formats that have inspired the writers here at Reedsy. With 20 different works to explore, we hope they will inspire you, too.
People have been writing creatively for almost as long as we have been able to hold pens. Just think of long-form epic poems like The Odyssey or, later, the Cantar de Mio Cid — some of the earliest recorded writings of their kind.
Poetry is also a great place to start if you want to dip your own pen into the inkwell of creative writing. It can be as short or long as you want (you don’t have to write an epic of Homeric proportions), encourages you to build your observation skills, and often speaks from a single point of view .
Here are a few examples:
“Ozymandias” by Percy Bysshe Shelley
Nothing beside remains. Round the decay Of that colossal Wreck, boundless and bare The lone and level sands stretch far away.

This classic poem by Romantic poet Percy Shelley (also known as Mary Shelley’s husband) is all about legacy. What do we leave behind? How will we be remembered? The great king Ozymandias built himself a massive statue, proclaiming his might, but the irony is that his statue doesn’t survive the ravages of time. By framing this poem as told to him by a “traveller from an antique land,” Shelley effectively turns this into a story. Along with the careful use of juxtaposition to create irony, this poem accomplishes a lot in just a few lines.
“Trying to Raise the Dead” by Dorianne Laux
A direction. An object. My love, it needs a place to rest. Say anything. I’m listening. I’m ready to believe. Even lies, I don’t care.
Poetry is cherished for its ability to evoke strong emotions from the reader using very few words which is exactly what Dorianne Laux does in “ Trying to Raise the Dead .” With vivid imagery that underscores the painful yearning of the narrator, she transports us to a private nighttime scene as the narrator sneaks away from a party to pray to someone they’ve lost. We ache for their loss and how badly they want their lost loved one to acknowledge them in some way. It’s truly a masterclass on how writing can be used to portray emotions.
If you find yourself inspired to try out some poetry — and maybe even get it published — check out these poetry layouts that can elevate your verse!
Song Lyrics
Poetry’s closely related cousin, song lyrics are another great way to flex your creative writing muscles. You not only have to find the perfect rhyme scheme but also match it to the rhythm of the music. This can be a great challenge for an experienced poet or the musically inclined.
To see how music can add something extra to your poetry, check out these two examples:
“Hallelujah” by Leonard Cohen
You say I took the name in vain I don't even know the name But if I did, well, really, what's it to ya? There's a blaze of light in every word It doesn't matter which you heard The holy or the broken Hallelujah
Metaphors are commonplace in almost every kind of creative writing, but will often take center stage in shorter works like poetry and songs. At the slightest mention, they invite the listener to bring their emotional or cultural experience to the piece, allowing the writer to express more with fewer words while also giving it a deeper meaning. If a whole song is couched in metaphor, you might even be able to find multiple meanings to it, like in Leonard Cohen’s “ Hallelujah .” While Cohen’s Biblical references create a song that, on the surface, seems like it’s about a struggle with religion, the ambiguity of the lyrics has allowed it to be seen as a song about a complicated romantic relationship.
“I Will Follow You into the Dark” by Death Cab for Cutie
If Heaven and Hell decide that they both are satisfied Illuminate the no's on their vacancy signs If there's no one beside you when your soul embarks Then I'll follow you into the dark

You can think of song lyrics as poetry set to music. They manage to do many of the same things their literary counterparts do — including tugging on your heartstrings. Death Cab for Cutie’s incredibly popular indie rock ballad is about the singer’s deep devotion to his lover. While some might find the song a bit too dark and macabre, its melancholy tune and poignant lyrics remind us that love can endure beyond death.
Plays and Screenplays
From the short form of poetry, we move into the world of drama — also known as the play. This form is as old as the poem, stretching back to the works of ancient Greek playwrights like Sophocles, who adapted the myths of their day into dramatic form. The stage play (and the more modern screenplay) gives the words on the page a literal human voice, bringing life to a story and its characters entirely through dialogue.
Interested to see what that looks like? Take a look at these examples:
All My Sons by Arthur Miller
“I know you're no worse than most men but I thought you were better. I never saw you as a man. I saw you as my father.”

Arthur Miller acts as a bridge between the classic and the new, creating 20th century tragedies that take place in living rooms and backyard instead of royal courts, so we had to include his breakout hit on this list. Set in the backyard of an all-American family in the summer of 1946, this tragedy manages to communicate family tensions in an unimaginable scale, building up to an intense climax reminiscent of classical drama.
💡 Read more about Arthur Miller and classical influences in our breakdown of Freytag’s pyramid .
“Everything is Fine” by Michael Schur ( The Good Place )
“Well, then this system sucks. What...one in a million gets to live in paradise and everyone else is tortured for eternity? Come on! I mean, I wasn't freaking Gandhi, but I was okay. I was a medium person. I should get to spend eternity in a medium place! Like Cincinnati. Everyone who wasn't perfect but wasn't terrible should get to spend eternity in Cincinnati.”
A screenplay, especially a TV pilot, is like a mini-play, but with the extra job of convincing an audience that they want to watch a hundred more episodes of the show. Blending moral philosophy with comedy, The Good Place is a fun hang-out show set in the afterlife that asks some big questions about what it means to be good.
It follows Eleanor Shellstrop, an incredibly imperfect woman from Arizona who wakes up in ‘The Good Place’ and realizes that there’s been a cosmic mixup. Determined not to lose her place in paradise, she recruits her “soulmate,” a former ethics professor, to teach her philosophy with the hope that she can learn to be a good person and keep up her charade of being an upstanding citizen. The pilot does a superb job of setting up the stakes, the story, and the characters, while smuggling in deep philosophical ideas.
Personal essays
Our first foray into nonfiction on this list is the personal essay. As its name suggests, these stories are in some way autobiographical — concerned with the author’s life and experiences. But don’t be fooled by the realistic component. These essays can take any shape or form, from comics to diary entries to recipes and anything else you can imagine. Typically zeroing in on a single issue, they allow you to explore your life and prove that the personal can be universal.
Here are a couple of fantastic examples:
“On Selling Your First Novel After 11 Years” by Min Jin Lee (Literary Hub)
There was so much to learn and practice, but I began to see the prose in verse and the verse in prose. Patterns surfaced in poems, stories, and plays. There was music in sentences and paragraphs. I could hear the silences in a sentence. All this schooling was like getting x-ray vision and animal-like hearing.

This deeply honest personal essay by Pachinko author Min Jin Lee is an account of her eleven-year struggle to publish her first novel . Like all good writing, it is intensely focused on personal emotional details. While grounded in the specifics of the author's personal journey, it embodies an experience that is absolutely universal: that of difficulty and adversity met by eventual success.
“A Cyclist on the English Landscape” by Roff Smith (New York Times)
These images, though, aren’t meant to be about me. They’re meant to represent a cyclist on the landscape, anybody — you, perhaps.
Roff Smith’s gorgeous photo essay for the NYT is a testament to the power of creatively combining visuals with text. Here, photographs of Smith atop a bike are far from simply ornamental. They’re integral to the ruminative mood of the essay, as essential as the writing. Though Smith places his work at the crosscurrents of various aesthetic influences (such as the painter Edward Hopper), what stands out the most in this taciturn, thoughtful piece of writing is his use of the second person to address the reader directly. Suddenly, the writer steps out of the body of the essay and makes eye contact with the reader. The reader is now part of the story as a second character, finally entering the picture.
Short Fiction
The short story is the happy medium of fiction writing. These bite-sized narratives can be devoured in a single sitting and still leave you reeling. Sometimes viewed as a stepping stone to novel writing, that couldn’t be further from the truth. Short story writing is an art all its own. The limited length means every word counts and there’s no better way to see that than with these two examples:
“An MFA Story” by Paul Dalla Rosa (Electric Literature)
At Starbucks, I remembered a reading Zhen had given, a reading organized by the program’s faculty. I had not wanted to go but did. In the bar, he read, "I wrote this in a Starbucks in Shanghai. On the bank of the Huangpu." It wasn’t an aside or introduction. It was two lines of the poem. I was in a Starbucks and I wasn’t writing any poems. I wasn’t writing anything.

This short story is a delightfully metafictional tale about the struggles of being a writer in New York. From paying the bills to facing criticism in a writing workshop and envying more productive writers, Paul Dalla Rosa’s story is a clever satire of the tribulations involved in the writing profession, and all the contradictions embodied by systemic creativity (as famously laid out in Mark McGurl’s The Program Era ). What’s more, this story is an excellent example of something that often happens in creative writing: a writer casting light on the private thoughts or moments of doubt we don’t admit to or openly talk about.
“Flowering Walrus” by Scott Skinner (Reedsy)
I tell him they’d been there a month at least, and he looks concerned. He has my tongue on a tissue paper and is gripping its sides with his pointer and thumb. My tongue has never spent much time outside of my mouth, and I imagine it as a walrus basking in the rays of the dental light. My walrus is not well.
A winner of Reedsy’s weekly Prompts writing contest, ‘ Flowering Walrus ’ is a story that balances the trivial and the serious well. In the pauses between its excellent, natural dialogue , the story manages to scatter the fear and sadness of bad medical news, as the protagonist hides his worries from his wife and daughter. Rich in subtext, these silences grow and resonate with the readers.
Want to give short story writing a go? Give our free course a go!

FREE COURSE
How to Craft a Killer Short Story
From pacing to character development, master the elements of short fiction.
Perhaps the thing that first comes to mind when talking about creative writing, novels are a form of fiction that many people know and love but writers sometimes find intimidating. The good news is that novels are nothing but one word put after another, like any other piece of writing, but expanded and put into a flowing narrative. Piece of cake, right?
To get an idea of the format’s breadth of scope, take a look at these two (very different) satirical novels:
Convenience Store Woman by Sayaka Murata
I wished I was back in the convenience store where I was valued as a working member of staff and things weren’t as complicated as this. Once we donned our uniforms, we were all equals regardless of gender, age, or nationality — all simply store workers.

Keiko, a thirty-six-year-old convenience store employee, finds comfort and happiness in the strict, uneventful routine of the shop’s daily operations. A funny, satirical, but simultaneously unnerving examination of the social structures we take for granted, Sayaka Murata’s Convenience Store Woman is deeply original and lingers with the reader long after they’ve put it down.
Erasure by Percival Everett
The hard, gritty truth of the matter is that I hardly ever think about race. Those times when I did think about it a lot I did so because of my guilt for not thinking about it.
Erasure is a truly accomplished satire of the publishing industry’s tendency to essentialize African American authors and their writing. Everett’s protagonist is a writer whose work doesn’t fit with what publishers expect from him — work that describes the “African American experience” — so he writes a parody novel about life in the ghetto. The publishers go crazy for it and, to the protagonist’s horror, it becomes the next big thing. This sophisticated novel is both ironic and tender, leaving its readers with much food for thought.
Creative Nonfiction
Creative nonfiction is pretty broad: it applies to anything that does not claim to be fictional (although the rise of autofiction has definitely blurred the boundaries between fiction and nonfiction). It encompasses everything from personal essays and memoirs to humor writing, and they range in length from blog posts to full-length books. The defining characteristic of this massive genre is that it takes the world or the author’s experience and turns it into a narrative that a reader can follow along with.
Here, we want to focus on novel-length works that dig deep into their respective topics. While very different, these two examples truly show the breadth and depth of possibility of creative nonfiction:
Men We Reaped by Jesmyn Ward
Men’s bodies litter my family history. The pain of the women they left behind pulls them from the beyond, makes them appear as ghosts. In death, they transcend the circumstances of this place that I love and hate all at once and become supernatural.
Writer Jesmyn Ward recounts the deaths of five men from her rural Mississippi community in as many years. In her award-winning memoir , she delves into the lives of the friends and family she lost and tries to find some sense among the tragedy. Working backwards across five years, she questions why this had to happen over and over again, and slowly unveils the long history of racism and poverty that rules rural Black communities. Moving and emotionally raw, Men We Reaped is an indictment of a cruel system and the story of a woman's grief and rage as she tries to navigate it.
Cork Dork by Bianca Bosker
He believed that wine could reshape someone’s life. That’s why he preferred buying bottles to splurging on sweaters. Sweaters were things. Bottles of wine, said Morgan, “are ways that my humanity will be changed.”
In this work of immersive journalism , Bianca Bosker leaves behind her life as a tech journalist to explore the world of wine. Becoming a “cork dork” takes her everywhere from New York’s most refined restaurants to science labs while she learns what it takes to be a sommelier and a true wine obsessive. This funny and entertaining trip through the past and present of wine-making and tasting is sure to leave you better informed and wishing you, too, could leave your life behind for one devoted to wine.
Illustrated Narratives (Comics, graphic novels)
Once relegated to the “funny pages”, the past forty years of comics history have proven it to be a serious medium. Comics have transformed from the early days of Jack Kirby’s superheroes into a medium where almost every genre is represented. Humorous one-shots in the Sunday papers stand alongside illustrated memoirs, horror, fantasy, and just about anything else you can imagine. This type of visual storytelling lets the writer and artist get creative with perspective, tone, and so much more. For two very different, though equally entertaining, examples, check these out:
Calvin & Hobbes by Bill Watterson
"Life is like topography, Hobbes. There are summits of happiness and success, flat stretches of boring routine and valleys of frustration and failure."
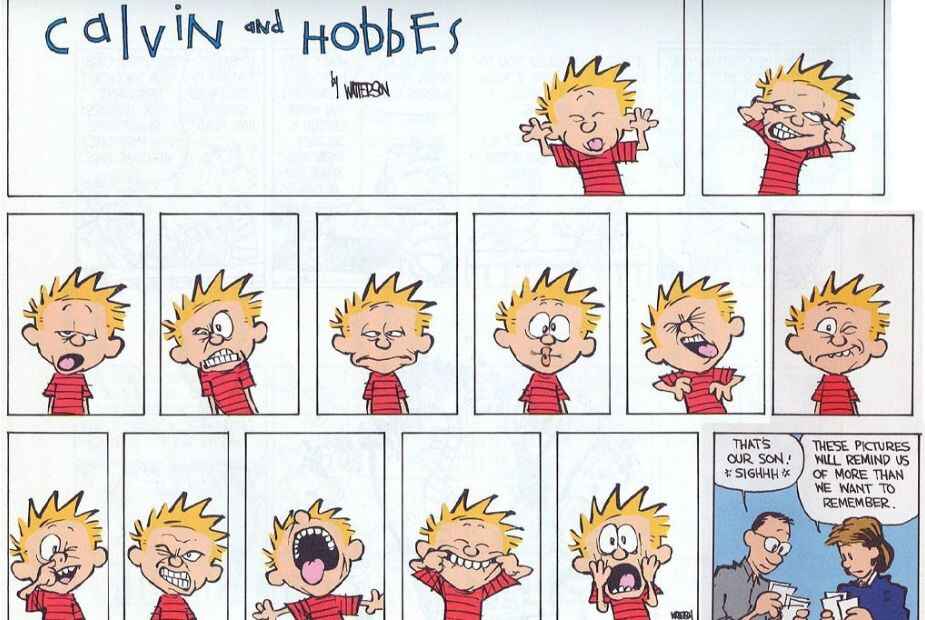

This beloved comic strip follows Calvin, a rambunctious six-year-old boy, and his stuffed tiger/imaginary friend, Hobbes. They get into all kinds of hijinks at school and at home, and muse on the world in the way only a six-year-old and an anthropomorphic tiger can. As laugh-out-loud funny as it is, Calvin & Hobbes ’ popularity persists as much for its whimsy as its use of humor to comment on life, childhood, adulthood, and everything in between.
From Hell by Alan Moore and Eddie Campbell
"I shall tell you where we are. We're in the most extreme and utter region of the human mind. A dim, subconscious underworld. A radiant abyss where men meet themselves. Hell, Netley. We're in Hell."
Comics aren't just the realm of superheroes and one-joke strips, as Alan Moore proves in this serialized graphic novel released between 1989 and 1998. A meticulously researched alternative history of Victorian London’s Ripper killings, this macabre story pulls no punches. Fact and fiction blend into a world where the Royal Family is involved in a dark conspiracy and Freemasons lurk on the sidelines. It’s a surreal mad-cap adventure that’s unsettling in the best way possible.
Video Games and RPGs
Probably the least expected entry on this list, we thought that video games and RPGs also deserved a mention — and some well-earned recognition for the intricate storytelling that goes into creating them.
Essentially gamified adventure stories, without attention to plot, characters, and a narrative arc, these games would lose a lot of their charm, so let’s look at two examples where the creative writing really shines through:
80 Days by inkle studios
"It was a triumph of invention over nature, and will almost certainly disappear into the dust once more in the next fifty years."

Named Time Magazine ’s game of the year in 2014, this narrative adventure is based on Around the World in 80 Days by Jules Verne. The player is cast as the novel’s narrator, Passpartout, and tasked with circumnavigating the globe in service of their employer, Phileas Fogg. Set in an alternate steampunk Victorian era, the game uses its globe-trotting to comment on the colonialist fantasies inherent in the original novel and its time period. On a storytelling level, the choose-your-own-adventure style means no two players’ journeys will be the same. This innovative approach to a classic novel shows the potential of video games as a storytelling medium, truly making the player part of the story.
What Remains of Edith Finch by Giant Sparrow
"If we lived forever, maybe we'd have time to understand things. But as it is, I think the best we can do is try to open our eyes, and appreciate how strange and brief all of this is."
This video game casts the player as 17-year-old Edith Finch. Returning to her family’s home on an island in the Pacific northwest, Edith explores the vast house and tries to figure out why she’s the only one of her family left alive. The story of each family member is revealed as you make your way through the house, slowly unpacking the tragic fate of the Finches. Eerie and immersive, this first-person exploration game uses the medium to tell a series of truly unique tales.
Fun and breezy on the surface, humor is often recognized as one of the trickiest forms of creative writing. After all, while you can see the artistic value in a piece of prose that you don’t necessarily enjoy, if a joke isn’t funny, you could say that it’s objectively failed.
With that said, it’s far from an impossible task, and many have succeeded in bringing smiles to their readers’ faces through their writing. Here are two examples:
‘How You Hope Your Extended Family Will React When You Explain Your Job to Them’ by Mike Lacher (McSweeney’s Internet Tendency)
“Is it true you don’t have desks?” your grandmother will ask. You will nod again and crack open a can of Country Time Lemonade. “My stars,” she will say, “it must be so wonderful to not have a traditional office and instead share a bistro-esque coworking space.”
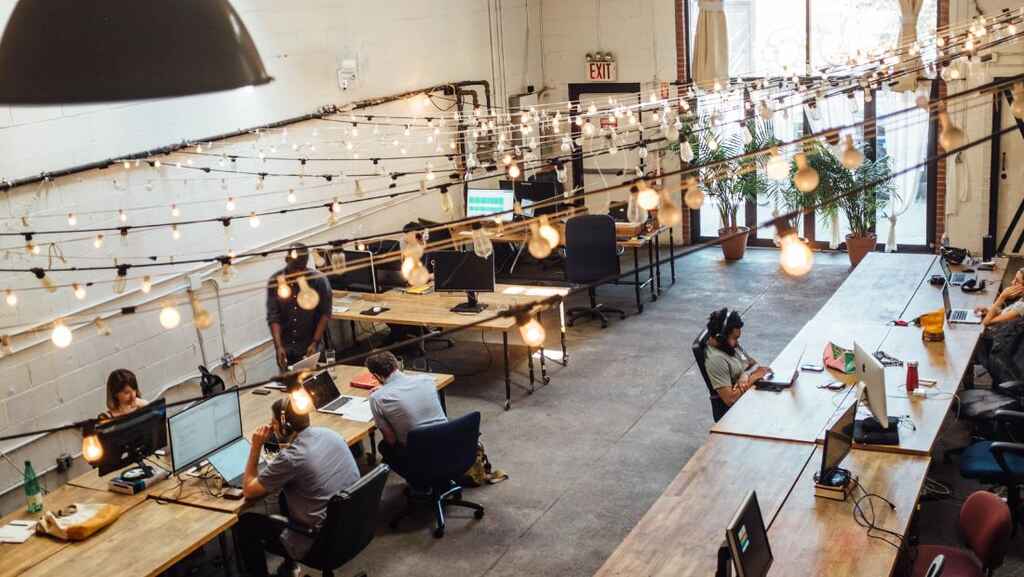

Satire and parody make up a whole subgenre of creative writing, and websites like McSweeney’s Internet Tendency and The Onion consistently hit the mark with their parodies of magazine publishing and news media. This particular example finds humor in the divide between traditional family expectations and contemporary, ‘trendy’ work cultures. Playing on the inherent silliness of today’s tech-forward middle-class jobs, this witty piece imagines a scenario where the writer’s family fully understands what they do — and are enthralled to hear more. “‘Now is it true,’ your uncle will whisper, ‘that you’ve got a potential investment from one of the founders of I Can Haz Cheezburger?’”
‘Not a Foodie’ by Hilary Fitzgerald Campbell (Electric Literature)
I’m not a foodie, I never have been, and I know, in my heart, I never will be.
Highlighting what she sees as an unbearable social obsession with food , in this comic Hilary Fitzgerald Campbell takes a hilarious stand against the importance of food. From the writer’s courageous thesis (“I think there are more exciting things to talk about, and focus on in life, than what’s for dinner”) to the amusing appearance of family members and the narrator’s partner, ‘Not a Foodie’ demonstrates that even a seemingly mundane pet peeve can be approached creatively — and even reveal something profound about life.
We hope this list inspires you with your own writing. If there’s one thing you take away from this post, let it be that there is no limit to what you can write about or how you can write about it.
In the next part of this guide, we'll drill down into the fascinating world of creative nonfiction.
Join a community of over 1 million authors
Reedsy is more than just a blog. Become a member today to discover how we can help you publish a beautiful book.
We have an app for that
Build a writing routine with our free writing app.

1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Enter your email or get started with a social account:

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.1: Intro to Creative Writing
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 132138

- Sybil Priebe
- North Dakota State College of Science via Independent Published
chapter 1: intro to creative writing:
Creative writing\(^7\) is any writing that goes outside the bounds of “normal”\(^8\) “professional,”\(^9\) journalistic, “academic,”\(^{10}\) or technical forms of literature, typically identified by an emphasis on narrative craft, character development, and the use of literary tropes or with various traditions of poetry and poetics. Due to the looseness of the definition, it is possible for writing such as feature stories to be considered creative writing, even though they fall under journalism, because the content of features is specifically focused on narrative and character development.
Both fictional and nonfictional works fall into this category, including such forms as novels, biographies, short stories, and poems. In the academic setting, creative writing is typically separated into fiction and poetry classes, with a focus on writing in an original style, as opposed to imitating pre-existing genres such as crime or horror. Writing for the screen and stage—screenwriting and playwrighting—are often taught separately but fit under the creative writing category as well.
Creative writing can technically be considered any writing of original composition.
the creative process: \(^{11}\)
Some people can simply sit down to write and have something to write about. For others, finding something to write about can be the hardest part of creative writing. Assuming that you are not in the first group, there are several things you can do to create ideas. Not all of these will work for all people, but most are at least useful tools in the process. Also, you never know when you might have an idea. Write down any ideas you have at any time and expand on them later.
For stories and poetry, the simplest method is to immerse yourself in the subject matter. If you want to write a short story, read a lot of short stories. If you want to write a poem, read poems. If you want to write something about love, read a lot of things about love, no matter the genre.
the writing process “reminder”\(^{12}\)
Please Note: Not all writers follow these steps perfectly and with each project, but let’s review them to cover our butts:
BRAINSTORMING
PROOFREADING
Outline\(^{13}\) your entire story so you know what to write. Start by writing a summary of your story in 1 paragraph. Use each sentence to explain the most important parts of your story. Then, take each sentence of your paragraph and expand it into greater detail. Keep working backward to add more detail to your story. This is known as the “snowflake method” of outlining.
getting started:
Find a comfortable space to write: consider the view, know yourself well enough to decide what you need in that physical space (music? coffee? blanket?).
Have the right tools: computer, notebook, favorite pens, etc.
Consider having a portable version of your favorite writing tool (small notebook or use an app on your phone?).
Start writing and try to make a daily habit out of it, even if you only get a paragraph or page down each day.
Keys to creativity: curiosity, passion, determination, awareness, energy, openness, sensitivity, listening, and observing...
getting ideas:
Ideas are everywhere! Ideas can be found:
Notebook or Image journal
Media: Magazines, newspapers, radio, TV, movies, etc.
Conversations with people
Artistic sources like photographs, family albums, home movies, illustrations, sculptures, and paintings.
Daily life: Standing in line at the grocery store, going to an ATM, working at your campus job, etc.
Music: Song lyrics, music videos, etc.
Beautiful or Horrible Settings
Favorite Objects
Favorite Books
How to generate ideas:
Play the game: "What if..."
Play the game: "I wonder..."
Use your favorite story as a model.
Revise favorite stories - nonfiction or fiction - into a different genre.
writer's block:\(^{14}\)
Writer’s block can happen to ANYONE, so here are some ways to break the block if it happens to you:
Write down anything that comes to mind.
Try to draw ideas from what has already been written.
Take a break from writing.
Read other peoples' writing to get ideas.
Talk to people. Ask others if they have any ideas.
Don't be afraid of writing awkwardly. Write it down and edit it later.
Set deadlines and keep them.
Work on multiple projects at a time; this way if you need to procrastinate on one project, you can work on another!
If you are jammed where you are, stop and write somewhere else, where it is comfortable.
Go somewhere where people are. Then people-watch. Who are these people? What do they do? Can you deduce\(^{15}\) anything based on what they are wearing or doing or saying? Make up random backstories for them, as if they were characters in your story.
peer workshops and feedback acronyms: \(^{16}\)
Having other humans give you feedback will help you improve misunderstandings within your work. Sometimes it takes another pair of eyes to see what you “missed” in your own writing. Please try not to get upset by the feedback; some people give creative criticism and others give negative criticism, but you will eventually learn by your own mistakes to improve your writing and that requires peer review and feedback from others.
If you are comfortable having your friends and family read your work, you could have them\(^{17}\) peer review your work. Have a nerdy friend who corrects your grammar? Pay them in pizza perhaps to read over your stuff!? If you are in college, you can use college tutors to review your work.
Peer Workshop activities can help create a “writing group vibe” to any course, so hopefully, that is a part of the creative writing class you are taking.
WWW and TAG
The acronyms involved with feedback – at least according to the educators of Twitter – are WWW and TAG. Here’s what they stand for, so feel free to use these strategies in your creative writing courses OR when giving feedback to ANYONE.
Are you open to the kinds of feedback you’ll get using that table above with the WWW/TAG pieces?
What do you typically want feedback on when it comes to projects? Why?
What do you feel comfortable giving feedback to classmates on? Why?
\(^7\)"Creative Writing." Wikipedia . 13 Nov 2016. 21 Nov 2016, 19:39 < https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Creative_writing >. Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License.
\(^8\)Whoa, what is normal anyway?
\(^9\)What IS the definition of “professionalism”?
\(^{10}\)Can’t academic writing be creative?
\(^{11}\)"Creative Writing/Introduction." Wikibooks, The Free Textbook Project . 10 May 2009, 04:14 UTC. 9 Nov 2016, 19:39
< https://en.wikibooks.org/w/index.php...&oldid=1495539 >. Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License.
\(^{12}\)It doesn’t really matter who created it; all you need to know is that you don’t HAVE to follow it perfectly. Not many people do.
\(^{13}\)Wikihow contributors. "How to Write Science Fiction." Wikihow. 29 May 2019. Web. 22 June 2019. http://www.wikihow.com/Write-Science-Fiction . Text available under Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0).
\(^{14}\)"Creative Writing/Fiction technique." Wikibooks, The Free Textbook Project . 28 Jun 2016, 13:38 UTC. 9 Nov 2016, 20:36
< https://en.wikibooks.org/w/index.php...&oldid=3093632 >. Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License.
\(^{15}\)Deduce = to reach a conclusion.
\(^{16}\)"Creative Writing/Peer Review." Wikibooks, The Free Textbook Project. 16 Aug 2016, 22:07 UTC. 9 Nov 2016, 20:12
< https://en.wikibooks.org/w/index.php...&oldid=3107005 >. Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License.
\(^{17}\)This textbook we’ll try to use they/them pronouns throughout to be inclusive of all humans.

Online Students
For All Online Programs
International Students
On Campus, need or have Visa
Campus Students
For All Campus Programs
What is Creative Writing?

Creative writing is any form of writing that exists outside of journalism, business writing, or academic writing. It expresses an author's unique voice, writing style, thoughts, and ideas in an engaging and imaginative manner, said Christopher Sullivan , MFA, an adjunct instructor in the creative writing and English program at Southern New Hampshire University (SNHU).
“Creative writing has no boundaries. It gives the writer permission to flex his or her creative muscles and utilize infinite amounts of imagery and imagination within their writing," he said.
What Makes a Good Piece of Creative Writing?

These include:
- Theme – The main idea or moral of a story.
- Setting – The time and geographic location within a narrative.
- Character and plot development – Usually intertwined, the author’s ability to grow a character’s ability to take action, which leads to conflict and the rising progression of the plot.
- Point-of-view – Told in the first, second, or third person, this is the way in which authors express the views of themselves or their characters.
- Voice – The way in which the author tells the story; for example, anxious, sparse in detail, looking back through time, etc.
- Tone and style – Style refers to the author's choice of diction, sentence structure, literary techniques, and use of rhythm, while style refers to the author’s attitude toward the story and the reader.
Within each of these areas of craft, authors use tools such as figurative language, dialogue, description, and conflict to give color and dimension to their characters and plot, she said.
What is Creative Writing and its Types?
In addition to fiction writing, creative writing includes the genres of poetry, creative nonfiction (such as memoir, autobiography, or personal essay), screenwriting, plays, and/ or graphic novels. Blogs and other digital media could also be considered forms of creative writing.
- Fiction – This type of prose is based on imaginary events and people, usually in the form of a novel or short story. Good novels appeal to the senses, embrace idiosyncrasies, and make people laugh or cry, wrote author Elizabeth Sims in a recent Writer's Digest blog post .
- Poetry – Much more than rhyming stanzas, poetry aims to “tell a story, enact a drama, convey ideas, offer vivid, unique description or express our inward spiritual, emotional, or psychological states,” according to poet Dan Rifenburgh, who wrote about the definition of poetry in an article published on the National Endowment for the Arts website.
- Memoirs – Memoirs not only recount the actual events of an author’s life from his or her perspective, they often serve as inspirational pieces that challenge readers to take action or make change. Jeff Goins, author of Wrecked and The In-Between, shares three basic rules for writing a good memoir on the blog, The Write Practice. Authors should also be prepared to show vulnerability and aspire to move the reader to a new way of thinking in search of the truth, he said.
- Screenwriting – Without a strong script, actors in our favorite movies would not follow a plot, engage in conflict, or participate in any kind of dialogue. Unlike other types of writing, a screenplay has to perform two jobs: it must be entertaining to the viewer and provide instructions to actors and directors, according to Ant Jackson, a blogger for The Writing Cooperative .
- Graphic novels – Similar to comic books, graphic novels combine words and images to tell a longer story. A blend of text and art, authors can provide visual punch to their dialogue in this format. Popular with both children and adults, graphic novels can better convey complex subject matter, thanks to a blend of both literary devices and pictures, according to Gal Beckerman , an editor for the New York Times Book Review.
- Blogs – Blogging itself isn’t a literary genre—it’s a platform that allows writers to share a variety of creative writing—poetry, short stories, or multimedia projects that combine words and images – with audiences on the internet.
Writers often spend years practicing their craft, and learned the basics in degree programs specifically focused on creative writing.
Explore Creative Writing Programs
Pursuing a bachelor's degree in creative writing and English can help you hone your craft and experiment with different genres and forms, while you also focus on a specific type of writing, said Prokop.
Undergraduate creative writing programs typically include a mix of general education classes and courses in the humanities, in addition to creative writing classes. Introductory writing classes typically cover genre basics and explore some of the tools writers use to craft an engaging story.
"This is a perfect class for beginners or those looking to hone a basic skill, such as developing a plot," Prokop said.

Such programs also help writers build upon their foundational skills, too. For example, most students take English composition classes that utilize a variety of rhetorical modes (narration, description, cause and effect, and persuasion and argument, to name a few) that help them perfect their skills before they focus on a specific genre, Sullivan said.
“Most students interested in applying to the creative writing program typically have a solid foundation with writing mechanics. However, that doesn’t mean their mechanics have to be perfect—they are here to learn,” he said.
Some programs also allow students to concentrate on a specific genre (fiction writing, nonfiction writing, poetry, or screenwriting) and develop portfolios of work that can help them apply for MFA programs or promote themselves as writers.
What Jobs Can You Get with a Creative Writing Degree?
If you decide to major in creative writing, it doesn't automatically mean you'll become a published author—but it will give you the tools you need for job roles that require strong writing and communication skills.
Graduates who are serious about pursuing writing careers are encouraged to practice their craft, obtain feedback, and submit their work to publishers, Sullivan said.
“Throughout the creative writing program, students are given tools, resources, and lots of valuable feedback to strengthen their writing skills,” he said. “However, writing is a process. It takes a lot of hard work, networking, humility, and dedication to become a published author.”
Here are some jobs creative writing and English majors might also consider pursuing.
Writer or Author
Use your storytelling skills to pen children’s books, novels, biographies, essays, or memoirs. A bachelor’s degree is generally required for a full-time position as a writer or author, and additional experience gained through internships or any writing that improves skill--such as blogging—can help, too. Although it’s a highly competitive field, successful authors earned a median annual salary of $62,170 in 2018, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS).
Editors aren’t just grammar experts who correct mistakes. Publications rely on them to plan, review, and evaluate publications. Whether they work in a corporate environment or for print or digital publications, editors must be imaginative, curious, and knowledgeable in a broad range of topics in order to add value. Most editors have a bachelor’s degree and gain experience through internships, according to BLS. In 2018, editors earned a median annual salary of $59,480 , BLS reports.
Reporters, news correspondents, and broadcast news analysts use their research and storytelling skills to inform the public about news and events. They can work for news publications, digital publications, TV, or radio stations. Journalists typically hold a bachelor’s degree and gain work experience through college internships. The average annual wage for broadcast news analysts in 2018 was $66,880, while the average annual wage for reporters and correspondents in 2018 was $41,260, according to BLS .
Advertising, Promotions and/or Marketing Managers
Whether they are creating ad campaigns, promotional events, or looking at pricing strategies, professionals in advertising and marketing roles use their creativity and communication skills to generate interest in their organization’s products or services. A bachelor’s degree is required for most advertising, promotions, and marketing management positions. A creative writing degree can be particularly helpful to media directors who use radio, television, newspapers, magazines, the internet, or outdoor signs to create messages that effectively reach customers. The average annual salary for advertising and promotions managers was $117,130 in 2018; while the average annual salary for marketing managers was $134,290, according to BLS .
With a bachelor's degree in creative writing and English, you can polish your storytelling skills and position yourself for a variety of jobs that require imagination and solid communication skills.
Krysten Godfrey Maddocks ’11 is a writer and marketing/communication professional. Connect with her on LinkedIn .
Explore more content like this article

Why is Poetry Important? Celebrating National Poetry Month

Actor Stephanie Gould Surprised Onstage With Diploma Delivery

Associate Dean of Liberal Arts Dr. Robert Denning: A Faculty Q&A
About southern new hampshire university.

SNHU is a nonprofit, accredited university with a mission to make high-quality education more accessible and affordable for everyone.
Founded in 1932, and online since 1995, we’ve helped countless students reach their goals with flexible, career-focused programs . Our 300-acre campus in Manchester, NH is home to over 3,000 students, and we serve over 135,000 students online. Visit our about SNHU page to learn more about our mission, accreditations, leadership team, national recognitions and awards.

What is Creative Writing?

Written by Scott Wilson

Creative writing is any kind of writing that employs creative literary or poetic techniques in the service of either fiction or non-fiction writing. It involves original composition and expressiveness of the individual author.
Ask ten creative writing professors what creative writing is, and you’ll get eleven different answers. Turn to the dictionary and the definition invokes invention and incorporation of imagination. But what are the limits of imagination? Where does invention begin?
Every sentence in every work ever written began as an act of creation in the mind of the writer.
Creative writing may be most easily defined by what it is not…
- Technical writing
- Professional or business writing
- Scholarly or academic writing
Creative writing is the entire body of the writer’s craft that falls outside the boundaries of the ordinary.
Yet you will find many entries in the canon of those fields that might also be considered creative writing. No one would consign Truman Capote’s groundbreaking In Cold Blood to the sterile cells of mere journalism. But that haunting novel is unquestionably also an important work of investigative reporting.
So, what is creative writing, if a non-fiction novel of a horrific quadruple murder falls into the same scope as a classic of American literature like To Kill a Mockingbird ?
It has to do with style and art. Creative writing goes to the heart of the individual expressiveness of the writer. It breaks the boundaries of the typical. That’s an exercise of artistic skill that can happen in any topic, toward almost any goal. And it’s the heart of what it is to be a writer, no matter what you write about.
Defining creative writing isn’t easy. Rooms full of the best authorities routinely disagree. But what is creative writing , isn’t the most interesting question to ask here. Instead, we would be best served by asking another:
Why Is Creative Writing Important?

Storytellers were plying their craft thousands of years before the written word was invented. The creative spark doesn’t belong to words. It may not even depend on language. It draws instead on a deep part of what it is to be human. Invention, imagination, the urge to create… these are all deep and vital parts of the human experience.
Creative writing is important because it is evocative.
That well of creativity flows forth in many arts and forms of expression. But in creative writing it has found a medium where it can be both preserved and shared. It’s a method of human connection that has no expiration date, no geographical or even cultural limit.
Writers touch the souls of their contemporaries first. But like Shakespeare, Wordsworth, and Lady Murasaki, their reach may also span generations.
Creative Writing Fuels Communication in All Forms of Writing
Although fiction is the first refuge of creative writing, that expressiveness serves the purposes of just about any kind of author.
The goals of most other forms of writing are focused on various kinds of literal communication. A journalist seeks to convey the facts and the context of important news stories. Technical writers need to communicate the details of operating programs and machinery, clearly describing all kinds of minute details with zero ambiguity. Business communications are created with a view toward clarity and concision—helping readers get the main points of the piece quickly and without confusion.
Creative writing can also help to serve these purposes.
Creative writing taps into a different level of communication. While it may, and often does, aspire to other goals like offering clarity and detail, it also goes toward developing emotional connection. The reader will take away more than mere words from a piece of creative writing.
Creative Writing is Important For Making Other Kinds of Writing Compelling
Just as importantly, creative writing entertains. In a story about the importance of algorithmic and high-frequency trading, all kinds of technical details must be absorbed to make sense of the issues. Both technological and economic concepts have to be introduced. In a comprehensive article about the subject, readers from outside the field could be expected to nod off about two pages in.
But put the story in the hands of Michael Lewis, and you get Flash Boys , a New York Times Best Seller.
It’s not important that Flash Boys did well because it was entertaining, however. It’s important because the market trends and activities it described have real impacts on many of the readers. Retirement funds, college savings, family investments… all are affected by the story Flash Boys tells. Today, millions of readers who would never otherwise have understood how their investments were being handled can make an informed assessment… thanks to creative writing.
How To Separate Creative Writing From Less Creative Forms of Writing

In general, it’s safe to say that a piece of writing is creative when it makes use of literary devices such as:
- Narrative development
- Imagination and invention
In Cold Blood passes this test due to Capote’s use of characterization, plot development, and world-building. It’s considered today to be a pioneering example of the non-fiction novel, a paragon of the creative writing world.
The original crime reports, local newspaper articles, and subsequent court documents detail the same events with the same participants. Yet they are not works of creative writing. The incident is described in dry, straightforward, technical language. The timeline is linear and offered without consideration of pace or drama.
Both Capote and the authors of those other articles and documents set out to inform. But Capote’s goal was also to captivate.
New Journalism Tells the Story of How Creative Writing Has an Important Role in Non-Fiction

Books like Wolfe’s The Right Stuff mixed truth and dramatization, documentation and invention, to tell larger stories about serious events. In dramatizing those stories, New Journalism writers also drew more readers and achieved broader awareness of the stories.
At the same time, long-form New Journalism pieces, deeply researched and documented, were able to report stories in depth in a way that traditional journalism often did not. By invoking plot, characterization, and narrative structures, the New Journalists could keep readers involved in long and complex issues ranging from crime to politics to culture.
New Journalism is important in defining what is creative writing because it is clearly an example of both creative and journalistic writing. It demonstrates the ways that creative writing can serve other forms of writing and other kinds of writers.
Of course, it’s also possible to come at the divide from the other shore. Categories of writing that are clearly creative in nature include:
- Novels and novellas
- Flash fiction and short stories
- Plays and film scripts
These works incorporate elements of storytelling that may not always be present in other forms of writing. A newspaper article will often have a setting, action, and characters; creative writing will offer plot, pacing, and drama in describing the same story.
What is Creative Writing Coursework Like in College Degree Programs?

All university students are exposed to basic coursework in English language and communication skills. These all go to the elementary aspects of writing—the ability to construct a sentence, a paragraph, a paper. They teach grammatical rules and other elements that make a work readable to any reader of the English language.
Even the general education requirements in college programs touch on creative writing, however. Students may be assigned to write essays that explore creative styles and imagination. They’ll be assigned to read novels and stories that are time-tested examples of the finest kinds of creative writing. And they’ll be asked to explore their impressions and feelings, and to exercise their imaginations and analyze the intent of the author.
Creative writing programs go beyond the basics to touch the imagination of the writer.
Creative writing exists just on the other side of those general English and literature courses. Students in creative writing classes will be asked to take the extra step of creating their own stories using the techniques they have learned.
In fact, they may be encouraged to break the same rules that were so laboriously learned in their regular English writing classes. Creative writing works to allow writers to tap into their own imagination and emotion to forge a deeper connection with readers.
Student Workshops Offer an Interactive Way of Learning What Creative Writing Is All About
Creative writing degrees will go much further into developing a sense of what creative writing is. they continue to include many reading assignments. but instructors also introduce concepts such as:.
Genre is the method used to categorize written works. Creative writing programs explore the tropes and expectations that exist for different genres and deconstruct them for better understanding.
Story structure and form
The structure and form of a novel and a short story are very different. Creative writing programs explore different formats and how they impact creative storytelling.
Plot is not a universal feature of creative writing, but a good plot can make or break a creative work. Classes look at the features and composition of plot, and also teach plotting.
Voice, tone, and creative expression all come out of the narration of a piece of creative writing. Creative writing courses explore both the textbook forms of narrative and show how to use it to serve plot and story.
Style and rhythm
One clear feature of creative writing in all genres is that it rests on a sense of rhythm and of styling that other types of writing ignore. Many courses found in creative writing degree programs explore the ways in which writing style serves story and hooks the reader.
In addition to formal classes, students will better learn why creative writing is important and the purposes it serves through workshops. These informal gatherings are designed to foster discussion, to present examples of different types of writing, and to critique and hone individual creative writing skills .
Through that process, creative writing degrees help students better identify what creative writing is and how to use it effectively.

Creativity is Important No Matter What Your Career Goals in Writing May Be

Creative writing training allows writers in any genre to develop more complete, more meaningful, and more memorable ways to get a point across. Using the skills and techniques learned in creative writing courses can inject humor, gravity, and other sensations into any piece of writing. And those very techniques can improve concision and clarity.
Figuring out what creative writing is and what it is not, is the first thing you should leave behind in a writing career. The dry definitions of the dictionary or droning English professors are the last place you should look.
Creative writing is the process of engaging your imagination and talent to serve the purpose of whatever piece of writing you are working on. And that’s why creative writing is important.
What is Creative Writing?
Explore eight forms of creative writing, with tips and creative writing exercises to get you started.
You can bring a creative approach to any kind of writing—a recipe, a textbook, or an email, for example—but “creative writing” means something more specific. The creative writing category can be defined both by what it includes and excludes.
Creative writers are usually not aiming to transmit factual information to people who can use it (as in a recipe, technical writing, academic writing, or even an email). Rather, creative writers tend to have two primary goals that set their writing apart from other forms. Specifically, creative writers aim to: (1) express their unique imaginative perspective and (2) evoke an emotional response in the reader.
4. Creative Nonfiction
1. stand-up comedy, 2. speeches, 3. musical lyrics, 4. journaling, the bottom line on creative writing forms, the four primary categories of creative writing.

Suppose you study creative writing in the academic context, particularly in an MFA program. In that case, you will typically choose one or more of four big categories of writing: fiction, poetry, creative nonfiction, and drama (plays and screenplays).
In the context of creative writing, fiction is generally defined to include novels, novellas, and short stories. Fiction is imaginative (generally non-factual) storytelling constructed to take the reader on an emotional journey. Some of the essential literary devices that define fiction writing are setting, character development, point of view, linear cause and effect, a structure with a beginning/middle/end, dialogue, and exposition.
Some experimental fiction writers deliberately play with or even omit some of these conventions (for example, Kurt Vonnegut experiments with non-linearity in Slaughterhouse Five). However, they are present in nearly all fiction to one degree or another.
Because fiction is, by definition, not factual, it requires the reader to suspend their disbelief to one degree or another. Of course, some fiction is realist, meaning that it includes places, people, and events that either are real or could have been real. For example, in Harper Lee’s classic novel To Kill A Mockingbird, the town of Maycomb, the character Scout, and the plot events were made up. However, Lee’s writing was inspired by her childhood, and it is easy to imagine that it could have happened.
Non-realist fiction (such as science fiction, fantasy, or fabulism) uses settings, characters, or events that would be implausible if published as nonfiction but are believable in the context of the author’s fictional world. For example, Karen Russell’s short story “Orange World ” is about a new mother who makes a deal to breastfeed the devil in exchange for her baby’s safety. It would not be plausible as nonfiction, but the emotional urgency parents feel when it comes to protecting their children makes the story emotionally plausible within a fictional world in which the devil exists and makes deals.
Flash fiction (short stories under 1,000 words) are an excellent entry-point for experimenting with writing fiction. If brevity isn’t your strong suit, you can start writing fiction by creating an outline for a story or novel, or writing a detailed character sketch.
Poetry can take many forms, but generally, it is a style of creative writing that is: (1) focused on the aesthetic and rhythmic qualities of language, (2) condensed into a tight form with no inessential words, and (3) striving to express an idea or evoke an emotion that is difficult to put into words. Poetry can be fictional (referring to an imagined situation) or essentially nonfiction, based on the poet’s real experiences.
Some forms of poetry are much longer and denser (such as prose poems), while others are brief and leave lots of white space on the page. Some poetry is structured based on rules of rhyme and meter (such as a sonnet), while others are more anarchic (free verse).
Often poetry uses figurative language, such as similes, metaphors, and allegory, operates on multiple levels at once (the literal and the symbolic), or juxtaposes two unexpected elements. For example, Robert Frost’s short poem “The Road Not Taken” uses the metaphor of a walk in the woods to inspire the reader to think about how they choose the path they take through life.
To explore the possibilities that poetry has to offer, try choosing a subject and writing three poems about it using three different forms, such as free verse, a sonnet, and an erasure poem. An erasure poem is where you take a page of writing, such as a book page, and strategically redact most of the words with a pen or razor blade, so that the remaining words comprise the poem.
Have you seen our article on the 15 types of poetry every writer should know .

Although we usually think of creative writing being consumed directly via reading, other forms are consumed indirectly. Such as by observing performers who are enacting the writing. Common forms include theatrical plays, film screenplays, television scripts, and even operas.
Most drama uses a three-act structure similar to fiction. While drama is usually fiction, some (like the musicals Hamilton and Evita ) are based on a true story and fleshed out using fictional details.
Although these forms of creative writing tell a narrative story, much like fiction, they can use visual and auditory tools that aren’t available on the page. For example, in an early scene in Jordan Peel’s screenplay for the film Get Out , the protagonist and his girlfriend are driving and chatting when “A shadow darts across the road in front of the hood of the car. Its hind legs SMACK the hood of the car with a loud THWAT-THWAT.” Reading that description does not evoke fear, but the film’s audiovisual representation of the car hitting a deer is an effective jump-scare.
Plays and screenplays tend to use a specific format, which consists almost entirely of dialogue, along with very brief passages describing what the actors should do and how the setting should look. If you want to write this form, it is a good idea to watch lots of plays and movies and read plays and screenplays. You can find many film screenplays online with a simple Google search.
Creative nonfiction differs from fiction, poetry, and drama in that it transmits factual information to the reader. However, its purpose is generally to impact the reader’s thoughts or feelings rather than to provide actionable information (as in the case of other nonfiction, such as a recipe or self-help book). Creative nonfiction can be long-form (such as a memoir) or short form (such as a personal essay) and is virtually always in the first person.
What makes a piece of writing creative nonfiction, as opposed to other forms of nonfiction (such as journalism), is that creative nonfiction borrows the tools of other forms of creative storytelling (particularly fiction and poetry) to tell a true story in an emotionally compelling way. A creative essay might combine the lyricism of poetry, the deep characterization of a novel, and the three-act structure of a play, for example.
Creative nonfiction can also borrow elements of other nonfiction forms. For example, this excerpt from Maggie Nelson’s memoir Bluets combines poetic phrasing, the dramatization of a scene in prose, and an exploration of the theoretical writings of Goethe and Wittgenstein.
According to expert Phillip Lopate, one of the key concepts in creative nonfiction is the “double-perspective.” This is how personal essays and memoirs allow a writer to show not only their perspective when an event happened but their wiser retrospective understanding of that event. To practice creative nonfiction, try identifying an event that you’ve come to understand differently over time and write about that shift in your mindset.
Four Additional Forms of Creative Writing
While fiction, creative nonfiction, poetry, and playwriting/screenwriting are the most common genres included in academic creative writing programs, many other forms of writing fall into that category. Four examples are stand-up comedy, speech-writing, songwriting, and journaling.
Of course, any form of creative writing can include jokes, comedic scenes, or can have a comedic structure in the classical sense (Aristotle defined comedy as a story in which a ridiculous character starts low and ends high, in a happy ending). However, a stand-up comedy set is its own beast.
Stand-up comedy sets are inarguably a form of creative writing. A comedian’s primary objectives are to express the comedian’s unique perspective and create an emotional response in the audience. Like drama, comedy combines both writing and performance. Like poetry, stand-up sets are very tightly written, with the mindset that every word matters.
Most stand-up sets are written as narrative nonfiction, and many contain elements of social commentary. Two of the most impactful comedy sets in the last decade, for example, were Hannah Gadsby’s Peabody and Grammy Award-winning show Nanette , which addressed the prejudice she’d experienced as a lesbian, and the album Tig Notaro Live , a Grammy-nominated comedy album about Notaro’s cancer diagnosis that topped the Billboard charts.
While stand-up sets typically describe things that happened to the comedian, they are not limited to truthfulness like other nonfiction. It is not considered unethical to exaggerate, fictionalize, or even fabricate events described in a stand-up set, as long as it improves the jokes.
As in Gadsby and Notaro’s sets, sometimes the best comedy has an edge and addresses very serious subjects. If you want to try writing comedy, a good exercise is to identify an extremely negative experience in your life and look for a comedic perspective on it.
For more help on writing comedy, we can recommend six great comedy writing books .
Stand-up comedy and dramatic monologs are essentially speeches, and it is only fair to characterize other forms of speech-writing as creative writing. Of course, some speeches are improvised. Many, however, are the result of creative writing, revision, and memorization.
Speeches falling under the rubric of creative writing could include anything from the president’s congressional State of the Union address to the best man speech at your friend’s wedding. In either case, the writer of the speech typically aims to express a unique perspective and generate a particular emotional response in the listener (persuading them to trust the president or to believe that the bride and groom are soulmates, for example).
Most speeches have a higher expectation of truthfulness than comedy sets and certainly more than dramatic monologs. However, they also integrate elements of poetry and fiction, such as the use of themes and motifs.
Many people learn how to write speeches by participating in high school or college-level speech and debate or joining groups like Toastmasters. You could also find opportunities to practice by volunteering in the context of activism or community education. You might also be interested in these essays about creative writing .
The overlap between theater and opera makes it evident that writing music with lyrics should be included in the umbrella category of creative writing. However, any argument that creative writing shouldn’t include song lyrics was demolished in 2016, when Bob Dylan was awarded the Nobel Prize for Literature.
The overlap between lyrics and poetry is obvious. Both are short, efficient forms, which are always focused on the rhythm of language and often on rhyme. However, it is also common for lyrics to tell a fictional story, such as in Dylan’s song “Tangled Up in Blue,” or even nonfictional stories, as in his song “Hurricane,” about boxer Rubin Carter being framed for murder. Song lyrics may also include jokes. Like drama, lyrics are usually consumed by observing performers, rather than by reading.
Notwithstanding these overlaps, what sets lyrics apart from other creative writing categories (other than opera or musicals) is that lyrics are set to music. This requires a high level of skill in handling rhythm because not only must the internal rhythm of the lyrics work (as in a poem), they must resonate well with the music supporting them. If you don’t have a band, look for a karaoke version of a song you know and love to practice writing song lyrics. Then write your own new lyrics for it.
Journal writing is a little harder to fit in the creative writing category, as we’ve defined it. Although it is the ultimate form of self-expression, journals are typically not meant to be read by others. But, of course, if you become famous enough, your diary might one day become of interest to the public and publishable (such as Anne Frank’s The Diary of a Young Girl ).
Freewriting about your own life and experience is a valuable training technique for creative writers. The popular book and methodology The Artist’s Way , by Julia Cameron, advises hand-writing three pages every day, regardless of the content, in order to increase and enhance the creative drive for all artists, not just writers. As Virginia Woolf put it, “The habit of writing for my eye is good practice. It loosens the ligaments.”
However, a personal diary describing your secrets and feelings about your life is only one way to use a journal. Some people use journaling to brainstorm and pre-write in preparation for writing fiction or other forms. You can even take diary entries and revise them into m a memoir or poetry.
There is enormous overlap between the different types of creative writing, and practicing any of them will improve your writing skills, so there’s no reason to silo yourself. For example, poets can deepen their sense of meter by writing lyrics, journaling fans can write personal essays to share their insights with readers, and fiction writers can improve their dialogue by experimenting with writing drama. So stop pigeonholing yourself as a creative writer, and you may find your creativity far exceeds your expectations.

Bryan Collins is the owner of Become a Writer Today. He's an author from Ireland who helps writers build authority and earn a living from their creative work. He's also a former Forbes columnist and his work has appeared in publications like Lifehacker and Fast Company.
View all posts
Places on our 2024 summer school are filling fast. Don’t miss out. Enrol now to avoid disappointment
- What Is Creative Writing? The ULTIMATE Guide!

At Oxford Royale Academy, we offer a range of summer school programmes that have become extremely popular amongst students of all ages. The subject of creative writing continues to intrigue many academics as it can help to develop a range of skills that will benefit you throughout your career and life.
Nevertheless, that initial question is one that continues to linger and be asked time and time again: what is creative writing? More specifically, what does it mean or encompass? How does creative writing differ from other styles of writing?
During our Oxford Summer School programme , we will provide you with in-depth an immersive educational experience on campus in the colleges of the best university in the world. However, in this guide, we want to provide a detailed analysis of everything to do with creative writing, helping you understand more about what it is and why it could benefit you to become a creative writer.
The best place to start is with a definition.
What is creative writing?
The dictionary definition of creative writing is that it is original writing that expresses ideas and thoughts in an imaginative way. [1] Some academics will also define it as the art of making things up, but both of these definitions are too simplistic in the grand scheme of things.
It’s challenging to settle on a concrete definition as creative writing can relate to so many different things and formats. Naturally, as the name suggests, it is all built around the idea of being creative or imaginative. It’s to do with using your brain and your own thoughts to create writing that goes outside the realms of what’s expected. This type of writing tends to be more unique as it comes from a personal place. Each individual has their own level of creativity, combined with their own thoughts and views on different things. Therefore, you can conjure up your own text and stories that could be completely different from others.
Understanding creative writing can be challenging when viewed on its own. Consequently, the best way to truly understand this medium is by exploring the other main forms of writing. From here, we can compare and contrast them with the art of creative writing, making it easier to find a definition or separate this form of writing from others.
What are the main forms of writing?
In modern society, we can identify five main types of writing styles [1] that will be used throughout daily life and a plethora of careers:
- Narrative Writing
- Descriptive Writing
- Persuasive Writing
- Expository Writing
- Creative Writing
Narrative writing refers to storytelling in its most basic form. Traditionally, this involves telling a story about a character and walking the readers through the journey they go on. It can be a long novel or a short story that’s only a few hundred words long. There are no rules on length, and it can be completely true or a work of fiction.
A fundamental aspect of narrative writing that makes it different from other forms is that it should includes the key elements of storytelling. As per UX Planet, there are seven core elements of a good story or narrative [2] : the plot, characters, theme, dialogue, melody, decor and spectacle. Narrative writing will include all of these elements to take the ready on a journey that starts at the beginning, has a middle point, but always comes to a conclusion. This style of writing is typically used when writing stories, presenting anecdotes about your life, creating presentations or speeches and for some academic essays.
Descriptive writing, on the other hand, is more focused on the details. When this type of writing is used, it’s focused on capturing the reader’s attention and making them feel like they are part of the story. You want them to live and feel every element of a scene, so they can close their eyes and be whisked away to whatever place or setting you describe.
In many ways, descriptive writing is writing as an art form. Good writers can be given a blank canvas, using their words to paint a picture for the audience. There’s a firm focus on the five senses all humans have; sight, smell, touch, sound and taste. Descriptive writing touches on all of these senses to tell the reader everything they need to know and imagine about a particular scene.
This is also a style of writing that makes good use of both similes and metaphors. A simile is used to describe something as something else, while a metaphor is used to show that something is something else. There’s a subtle difference between the two, but they both aid descriptive writing immensely. According to many writing experts, similes and metaphors allow an author to emphasise, exaggerate, and add interest to a story to create a more vivid picture for the reader [3] .
Looking at persuasive writing and we have a form of writing that’s all about making yourself heard. You have an opinion that you want to get across to the reader, convincing them of it. The key is to persuade others to think differently, often helping them broaden their mind or see things from another point of view. This is often confused with something called opinionative writing, which is all about providing your opinions. While the two seem similar, the key difference is that persuasive writing is built around the idea of submitting evidence and backing your thoughts up. It’s not as simple as stating your opinion for other to read; no, you want to persuade them that your thoughts are worth listening to and perhaps worth acting on.
This style of writing is commonly used journalistically in news articles and other pieces designed to shine a light on certain issues or opinions. It is also typically backed up with statistical evidence to give more weight to your opinions and can be a very technical form of writing that’s not overly emotional.
Expository writing is more focused on teaching readers new things. If we look at its name, we can take the word exposure from it. According to Merriam-Webster [4] , one of the many definitions of exposure is to reveal something to others or present them with something they otherwise didn’t know. In terms of writing, it can refer to the act of revealing new information to others or exposing them to new ideas.
Effectively, expository writing focuses on the goal of leaving the reader with new knowledge of a certain topic or subject. Again, it is predominately seen in journalistic formats, such as explainer articles or ‘how-to’ blogs. Furthermore, you also come across it in academic textbooks or business writing.
This brings us back to the centre of attention for this guide: what is creative writing?
Interestingly, creative writing is often seen as the style of writing that combines many of these forms together in one go. Narrative writing can be seen as creative writing as you are coming up with a story to keep readers engaged, telling a tale for them to enjoy or learn from. Descriptive writing is very much a key part of creative writing as you are using your imagination and creative skills to come up with detailed descriptions that transport the reader out of their home and into a different place.
Creative writing can even use persuasive writing styles in some formats. Many writers will combine persuasive writing with a narrative structure to come up with a creative way of telling a story to educate readers and provide new opinions for them to view or be convinced of. Expository writing can also be involved here, using creativity and your imagination to answer questions or provide advice to the reader.
Essentially, creative writing can combine other writing types to create a unique and new way of telling a story or producing content. At the same time, it can include absolutely none of the other forms at all. The whole purpose of creative writing is to think outside the box and stray from traditional structures and norms. Fundamentally, we can say there are no real rules when it comes to creative writing, which is what makes it different from the other writing styles discussed above.
What is the purpose of creative writing?
Another way to understand and explore the idea of creative writing is to look at its purpose. What is the aim of most creative works of writing? What do they hope to provide the reader with?
We can look at the words of Bryanna Licciardi, an experienced creative writing tutor, to understand the purpose of creative writing. She writes that the primary purpose is to entertain and share human experiences, like love or loss. Writers attempt to reveal the truth with regard to humanity through poetics and storytelling. [5] She also goes on to add that the first step of creative writing is to use one’s imagination.
When students sign up to our creative writing courses, we will teach them how to write with this purpose. Your goal is to create stories or writing for readers that entertain them while also providing information that can have an impact on their lives. It’s about influencing readers through creative storytelling that calls upon your imagination and uses the thoughts inside your head. The deeper you dive into the art of creative writing, the more complex it can be. This is largely because it can be expressed in so many different formats. When you think of creative writing, your instinct takes you to stories and novels. Indeed, these are both key forms of creative writing that we see all the time. However, there are many other forms of creative writing that are expressed throughout the world.
What are the different forms of creative writing?
Looking back at the original and simple definition of creative writing, it relates to original writing in a creative and imaginative way. Consequently, this can span across so many genres and types of writing that differ greatly from one another. This section will explore and analyse the different types of creative writing, displaying just how diverse this writing style can be – while also showcasing just what you’re capable of when you learn how to be a creative writer.
The majority of students will first come across creative writing in the form of essays . The point of an essay is to present a coherent argument in response to a stimulus or question. [6] In essence, you are persuading the reader that your answer to the question is correct. Thus, creative writing is required to get your point across as coherently as possible, while also using great descriptive writing skills to paint the right message for the reader.
Moreover, essays can include personal essays – such as writing a cover letter for work or a university application. Here, great creativity is needed to almost write a story about yourself that captivates the reader and takes them on a journey with you. Excellent imagination and persuasive writing skills can help you tell your story and persuade those reading that you are the right person for the job or university place.
Arguably, this is the most common way in which creative writing is expressed. Fictional work includes novels, novellas, short stories – and anything else that is made up. The very definition of fiction by the Cambridge Dictionary states that it is the type of book or story that is written about imaginary characters and events not based on real people and facts. [7] As such, it means that your imagination is called upon to create something out of nothing. It is a quintessential test of your creative writing skills, meaning you need to come up with characters, settings, plots, descriptions and so much more.
Fictional creative writing in itself takes on many different forms and can be completely different depending on the writer. That is the real beauty of creative writing; you can have entirely different stories and characters from two different writers. Just look at the vast collection of fictional work around you today; it’s the perfect way to see just how versatile creative writing can be depending on the writer.
Similarly, scripts can be a type of creative writing that appeals to many. Technically, a script can be considered a work of fiction. Nevertheless, it depends on the script in question. Scripts for fictional television shows, plays or movies are obviously works of fiction. You, the writer, has come up with the characters and story of the show/play/movie, bringing it all to life through the script. But, scripts can also be non-fictional. Creating a play or movie that adapts real-life events will mean you need to write a script based on something that genuinely happened.
Here, it’s a perfect test of creative writing skills as you take a real event and use your creative talents to make it more interesting. The plot and narrative may already be there for you, so it’s a case of using your descriptive writing skills to really sell it to others and keep readers – or viewers – on the edge of their seats.
A speech is definitely a work of creative writing. The aim of a speech can vary depending on what type of speech it is. A politician delivering a speech in the House of Commons will want to get a point across to persuade others in the room. They’ll need to use creative writing to captivate their audience and have them hanging on their every word. A recent example of a great speech was the one by Sir David Attenborough at the recent COP26 global climate summit. [8] Listening to the speech is a brilliant way of understanding how creative writing can help get points across. His speech went viral around the world because of how electrifying and enthralling it is. The use of many descriptive and persuasive words had people hanging onto everything he said. He really created a picture and an image for people to see, convincing them that the time is now to work on stopping and reversing climate change.
From this speech to a completely different one, you can see creative writing at play for speeches at weddings and other jovial events. Here, the purpose is more to entertain guests and make them laugh. At the same time, someone giving a wedding speech will hope to create a lovely story for the guests to enjoy, displaying the true love that the married couple share for one another. Regardless of what type of speech an individual is giving, creative writing skills are required for it to be good and captivating.
Poetry & Songs
The final example of creative writing is twofold; poetry and songs. Both of these formats are similar to one another, relying on creativity to deliver a combination of things. Poetry can take so many forms and styles, but it aims to inspire readers and get them thinking. Poems often have hidden meanings behind them, and it takes a great deal of imagination and creativity to come up with these meanings while also creating a powerful poem. Some argue that poetry is the most creative of all creative writing forms.
Songwriting is similar in that you use creativity to come up with lyrics that can have powerful meanings while also conjuring up a story for people. The best songwriters will use lyrics that stay in people’s minds and get them thinking about the meaning behind the song. If you lack imagination and creativity, you will never be a good songwriter.
In truth, there are so many other types and examples of creative writing that you can explore. The ones listed above are the most common and powerful, and they all do a great job of demonstrating how diverse creative writing can be. If you can hone your skills in creative writing, it opens up many opportunities for you in life. Primarily, creative writing focuses on fictional pieces of work, but as you can see, non-fiction also requires a good deal of creativity.
What’s needed to make a piece of creative writing?
Our in-depth analysis of creative writing has led to a point where you’re aware of this style of writing and its purpose, along with some examples of it in the real world. The next question to delve into is what do you need to do to make a piece of creative writing. To phrase this another way; how do you write something that comes under the creative heading rather than another form of writing?
There is an element of difficulty in answering this question as creative writing has so many different types and genres. Consequently, there isn’t a set recipe for the perfect piece of creative writing, and that’s what makes this format so enjoyable and unique. Nevertheless, we can discover some crucial elements or principles that will help make a piece of writing as creative and imaginative as possible:
A target audience
All creative works will begin by defining a target audience. There are many ways to define a target audience, with some writers suggesting that you think about who is most likely to read your work. However, this can still be challenging as you’re unsure of the correct demographic to target. Writer’s Digest makes a good point of defining your target audience by considering your main motivation for writing in the first place. [9] It’s a case of considering what made you want to start writing – whether it’s a blog post, novel, song, poem, speech, etc. Figuring out your motivation behind it will help you zero in on your target audience.
Defining your audience is vital for creative writing as it helps you know exactly what to write and how to write it. All of your work should appeal to this audience and be written in a way that they can engage with. As a simple example, authors that write children’s stories will adapt their writing to appeal to the younger audience. Their stories include lots of descriptions and words that children understand, rather than being full of long words and overly academic writing.
Establishing the audience lets the writer know which direction to take things in. As a result, this can aid with things like character choices, plot, storylines, settings, and much more.
A story of sorts
Furthermore, great works of creative writing will always include a story of sorts. This is obvious for works such as novels, short stories, scripts, etc. However, even for things like poems, songs or speeches, a story helps make it creative. It gives the audience something to follow, helping them make sense of the work. Even if you’re giving a speech, setting a story can help you create a scene in people’s minds that makes them connect to what you’re saying. It’s a very effective way of persuading others and presenting different views for people to consider.
Moreover, consider the definition of a story/narrative arc. One definition describes it as a term that describes a story’s full progression. It visually evokes the idea that every story has a relatively calm beginning, a middle where tension, character conflict and narrative momentum builds to a peak and an end where the conflict is resolved. [10]
Simplifying this, we can say that all works of creative writing need a general beginning, middle and end. It’s a way of bringing some sort of structure to your writing so you know where you are going, rather than filling it with fluff or waffle.
A good imagination
Imagination is a buzzword that we’ve used plenty of times throughout this deep dive into creative writing. Every creative writing course you go on will spend a lot of time focusing on the idea of using your imagination. The human brain is a marvellously powerful thing that holds the key to creative freedom and expressing yourself in new and unique ways. If you want to make something creative, you need to tap into your imagination.
People use their imagination in different ways; some will be able to conjure up ideas for stories or worlds that exist beyond our own. Others will use theirs to think of ways of describing things in a more creative and imaginative way. Ultimately, a good imagination is what sets your work apart from others within your genre. This doesn’t mean you need to come up with the most fantastical novel of all time to have something classified as creative writing. No, using your imagination and creativity can extend to something as simple as your writing style.
Ultimately, it’s more about using your imagination to find your own personal flair and creative style. You will then be able to write unique pieces that stand out from the others and keep audiences engaged.
How can creative writing skills benefit you?
When most individuals or students consider creative writing, they imagine a world where they are writing stories for a living. There’s a common misconception that creative writing skills are only beneficial for people pursuing careers in scriptwriting, storytelling, etc. Realistically, enhancing ones creative writing skills can open up many windows of opportunity throughout your education and career.
- Improve essay writing – Naturally, creative writing forms a core part of essays and other written assignments in school and university. Improving your skills in this department can help a student get better at writing powerful essays and achieving top marks. In turn, this can impact your career by helping you get better grades to access better jobs in the future.
- Become a journalist – Journalists depend on creative writing to make stories that capture audiences and have people hanging on their every word. You need high levels of creativity to turn a news story into something people are keen to read or watch.
- Start a blog – In modern times, blogging is a useful tool that can help people find profitable and successful careers. The whole purpose of a blog is to provide your opinions to the masses while also entertaining, informing and educating. Again, having a firm grasp of creative writing skills will aid you in building your blog audience.
- Write marketing content – From advert scripts to content on websites, marketing is fuelled by creative writing. The best marketers will have creative writing skills to draw an audience in and convince them to buy products. If you can learn to get people hanging on your every word, you can make it in this industry.
These points all demonstrate the different ways in which creative writing can impact your life and alter your career. In terms of general career skills, this is one that you simply cannot go without.
How to improve your creative writing
One final part of this analysis of creative writing is to look at how students can improve. It begins by reading as much as you can and taking in lots of different content. Read books, poems, scripts, articles, blogs – anything you can find. Listen to music and pay attention to the words people use and the structure of their writing. It can help you pick up on things like metaphors, similes, and how to use your imagination. Of course, writing is the key to improving; the more you write, the more creative you can get as you will start unlocking the powers of your brain.
Conclusion: What is creative writing
In conclusion, creative writing uses a mixture of different types of writing to create stories that stray from traditional structures and norms. It revolves around the idea of using your imagination to find a writing style that suits you and gets your points across to an audience, keeping them engaged in everything you say. From novels to speeches, there are many forms of creative writing that can help you in numerous career paths throughout your life.
[1] SkillShare: The 5 Types of Writing Styles with Examples
[2] Elements of Good Story Telling – UX Planet
[3] Simile vs Metaphor: What’s the Difference? – ProWritingAid
[4] Definition of Exposure by Merriam-Webster
[5] The Higher Purpose of Creative Writing | by Terveen Gill
[6] Essay purpose – Western Sydney University
[7] FICTION | meaning in the Cambridge English Dictionary
[8] ‘Not fear, but hope’ – Attenborough speech in full – BBC News
[9] Writer’s Digest: Who Is Your Target Reader?
[10] What is a Narrative Arc? • A Guide to Storytelling Structure

Ebooks, Publishing, and Everything in Between
- Downloads & Pricing
- Advertising
Exploring the Different Types of Creative Writing
- on Sep 26, 2022
- in Writing Tips
- Last update: November 16th, 2023
Writing comes in all forms and sizes. But in order for a work to be considered creative writing, it must come from a place of imagination and emotion.
This is something many people pursuing a creative writing degree online at first struggle to get a handle on. Take for example what Franz Kafa said about creative writing, “Don’t bend; don’t water it down; don’t try to make it logical; don’t edit your own soul according to the fashion. Rather, follow your most intense obsessions mercilessly.”
Many authors who choose to follow Kafka’s advice—to write “mercilessly” and from the soul—find it comforting that their writing doesn’t have to conform to one style. But this variety of types and forms might leave some writers a bit confused.
That’s why, in this article, we are going to walk you through the most popular types of creative writing, with some great examples from authors who absolutely rocked their respective forms.

In this article:
- Creative Writing Definition
- Creative Writing Techniques
- Free Writing
- Journal Diaries
- Personal Essays
- Short Fiction
- Novels/Novellas
What Is Creative Writing?
Think of creative writing as a form of artistic expression. Authors bring this expression to life using their imagination, personal writing style, and personality.
Creative writing is also different from straightforward academic or technical writing. For instance, an economics book like Khalid Ikram’s The Political Economy of Reforms in Egypt is an academic monograph. This means that readers would rightfully expect it to contain analytic rather than creative writing.
So what are some elements that make a written piece more creative than analytic?
Popular Techniques Used in Creative Writing
Despite the fact that creative writing can be “freer” and less traditional than academic writing, it is likely to contain one or more of the following six elements:
1. Literary Devices
Many creative writers use literary devices to convey the meaning and themes of their work. Some common literary devices are allegories , metaphors and similes , foreshadowing , and imagery . These all serve to make the writing more vivid and descriptive .
2. Narrative
Authors often use this technique to engage readers through storytelling. Narrative isn’t limited to novels and short stories; poems, autobiographies, and essays can be considered narratives if they tell a story. This can be fiction (as in novels) or nonfiction (as in memoirs and essays).
3. Point of View
All creative writing must have a point of view; that’s what makes it imaginative and original. The point of view is the perspective from which the author writes a particular piece. Depending on the type of work, the point of view can be first person, third person omniscient, third person limited , mixed (using third- and first-person writing), or—very rarely—second person.
4. Characterization
Characterization is the process by which authors bring their characters to life by assigning them physical descriptions, personality traits, points of view, background and history, and actions. Characterization is key in creative writing because it helps drive the plot forward.
5. Dialogue
An important element used in many creative writing works is dialogue . Assigning
dialogue to characters is a way for authors to show their characters’ different traits without explicitly listing them.
Dialogue also immerses readers in the narrative’s action by highlighting the emotions and tensions between characters. Like characterization, it also helps drive the plot forward.
6. Plot
The plot is the sequence of events that make up a narrative and establish the themes and conflicts of a work . Plots will usually include an exp osi tion (the introduction), rising action (the complications), climax (the peak in action and excitement), falling action (the revelations and slowing down of events), and denouement (the conclusion).

The Main Types of Creative Writing (With Examples)
What’s great about creative writing is that there are so many types to choose from. In this section, we’ll walk you through the most popular types of creative writing, along with some examples.
Type 1: Free writing
Free writing, also known as stream-of-consciousness writing, is a technique that allows words and images to spill onto the page without giving thought to logic, sequence, or grammar. Although authors often use it as an exercise to get rid of the infamous writer’s block , free writing is also useful within a larger work.
For instance, let’s take a look at this excerpt from Toni Morrison’s novel Beloved.
Beloved by Toni Morrison [an excerpt]
the air is heavy I am not dead I am not there is a house there is what she whispered to me I am where she told me I am not dead I sit the sun closes my eyes when I open them I see the face I lost Sethe’s is the face that left me Sethe sees me see her and I see the smile her smiling face is the place for me it is the face I lost she is my face smiling at me
Note how the author uses free writing to convey the character’s disjointed and agitated thoughts. Even punctuation has been set aside here, adding to the rush of the character’s fear and confusion. The imagery is powerful (“the sun closes my eyes”; “her smiling face is the place for me”) and relies on repetitions like “I am not dead” and “I see” to immerse the readers in the character’s disturbed mental state.
Type 2: Journals and Diaries
A journal is a written account of an author’s experiences, activities, and feelings. A diary is an example of a journal, in which an author documents his/her life frequently.
Journals and diaries can be considered creative writing, particularly if they offer more than just a log of events. For instance, if a diary entry discusses how the writer ran into an old friend, it might include details of the writer’s emotions and probably use literary devices to convey these feelings.
It’s almost impossible to read the word “diary” and not think of Anne Frank. Let’s look at this excerpt from her work The Diary of a Young Girl .
Anne Frank: The Diary of a Young Girl [an excerpt]
Saturday, 20 June, 1942: I haven’t written for a few days, because I wanted first of all to think about my diary. It’s an odd idea for someone like me to keep a diary; not only because I have never done so before, but because it seems to me that neither I—nor for that matter anyone else—will be interested in the unbosomings of a thirteen-year-old schoolgirl. Still, what does that matter? I want to write, but more than that, I want to bring out all kinds of things that lie buried deep in my heart.
In the extract above, Anne adopts a reflective tone. She uses the rhetorical question “what does that matter?” to illustrate how she arrived at the conclusion that this diary will help bring out what is “buried deep in her heart.”
In this way, the diary serves as a log of events that happened in Anne’s life, but also as a space for Anne to reflect on them, and to explore her resulting emotions.
Type 3: Memoir
Although they might seem similar at first, memoirs and diaries are two different creative writing types. While diaries offer a log of events recorded at frequent intervals, memoirs allow the writer to select key moments and scenes that help shed light on the writer’s life.
Let’s examine this excerpt from the memoir of Roxanne Gay, author of Bad Feminist .
Hunger: A Memoir of (My) Body by Roxanne Gay:
I ate and ate and ate in the hopes that if I made myself big, my body would be safe. I buried the girl I was because she ran into all kinds of trouble. I tried to erase every memory of her, but she is still there, somewhere . . . I was trapped in my body, one that I barely recognized or understood, but at least I was safe.
Roxanne Gay offers readers a powerful work on anxiety, food, and body image by taking them on a journey through her past . Using evocative imagery in the excerpt above (“I buried the girl I was”; “I was trapped in my body”) the author shares her psychological trauma and resulting tumultuous relationship with food.
As with most memoirs—and diaries—this one is intimate, allowing readers into the dark crevices of the author’s mind. However, unlike a diary, this memoir does not provide an account of the writer’s day-to-day life, but rather focuses on certain events—big and small—that the author feels made her who she is today.
Type 4: Letters
Unlike diary and journal entries—which usually don’t have a specific recipient—letters address one target reader. Many famous authors have had collections of their letters published, revealing a side of them that isn’t visible in other works.
Letter writing uncovers the nature of the relationship between sender and recipient, and can include elements of creative writing such as imagery, opinion, humor, and feeling.
Here is an excerpt from a letter by Truman Capote, author of Breakfast at Tiffany’s and In Cold Blood .
Too Brief a Treat: The Letters of Truman Capote , edited by Gerald Clarke
Dear Bob; Have come, am here, am slowly freezing to death; my fingers are pencils of ice. But really, all told, I think this is quite a place, at least so far. The company is fairly good… I have a bedroom in the mansion (there are bats circulating in some of the rooms, and Leo keeps his light on all night, for the wind blows eerily, doors creak, and the faint cheep cheep of the bats cry in the towers above: no kidding.
In his letter to editor and friend Robert “Bob” Linscott, Truman paints a scene of his new setting . He uses hyperbole (“freezing to death”) and a powerful metaphor (“my fingers are pencils of ice”) to convey the discomforting cold weather. Truman also uses sound imagery (“doors creak”; “wind blows eerily”; “cheep cheep of the bats”) to communicate the creepy, sinister mood to his reader.
Type 5: Personal Essays
Many of us don’t normally think of essays as creative writing, but that’s probably because our minds go to academic research essays. However, there are many types of essays that require creative rather than analytic writing, including discursive essays, descriptive essays, and personal essays.
A personal essay, also known as a narrative essay, is a piece of nonfiction work that offers readers a story drawn from the author’s personal experience. This is different from a memoir, in which the primary focus is on the author and their multiple experiences.
A personal essay, on the other hand, focuses on a message or theme , and the author’s personal experience is there to communicate that theme using memorable characters and setting , as well as engaging events . These, of course, all have to be true, otherwise the personal essay would turn into a fictional short story.
Here is an excerpt from a personal essay by writers Chantha Nguon and Kim Green.
The Gradual Extinction of Softness by Chantha Nguon and Kim Green
In 1975, the Khmer Rouge informed the Cambodian people that we had no history, but we knew it was a lie. Cambodia has a rich past, a mosaic of flavors from near and far: South Indian traders gave us Buddhism and spicy curries; China brought rice noodles and astrology; and French colonizers passed on a love of strong coffee, flan, and a light, crusty baguette. We lifted the best tastes from everywhere and added our own.
The opening of this paragraph establishes the author’s strong and unwavering opinion : “we knew it was a lie.” Instead of providing a history of Cambodia, she demonstrates the country’s rich past by discussing its diverse “flavors”: “spicy curries”; “strong coffee”; “light, crusty baguette”, etc.
Using gustatory imagery , which conveys a sense of taste , the authors reveal their personal version of what makes Cambodia wonderful. The writer communicates the essay’s theme of food and memories through a story of her childhood.
Type 6: Poetry
Robert Frost once wrote: “Poetry is when an emotion has found its thought and the thought has found words.” Good poetry is effective because it uses the power of imagery to convey what it is to be human. Every word in a poem counts, and the best poems are those that evoke the reader’s emotions without unpacking too much.
As one of the most diverse types of creative writing, poetry can come in many forms. Some poets prefer to write in the more traditional forms such as sonnets , villanelles , and haikus , where you have particular structures, rhyme, and rhythm to follow. And others prefer the freedom of free verse and blackout poetry .
Let’s take a look at this excerpt from Maya Angelou’s powerful lyric poem , “Still I Rise.”
“Still I Rise” from And Still I Rise: A Book of Poems by Maya Angelou
Out of the huts of history’s shame I rise Up from a past that’s rooted in pain I rise I’m a black ocean, leaping and wide, Welling and swelling I bear in the tide. Leaving behind nights of terror and fear I rise Into a daybreak that’s wondrously clear I rise Bringing the gifts that my ancestors gave, I am the dream and the hope of the slave. I rise I rise I rise.
Packed with powerful language, this excerpt from Angelou’s poem gives us absolute
chills! The refrain “I rise” is repeated 7 times in these two verses alone,
hammering home the idea that the speaker cannot be defeated.
The imagery, repetition, and rhyme scheme all work together to convey the emotions of pride and resilience. Both verses also rely heavily on metaphors (“I’m a black ocean”; “I am the dream and the hope of the slave”) to convey the speaker’s power. She is not like an ocean or a dream; she is both, and she is unstoppable.
Type 7: Song Lyrics
Song lyrics are in many ways similar to poems, except that lyrics are meant to be sung . They are a form of creative writing that allows writers to surpass the rules of grammar and punctuation in favor of creating rhyme and rhythm . This means that the creativity of a song lyricist is free from the traditional restrictions of language.
Type 8: Scripts
Scriptwriting is a form of creative writing that relies heavily on character dialogue , stage directions , and setting . Scripts are written for films and TV shows (known as screenplays and teleplays), stage plays, commercials, and radio and podcast programs.
Like song lyrics, scripts are written with the intention of reaching a non-reading audience. In other words, scriptwriters must bear in mind how their writing will be 1) interpreted by other storytellers , such as directors, designers, etc., and 2) performed by actors.
Let’s examine the iconic opening scene from the screenplay of the film Forrest Gump .
Forrest Gump , screenplay by Eric Roth [an excerpt]
THE MAN Hello, I’m Forrest. I’m Forrest Gump. She nods, not much interested. He takes an old candy kiss out of his pocket. Offering it to her: FORREST (cont’d) Do you want a chocolate? She shakes “no.” He unwraps it, popping it in his mouth. FORREST (cont’d) I could eat about a million and a half of these. Mama said, “Life was just a box of chocolates. You never know what you gonna get.”
From the dialogue and stage directions in this opening scene, the audience can see that there is something innocent, kind-hearted, and simple about the character Forrest Gump. This is conveyed through the way he introduces himself with a slight repetition (“I’m Forrest. I’m Forrest Gump.”) to a complete stranger, and the way he quotes his mother to her.
Moreover, the action of Forrest “popping” the candy in his mouth is almost childlike , and that the stranger is reluctant to communicate with him foreshadows the fact that the people Forrest meets are initially suspicious of him and his innocence. Thus, the pauses and silences in the scene are just as important to the work as what is explicitly said.
Type 9: Short Fiction
Short fiction is a form of creative fiction writing that typically falls between 5,000 to 10,000 words ; however, there is definitely room to go lower than 5,000 words, depending on the topic.
For instance, flash fiction is a form of short fiction that can be 1,000 words or less. In the case of flash fiction, the author unpacks the “skeleton” of a story in as few words as possible. For instance, legend has it that Ernest Hemingway wrote a 6-word “story”:
For sale: baby shoes, never worn.
In just six words, the reader is led to understand that this is a story of death and loss.
Nevertheless, the average short story is usually structured around the following elements: characterization , setting , plot , and conflict . Many fiction authors start out writing short fiction because it enables them to nail all the essential elements, which they can then expand upon in longer works.
Let’s look at an excerpt from Janet Frame’s short story, “The Bath”
“The Bath” by Janet Frame [an excerpt]
She leaned forward, feeling the pain in her back and shoulder. She grasped the rim of the bath but her fingers slithered from it almost at once. She would not pancic, she told herself; she would try gradually, carefully, to get out. Again she leaned forward; again her grip loosened as if iron hands had deliberately uncurled her stiffened blue fingers from their trembling hold. Her heart began to beat faster, her breath came more quickly, her mouth was dry. She moistened her lips. If I shout for help, she thought, no-one will hear me. No-one in the world will hear me. No-one will know I’m in the bath and can’t get out.
In this paragraph, there is an image of a frail, old woman, physically unable to get out of her bathtub. The diction , or word choice, serves to convey the woman’s sense of fear and helplessness. For instance, words like “grasped,” “slithered,” “uncurled,” and “stiffened,” demonstrate the immense effort it takes for her to try to get out.
The image of her “moistening” her lips illustrates that fear has turned her mouth dry. And the repetition of “no-one” in the last few sentences highlights the woman’s loneliness and entrapment —two of the story’s main themes. Indeed, the bath symbolizes the unavoidable obstacles brought about by old age.
Type 10: Novellas / Novels
Novels are one of the most popular forms of creative writing. Though they vary in length, depending on the subject, they’re generally considered a long form of fiction , typically divided into chapters .
Novellas, on the other hand, are shorter than novels but longer than short stories. Like short stories, novels, and novellas contain characters , plot , dialogue , and setting ; however, their longer forms allow writers a chance to delve much deeper into those elements.
Type 11: Speeches
Speeches are a form of writing similar to essays in that both forms are non-fiction , and both usually entail a discussion of the writer’s personal experiences and include engaging events and a particular theme.
However, speeches differ from essays in that the former are meant to be recited (usually in front of an audience), and tend to be persuasive and inspirational. For instance, think of the purpose of graduation speeches and political speeches: they aim to inspire and move listeners.
One of the most well-known speeches from the 20th century is Martin Luther King’s “I Have a Dream”. Let’s examine the excerpt below:
“I Have a Dream” by Martin Luther King [an excerpt]
Now is the time to make real the promises of democracy. Now is the time to rise from the dark and desolate valley of segregation to the sunlit path of racial justice. Now is the time to lift our nation from the quicksands of racial injustice to the solid rock of brotherhood. Now is the time to make justice a reality for all of God’s children.
What immediately catches the eye (and ear) in this paragraph is the speaker’s usage of anaphora : the repetition of the phrase “now is the time” serves to emphasize the urgency of the matter being discussed (i.e. the prevalence of racial injustice).
The speaker’s repetition of the pronoun “our” is an appeal to his audience’s emotions and their sense of unity. Both he and they are in this together, and thus he is motivating them to take on the challenge as one.
Moreover, the use of figurative language is abundant here and can be found in similar inspirational and motivational styles of creative writing. The imagery created by the metaphor and alliteration in “the d ark and d esolate valley of segregation,” and its juxtaposition with “sunlit path of racial justice,” together aim to convey the speaker’s main message. Segregation has brought nothing but darkness and ruin to American society, but there is hope and light on the path toward racial equality.
Final Thoughts
Creative writing acts as a medium for artistic expression. It can come in a variety of forms, from screenplays and speeches to poetry and flash fiction. But what groups all of these different types of creative writing under the “creative” umbrella, regardless of form, is their display of a writer’s imagination, creativity, and linguistic prowess.
How to Write the Best Book Introduction
Making Use of Humor in Writing
4 Different Types of Writing You Need to Understand
I appreciate you offering such a thought-provoking perspective. It should be useful for academic writing in addition to creative writing, in my opinion. Each method you listed is pertinent and appropriate.
You’re absolutely right! Many of these writing methods can be applied to both creative and academic writing, enhancing the depth and effectiveness of communication.
Robert smith enago
Thank you for sharing this enlightening blog post on the various types of creative writing. Your exploration of different writing methods and styles provides an inspiring perspective on the boundless possibilities within the realm of creativity.
It is remarkable to see how creative writing encompasses an array of forms, each with its unique allure and artistic essence. From poetry, fiction, and drama to screenwriting, creative nonfiction, and even songwriting, each avenue offers writers a chance to express their thoughts, emotions, and imagination in captivating ways.
We truly appreciate your kind words! Creative writing is indeed a vast and fascinating world with endless opportunities for self-expression 🙂
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Currently you have JavaScript disabled. In order to post comments, please make sure JavaScript and Cookies are enabled, and reload the page. Click here for instructions on how to enable JavaScript in your browser.

Kotobee is the complete end-to-end ebook solution for you and your business. Export multiple formats. Deliver securely.
Create, publish, and sell ebooks with ease
Kotobee es la solución completa de ebooks de extremo a extremo para usted y su empresa.
Cree, publique y venda libros electrónicos con facilidad

Recent Posts
- LMS Integration: Types, Examples, and Best Practices
- How to Edit a Book for Publishing: Tips & Best Practices
- Book Royalties: What They Are and How to Earn the Best Rates
- Game-Based Learning: What It Is, and How to Apply It
- How to Publish a Book for Free and Maximize Your Profit
- Entries feed
- Comments feed
- WordPress.org
A Look Into Creative Writing | Oxford Summer Courses
Exploring the magic of creative writing with oxford summer courses.
Subscribe to our newsletter to receive helpful tips, tutorials, and thought-provoking articles that can inform and inspire your professional development. Sign up here .
Defining Creative Writing
Creative writing , as taught at Oxford Summer Courses, is the process of crafting original and imaginative works of literature, poetry, prose, or scripts. It transcends conventional writing, encouraging individuals to explore language, structure, and narrative. Whether it's a heartfelt poem, a captivating short story, or a thought-provoking novel, creative writing allows us to communicate our unique perspectives and experiences with the world.
The Magic of Imagination
Creative Writing is a catalyst that sparks our creativity and empowers us to breathe life into our ideas on the page. With Oxford Summer Courses, aspiring writers aged 16-24 can embark on an extraordinary journey of creative expression and growth. Immerse yourself in the captivating realms of Oxford and Cambridge as you explore our inspiring creative writing programs. Teleport readers to distant lands, realms of fantasy and creation, introduce them to captivating characters, and craft new worlds through the transformative art of storytelling. Discover more about our creative writing course here . Unleash your imagination and unlock the writer within.
What Are the Different Types of Creative Writing?
Creative Writing comes in many forms, encompassing a range of genres and styles. There are lots of different types of Creative Writing, which can be categorised as fiction or non-fiction. Some of the most popular being:
- Biographies
- Fiction: novels, novellas, short stories, etc.
- Poetry and Spoken word
- Playwriting/Scriptwriting
- Personal essays
At Oxford Summer Courses, students have the opportunity to delve into these various types of Creative Writing during the Summer School.
The Benefits of Creative Writing with Oxford Summer Courses
Engaging in Creative Writing with Oxford Summer Courses offers numerous benefits beyond self-expression. By joining our dedicated Creative Writing summer school programme, you would:
- Foster self-discovery and gain a deeper understanding of your thoughts, emotions, and personal experiences.
- Improve your communication skills, honing your ability to express yourself effectively and engage readers through refined language and storytelling abilities.
- Enhance empathy by exploring diverse perspectives and stepping into the shoes of different characters, broadening your understanding of the world around you.
- Gain new skills for further education or work, expanding your repertoire of writing techniques and abilities to enhance your academic or professional pursuits.
- Nurture your creativity, encouraging you to think outside the box, embrace unconventional ideas, and challenge the status quo, fostering a life-long mindset of innovation and originality.
Embracing the Journey
To embark on a journey of creative writing, embrace curiosity, take risks, and surrender to the flow of imagination. Write regularly, read widely, embrace feedback from tutors and peers at Oxford Summer Courses. Begin to experiment with styles and genres, and stay persistent in your course of action. The path of creative writing requires dedication, practice, and an open mind. Join us as we provide tips to help you start your creative writing journey and unleash your full creative potential under the guidance of industry professionals.
Creative Writing is a remarkable voyage that invites us to unleash our imagination, share our stories, and inspire others. It offers countless personal and professional benefits, nurturing self-expression, empathy, and creativity. So, grab a pen, open your mind, and embark on this enchanting journey of creative writing with Oxford Summer Courses. Let your words paint a vivid tapestry that captivates hearts and minds under the guidance of experienced tutors from Oxford and Cambridge. Join us as we explore the magic of creative writing and discover the transformative power it holds within through the renowned Oxford Summer Courses summer school.
Ready to study Creative Writing? Apply now to Oxford Summer Courses and join a community of motivated learners from around the world. Apply here .
Share this article
Discover the enchantment of creative writing with Oxford Summer Courses. Unleash your imagination, explore different genres, and enhance your communication skills. Nurture self-expression, empathy, and creativity while gaining valuable writing techniques.
Limited Places Available!
Don't miss out limited places are available at our renowned summer school. secure your place today and dive into an unforgettable learning experience at oxford summer courses. apply now before it's too late..
Oxford Summer Courses LTD
18 Beaumont Street, Oxford, OX1 2NA, United Kingdom
+44 01865 818403

Juniors 9-12
Oxford 13-15
Oxford 16-17
Oxford 18-24
Cambridge 13-15
Cambridge 16-17
Advanced Cambridge 18-24
GDPR Notice
Privacy Policy
Terms and Conditions
Sign up to our newsletter
Oxford summer courses is an organisation which contracts with the colleges of the universities of oxford, cambridge and london for the use of facilities, but which has no formal connection with the universities of oxford, cambridge and london., oxford summer courses © 2024, oxford summer courses is a company registered in england and wales with company number 08011543.
What Is Creative Nonfiction?
By Lee Gutkind
I am often asked: “What is creative nonfiction?” Or, in some cases, “what the hell is creative nonfiction?” The answer—or answers—can be complicated because creative nonfiction may mean different things to different people, a characteristic that makes this form so elusive and alluring.
On its very baseline creative nonfiction is a literary genre. Some people call it the fourth genre, along with poetry, fiction and drama. And it’s an umbrella term for the many different ways one can write what is called creative nonfiction. Memoir, for example, personal essay, biography, narrative history and long form narrative reportage may all fit under the creative nonfiction umbrella. Recently, as the genre has evolved, there have been offshoots to the genre like speculative nonfiction, auto(biographical) fiction, lyric essay, and the visual essay, to name only a few.
Writers who write creative nonfiction are very different in voice, orientation and purpose. But what they have in common is that they are, in one way or the other, writing true stories that provide information about a variety of subjects, enriched by relevant thoughtful ideas, personal insight, and intimacies about life and the world we live in. And this scope and variety is exactly what makes creative nonfiction significant and, these days, so incredibly popular.
“Freedom” and “flexibility” are words I like to use when defining creative nonfiction, for the genre invites writers to push boundaries and open doors, offering them the opportunity to use all of the techniques of the fiction writer (or the poet)—dialogue, setting, description, inner point of view (seeing the world through the eyes of the person about whom they are writing)—in order to capture a reader’s attention and enlighten and intrigue them through nonfiction.
There are very few rules for writers of creative nonfiction. You can predict the future, speculate about the past, or imagine what could have happened or what someone might have been thinking, as long as you don’t violate the reader’s trust, and in the process your own credibility. There are, however, limits to the freedom and flexibility that make creative nonfiction so attractive and compelling—legal, ethical and moral issues that are challenging and, in many ways, impossible to clearly define. Freedom and flexibility—and daring—are governed by responsibility, not just to the people about whom we write, but to those who read and publish our work.
Nonfiction itself has had a bad rap in the literary world. For a long time, it was commonly believed that writing nonfiction was generally inferior to the writing of poetry and fiction. “Nonfiction is a pleasant way to walk,” Larry McMurtry once wrote, “but the novel puts one on horseback, and what cowboy, symbolic or real, would walk when he could ride?”
I remember reading this from McMurtry, who had written a great deal of nonfiction, in addition to his many novels and stories, and feeling more than a little annoyed and, at the same time, amused. He had to be joking, I thought. Or maybe he had just fallen off his horse. I pictured the comedian Rodney Dangerfield, who became rich and famous for the line “I get no respect,” which in many ways has been the story of creative nonfiction in a nutshell-up until present day.
The addition of the word “creative” to nonfiction was at first controversial, but it gradually reversed the belief that nonfiction was somehow second class, a cut below poetry and fiction. It liberated all writers, journalists especially, releasing them from longstanding rules and boundaries that had been so restrictive and inhibiting. For novelists, poets and essayists, “creative” encouraged experimentation and offered new avenues of expression. Scientists, physicians, engineers (Atul Gawande, Hope Jahren, Siddhartha Mukherjee, Henry Petroski, to name just a very few) were intrigued by the notion of being creative and began to write true stories that humanized and revealed the behind-the-scenes intimacies of their professions.
The interest in true stories motivated and opened doors for others who were not writers by trade to share their life experiences, finding meaning in the process and fulfillment in the connections they forged with readers.
This transition—an awakening to the potential and power of nonfiction that allowed and encouraged creativity—did not happen overnight and was not without resistance and often bitter infighting. Change was difficult for the literary, journalistic and academic communities, steeped in tradition and long resistant to new ideas, to accommodate. Indeed, the resistance in some corners far exceeded the scale of the change itself. The change was hardly drastic and was not really, when one looks back over the history of nonfiction, much of a change at all. Writers had been writing nonfiction that was creative and imaginative for centuries, familiar and famous names you will recognize–Daniel Defoe, George Orwell, Charles Dickens and many others—for centuries. The change, the adjustment that it precipitated, had much more to do with the approach or attitude toward nonfiction rather than its content and, of course, the idea that creative and nonfiction were not mutually exclusive. That change in approach and attitude is ongoing. The scope of nonfiction today, most especially what we call creative nonfiction, continues to evolve, informing and inspiring readers with stories that are true, compelling, revealing and always surprising.
“What is Creative Nonfiction” has been adapted from Lee Gutkind’s new book, The Fine Art of Literary Fist-Fighting: How a Bunch of Rabble-Rousers, Outsiders and Ne’er-do-wells Created Creative Nonfiction, to be published later this year by Yale University Press.
More About the Genre
Get started with the best CNF has to offer.
Brian Broome
Brenda Miller
Regeneration
Jennifer Lunden
The Butterfly Effect
Ruthann Robson
Notes from a Difficult Case
Email newsletter.
The best of Creative Nonfiction in your inbox. Sign up to stay up-to-date on genre-related news and updates from the Creative Nonfiction Foundation.
Explore Creative Nonfiction
Can’t get enough? Browse 25 years of archives.
View by Issue
View by Type
View by Topic
About Lee Gutkind

Lee Gutkind is the author and editor of more than thirty books, including You Can’t Make This Stuff Up: The Complete Guide to Writing Creative Nonfiction–from Memoir to Literary Journalism and Everything in Between , Almost Human: Making Robots Think, The Best Seat in Baseball: But You Have to Stand, Forever Fat: Essays by the Godfather, and the award-winning , Many Sleepless Nights: The World of Organ Transplantation.

Lee's Latest Book
My Last Eight Thousand Days
This revealing, candid, and vivid portrait of one man’s view of aging written by the man who played a crucial role in establishing literary, narrative nonfiction in the marketplace and in the academy, examines male aging in a way we’ve not seen before.
What is Creative Writing?
I can tell you the definition of creative writing, but it’s going to hurt. If you want to settle for the book definition, I’ll tell you where to stop.
What is creative writing?
The academic definition (to be said with a snooty British accent):
“Creative writing is considered to be any writing, fiction or non-fiction that goes outside the bounds of normal professional, journalistic, academic, and technical forms of literature. Works which fall into this category include most novels and epics, as well as many short stories and poems. Writing for the screen and stage, screenwriting and playwriting respectively, typically have their own programs of study, but fit under the creative writing category as well. - Wikipedia Alright, if you have gotten what you came for, feel free to exit stage right. If you are interested in getting the definition with balls, continue on.
What is creative writing to me?
Creative writing is writing from the heart. It’s the real stuff that doesn’t rely on college tricks and complex sentence structure; it relies on you!
I have a “Creative Writing Minor” from college , so that means I must have improved my capacity for creative writing throughout my four years there. Right? Wrong.
I started out with my strongest story: a dystopia centered on malfunctioning cell phones called “Hellular.” It was my most ambitious work of my entire college career and it was out of my system by my freshman year. What happened then? Why didn’t I grow? I got self-conscious about how creative writing was supposed to be. It was all downhill from there.
Consciously or unconsciously, my stories began to resemble the other students’ in the class. The stories had lost their uniqueness. Or perhaps, I was dragged down by the constant rush of my normal academic life. Either way, my stories had lost their flavor. What was I missing?
I wasn’t listening to myself. I wasn’t expressing my feelings. I was writing to impress or to improve my style or to get an A. But I should have been writing to let my soul breathe a little bit.
Creative writing is an expression of who you are. If you are closed off from yourself, if you hide the person that you are for fifteen to twenty four hours per day, and if you have locked yourself in to a dream that is no longer yours, you will be hard pressed to write creatively.
My philosophy about creative writing is that in order to truly do it justice, you must become a more open person who is really able to get in touch with the raw parts of yourself. You need to remove from your life all of the things that are clogging you up emotionally, physically, and spiritually. It is only then that you can express what you are meant to.
And if you aren’t bogged down by the outside world, what should you write about? If you are oppressed, you need to write about your tyrant. If you are in pain, you need to put your pain on the page. If you are in love with all of your heart and soul, then put all of that into a poem that can be used for all of eternity. Or at least, put most of it in there. Save a little for yourself :).
Build Creative Writing Ideas dot Com is a site devoted to opening you up to the writing that you can truly accomplish. We believe that if you can lead a better life, you can write a better book.
So, what is creative writing? Creative writing is in you. Are you going to let it out?
Related Articles to "What Is Creative Writing" Free Creative Writing Prompts #2: Love Free Creative Writing Prompts from the Heart, Part 1 Creative Writing Exercises #2: Relaxation
Done with "What Is Creative Writing?" Go back to "Creative Writing Tips"
Would you prefer to share this page with others by linking to it?
- Click on the HTML link code below.
- Copy and paste it, adding a note of your own, into your blog, a Web page, forums, a blog comment, your Facebook account, or anywhere that someone would find this page valuable.
- Latest Posts
- Privacy Policy
- Create a Website
- $1,000 Blog Tour
- Happiness Tour
- 5/11 Blog Tour
- Guest Posts
- Writing Prompts
- Writing Exercises
- Writing Tips
- Holiday Writing
- Writing Contest
- Comedy Channel
- Prompts eBook
- Kids Writing Book
- 9 to 5 Writer Book
- Writing Tips eBook
- Happiness Book
- TpT Reviews
- Read These Books
- Motivation Help
- Time Management
- Healthy Living
- Grades 9-10
- Grades 11-12
- First Grade
- Second Grade
- Third Grade
- Fourth Grade
- Fifth Grade
- 1,000 Character Writing Prompts
- 1,000 Creative Holiday Prompts
Write a Story Based on These Prompts or This Article!
Use the above prompts or article as inspiration to write a story or other short piece.
Enter Your Title
Add a Picture/Graphic Caption (optional)
Click here to upload more images (optional)
Author Information (optional)
To receive credit as the author, enter your information below.
Submit Your Contribution
- Check box to agree to these submission guidelines .
- I am at least 16 years of age.
- I understand and accept the privacy policy .
- I understand that you will display my submission on your website.
(You can preview and edit on the next page)
What Other Visitors Have Said
Click below to see contributions from other visitors to this page...
Click here to write your own.
- What's New?
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.
From writing to roleplays: ASU grad shares her experiences as a student, worker and creative force on campus
Editor’s note: This story is part of a series of profiles of notable spring 2024 graduates .

Grace Peserik, a writer for ASU Student Life and a communications aide for the School of Politics and Global Studies , spends her time outside of work writing fiction and playing tabletop roleplay games.
Now, as she prepares for graduation this spring, Peserik reflects on both her studies as an English literature major through The College of Liberal Arts and Sciences and her favorite memories as a Sun Devil at work.
The start of Peserik’s academic career at ASU was rather untraditional. She started taking classes during the COVID-19 pandemic in fall 2020, which was a difficult adjustment compared to the normal trajectory from high school into college life.
“It made my first year of college feel like we were in a limbo state,” Peserik said. “It was very odd for me personally because it is much harder to meet people and make friends when you are essentially on lockdown in your dorm.”
Since the height of the pandemic, Peserik has adjusted and found friends and communities she can engage with on campus.
Work experiences on campus
Before taking on her dual communications positions for Arizona State University as a student employee, Peserik began as an office aide for the ASU School of Art . Throughout her professional work experience, Peserik has had a wide range of responsibilities that have helped prepare her for entering the job market post-graduation.
“A lot of these positions have taught me to be more willing to advocate for myself and to feel confident in the things I am doing,” Peserik said. “As a writer, it is really critical to have those good communication skills.”
Perserik first honed her prose as a creative writer, working through genres ranging from young adult to sci-fi and fantasy. During her time with ASU Student Life, she has worked closely with many Sun Devils to help tell their stories on and off campus.
“One of my favorite pieces I’ve written at ASU Student Life was about a roleplaying game through Solis Diaboli ,” Peserik said. “It was one of the first stories that I pitched, and it was a fun piece to write.”
When asked about the importance of her work at ASU Student Life, Peserik expressed a sincere appreciation for the stories she got to tell during her employment. One of the latest pieces she worked on was about the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants and Children, also known as WIC.
“That one was a fairly big undertaking and took a lot of work to make happen,” Peserik said. “I am very proud that it's out there.”
Peserik enjoyed her time as a student employee at ASU and highly recommended it to other Sun Devils searching for reliable and adaptable employment.
“Student jobs are a great way to meet other people that aren’t necessarily in your major or academic program,” Peserik said. “Who doesn’t want to get a job that will also work around your school schedule?”
Life as an ASU student
One of Peserik’s favorite memories as an ASU student came about through a forensic anthropology class she took in her first year, a course she selected to fulfill her major’s science requirement. It taught her early on to explore the wide range of classes available at ASU, even if it isn’t one she would normally go for.
“I was told I needed to take a science class, and it was the only one that sounded particularly interesting to me,” Peserik said. “I learned so much about the human skeleton and the different ways to identify people based off their skeletal structure. You can tell what gender someone was assigned at birth from different aspects of their skull alone.”
During her time as a Sun Devil, Peserik has found hobbies outside of work and class, predominantly manifesting in her involvement with Solis Diaboli , the classical civilizations club at ASU alluded to above. She began her time with the club as a traditional member and eventually took on the role of president, having held office for close to two years.
“Solis Diaboli is essentially a bunch of people who enjoy Greco-Roman history getting together and playing games related to that,” Peserik said. “As president, I mostly planned our meetings and any of the fun events that we hosted.”
One of the events Peserik cherished during her time with Solis Diaboli was an escape room she helped build for their team. Peserik and others transformed a classroom into a wild, Greek mythology-themed space.
“The club members definitely made the escape room unsolvable,” Peserik said, reflecting on that night with a smile. “They broke more than one puzzle in trying to get out, but it was really fun, at the end of the day.”
Not only did Solis Diaboli give Peserik a community of friends on campus, but it also connected her to her long-term boyfriend.
“Not to sound mushy, but one of my favorite memories as a student has to be meeting my boyfriend here,” Peserik said. “I technically met him through Solis Diaboli, but I didn’t acknowledge him fully until we had a class together. From then on, he and I became very close friends and then ended up dating.”
In Peserik’s own words, all of her creative work also ties back to tabletop roleplay games, a hobby that she and her friends can join together in, suspending belief and relishing in a uniquely innovative atmosphere. Peserik gets to not only play these games, but she also takes on the role of writer from time to time, developing the plots and settings her friends then get to explore.
“I’m excited for this upcoming game we’re starting up,” Peserik said. “I’m writing a very weird Star Wars-esque story and making my friends play it. Our first session is next weekend.”
After her graduation this spring, Peserik is looking forward to pursuing a career that involves writing, such as content writing or running social media accounts for large companies. Her dream job is to one day write fiction full-time.
To find Peserik’s work for ASU Student Life, read more of our student stories here.
More Sun Devil community

From GED to JD, first-generation transfer student looks forward to full scholarship to law school
Editor’s note: This story is part of a series of profiles of notable spring 2024 graduates. James Starks isn’t your typical Dean’s Medal recipient, and that’s what makes them so captivating. Starks…

Double major, honors student encourages others to seek what is essential
Editor’s note: This story is part of a series of profiles of notable spring 2024 graduates. It seemed like nothing could stop Jacqueline Schisler, a Barrett Honors student working toward two…

ASU Online history grad decides to follow her heart
Editor’s note: This story is part of a series of profiles of notable spring 2024 graduates. Alexandra Oldfield always had an interest in history, but it wasn’t until she was on bed rest after a…
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Book News & Features
Ai is contentious among authors. so why are some feeding it their own writing.

Chloe Veltman

The vast majority of authors don't use artificial intelligence as part of their creative process — or at least won't admit to it.
Yet according to a recent poll from the writers' advocacy nonprofit The Authors Guild, 13% said they do use AI, for activities like brainstorming character ideas and creating outlines.
The technology is a vexed topic in the literary world. Many authors are concerned about the use of their copyrighted material in generative AI models. At the same time, some are actively using these technologies — even attempting to train AI models on their own works.
These experiments, though limited, are teaching their authors new things about creativity.
Best known as the author of technology and business-oriented non-fiction books like The Long Tail, lately Chris Anderson has been trying his hand at fiction. Anderson is working on his second novel, about drone warfare.
He says he wants to put generative AI technology to the test.
"I wanted to see whether in fact AI can do more than just help me organize my thoughts, but actually start injecting new thoughts," Anderson says.
Anderson says he fed parts of his first novel into an AI writing platform to help him write this new one. The system surprised him by moving his opening scene from a corporate meeting room to a karaoke bar.
Authors push back on the growing number of AI 'scam' books on Amazon
"And I was like, you know? That could work!" Anderson says. "I ended up writing the scene myself. But the idea was the AI's."
Anderson says he didn't use a single actual word the AI platform generated. The sentences were grammatically correct, he says, but fell way short in terms of replicating his writing style. Although he admits to being disappointed, Anderson says ultimately he's OK with having to do some of the heavy lifting himself: "Maybe that's just the universe telling me that writing actually involves the act of writing."
Training an AI model to imitate style
It's very hard for off-the-shelf AI models like GPT and Claude to emulate contemporary literary authors' styles.
The authors NPR talked with say that's because these models are predominantly trained on content scraped from the Internet like news articles, Wikipedia entries and how-to manuals — standard, non-literary prose.
But some authors, like Sasha Stiles , say they have been able to make these systems suit their stylistic needs.
"There are moments where I do ask my machine collaborator to write something and then I use what's come out verbatim," Stiles says.
The poet and AI researcher says she wanted to make the off-the-shelf AI models she'd been experimenting with for years more responsive to her own poetic voice.
So she started customizing them by inputting her finished poems, drafts, and research notes.
"All with the intention to sort of mentor a bespoke poetic alter ego," Stiles says.
She has collaborated with this bespoke poetic alter ego on a variety of projects, including Technelegy (2021), a volume of poetry published by Black Spring Press; and " Repetae: Again, Again ," a multimedia poem created last year for luxury fashion brand Gucci.
Stiles says working with her AI persona has led her to ask questions about whether what she's doing is in fact poetic, and where the line falls between the human and the machine.
read it again… pic.twitter.com/sAs2xhdufD — Sasha Stiles | AI alter ego Technelegy ✍️🤖 (@sashastiles) November 28, 2023
"It's been really a provocative thing to be able to use these tools to create poetry," she says.
Potential issues come with these experiments
These types of experiments are also provocative in another way. Authors Guild CEO Mary Rasenberger says she's not opposed to authors training AI models on their own writing.
"If you're using AI to create derivative works of your own work, that is completely acceptable," Rasenberger says.

Thousands of authors urge AI companies to stop using work without permission
But building an AI system that responds fluently to user prompts requires vast amounts of training data. So the foundational AI models that underpin most of these investigations in literary style may contain copyrighted works.
Rasenberger pointed to the recent wave of lawsuits brought by authors alleging AI companies trained their models on unauthorized copies of articles and books.
"If the output does in fact contain other people's works, that creates real ethical concerns," she says. "Because that you should be getting permission for."
Circumventing ethical problems while being creative
Award-winning speculative fiction writer Ken Liu says he wanted to circumvent these ethical problems, while at the same time creating new aesthetic possibilities using AI.
So the former software engineer and lawyer attempted to train an AI model solely on his own output. He says he fed all of his short stories and novels into the system — and nothing else.
Liu says he knew this approach was doomed to fail.
That's because the entire life's work of any single writer simply doesn't contain enough words to produce a viable so-called large language model.
"I don't care how prolific you are," Liu says. "It's just not going to work."
Liu's AI system built only on his own writing produced predictable results.
"It barely generated any phrases, even," Liu says. "A lot of it was just gibberish."
Yet for Liu, that was the point. He put this gibberish to work in a short story. 50 Things Every AI Working With Humans Should Know , published in Uncanny Magazine in 2020, is a meditation on what it means to be human from the perspective of a machine.
"Dinoted concentration crusch the dead gods," is an example of one line in Liu's story generated by his custom-built AI model. "A man reached the torch for something darker perified it seemed the billboding," is another.
Liu continues to experiment with AI. He says the technology shows promise, but is still very limited. If anything, he says, his experiments have reaffirmed why human art matters.
"So what is the point of experimenting with AIs?" Liu says. "The point for me really is about pushing the boundaries of what is art."
Audio and digital stories edited by Meghan Collins Sullivan .
- large language model
- mary rasenberger
- chris anderson
- sasha stiles
- authors guild
- The Student Experience
- Financial Aid
- Degree Finder
- Undergraduate Arts & Sciences
- Departments and Programs
- Research, Scholarship & Creativity
- Centers & Institutes
- Geisel School of Medicine
- Guarini School of Graduate & Advanced Studies
- Thayer School of Engineering
- Tuck School of Business
Campus Life
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Athletics & Recreation
- Student Groups & Activities
- Residential Life
English and Creative Writing
Department of english and creative writing.
- [email protected] Contact & Department Info Mail
- Undergraduate
- Modified Major
- Transfer Credit
- Creative Writing Concentration
- Past Honors
- Course Group I
- Course Group II
- Course Group III
- Course Group IV
- Courses - No Course Group
- Creative Writing Courses
- Courses (No Major Credit)
- Foreign Study Courses
- Independent Study and Honors
- The Historical Philosophy of W.E.B. Du Bois
- Creative Writing Prizes
- Department Prizes
- Undergraduate Fellowships
- Foreign Study
- London Foreign Study Program
- News & Events
- News & Events
- Illuminations
- Robert Hayden
- Black Nature Conference
- Sanborn Tea
Search form
The department of english and creative writing responds to the may 1, 2024 events and arrests on campus.

We the faculty and staff of the Dartmouth College Department of English and Creative Writing write to condemn the decision-making process that led to the presence of multiple militarized police units on our campus. One of these units, the New Hampshire Special Weapon and Tactics , defines itself as a highly-trained squad,
with expertise in weaponry and specialized tactics such as rappelling and building assaults. The purpose of the SWAT Unit is to be able to respond to high-risk incidents such as barricaded suspects, hostage takers, high-risk warrant service, active shooter situations and executive (VIP) security, as well as other incidents in which the lives and safety of the public are in extreme danger.
As in-person observers of the protest—representing a range of political views within the department—and as faculty who've consulted with students representing a range of political views, we affirm that the following played no role in the protest:
—barricaded suspects,
—hostage takers,
—standing warrants,
—active shooters,
—executive (VIP) security.
The decision to call in law enforcement, leading to the presence of militarized police, made this a case of "SWATting," the practice of summoning militarized police to a non-threatening situation to increase the risk of violence. This decision endangered the safety of every member of the Dartmouth community.
The protest in question obstructed nothing and threatened no violence. Before this administration took power, there was no precedent in Dartmouth history for responding with law enforcement to language that is not explicitly threatening. There is no precedent in Dartmouth history for responding to any protest with militarized police units created to respond to life-or-death situations.
Therefore, w e call for the College to formally revise its dissent policies, in consultation with the faculty, so that police and militarized police will never again be used in response to peaceful protest.
In solidarity with students and with the many departments and programs across our campus that have issued statements denouncing the administration's actions, we reiterate and affirm the demands articulated by our colleagues in the Department of History and African and African American Studies that the Dartmouth administration
- acknowledge publicly that the deployment of state police and armored vehicles was an excessive and punitive response to peaceful protests, which will not be repeated,
- announce publicly that you are asking prosecutors to dismiss all criminal charges against the faculty, students, and staff who were arrested on May 1—a request that in no way infringes on prosecutorial discretion—and charges against the two students arrested in the fall, Roan V. Wade and Kevin Engle, should also be dropped immediately,
- make it officially and publicly known that academic freedom includes the right to peacefully express support for Palestinian rights. The college should permit nonviolent protest and restore faith in fair process and commitment to free speech on campus.
This statement was agreed upon by a clear majority of 26 yes votes, with 1 no vote, 1 abstain vote, and 9 uncast ballots.
- Student Profile
- Faculty Profile
- Alumni Spotlight
- Campus News
- Student Life
- Teaching & Learning
- Community Engagement
- Stories for Media
- UBCO Events
- Search All Stories
UBCO’s Kevin Chong discusses identity and heritage in his latest novel
Author, creative writing professor accepts the challenge of navigating the complex landscape of asian heritage month.
May 7, 2024

Author Kevin Chong, a UBC Okanagan professor in the Faculty of Creative and Critical Studies, says Asian Heritage Month can present challenges and opportunities for Asian Canadian artists. Credits: Author photo by Iris Chia. Book cover courtesy of Simon & Schuster.
In The Double Life of Benson Yu , author Kevin Chong’s protagonist navigates a complicated future and a traumatic past by blurring the lines between fiction and reality as a graphic novelist.
As a creative writing professor in UBC Okanagan’s Faculty of Creative and Critical Studies , Chong must remain realistic when it comes to discussions around identity and self-discovery, especially during May—Asian Heritage Month.
He appreciates the nuanced ways the month can serve as both a spotlight and a platform for Asian-Canadian content while acknowledging the emotional and intellectual labour involved in representing one’s culture and heritage.
They are comparable to the issues Chong balanced delicately in Benson Yu , a novel that earned him a place on the Giller Prize Shortlist. Here, he discusses both his personal and professional insights into Asian Heritage Month.
How do you see Asian Heritage Month affecting the identity and self-perception of younger Asian Canadians?
I think a lot about my eight-year-old daughter and how I want her to learn about her Chinese and Asian-Canadian heritage. Cultural events like the Lunar New Year are certainly part of the equation. When there’s school programming tied to that or Asian Heritage Month, it allows her to know a little more about herself.
It’s nice to see yourself in the media one consumes—whether it’s on a screen or a page. I didn’t have that growing up. At times, I would have to find it in Asian culture from Asia—in Haruki Murakami novels or Hong Kong action movies like A Better Tomorrow . At other times, I think it gave me a more whitewashed sensibility. Nowadays, I feel as though younger Asian Canadians have more opportunities to see themselves in media.
What does Asian Heritage Month mean to you as an author and educator?
It’s a springboard for my work to be shared and discussed at events as well as online and print publications. Earlier in my career, I shied away from my heritage. I wanted to be a writer, first and foremost. In contrast, I see so many younger writers voluntarily placing their backgrounds and orientations in the first lines of their biographies. I’m sort of in awe of that pride. But I’d find Asian readers through this springboard. And more recently in my career, especially in my newest book, The Double Life of Benson Yu , I’ve leaned into what it means to be part of the Asian diaspora.
As an educator, it’s a reminder and a prompt to share Asian-Canadian content.
But there can be some emotional labour called upon to bloviate on being Asian and Asian Canadian. Not only does it take time away from my research, but it also makes me spiral into thinking about whether I’m qualified to speak about Asian-Canadian culture, what I should do to feel more qualified and whether I’m a “good” Asian Canadian. For better or worse, I’ve chosen to speak on the topic.
How do you believe Asian Heritage Month contributes to the appreciation of Asian culture?
Through the awareness it raises and the content of Asian-Canadian creators, Asian Heritage Month reveals the long history and lasting impact Asians have had as settlers in this province and country.
On my mother’s side, for instance, I have two great-grandfathers who emigrated to Canada—one in 1916, the other in 1920. To my delight, I was able to find them on the UBC Library’s Register of Chinese Immigrants to Canada, 1886-1949 .
I found their height, weight, occupation and the names of the ships they boarded to cross the Pacific. Because of the Head Tax, they raised their families in China—which is why I was born in Hong Kong and can claim to be both a fourth and first-generation Canadian. And yet, like every other Asian Canadian, I will always be considered a foreigner.
As we come to more deeply understand the histories of Asian Canadians, we learn there are so many different communities, many of whom had to overcome many racist obstacles and so many different waves of immigration.
How do Canadian academia and literature reflect Asian history and identity, and can Asian Heritage Month contribute to this?
According to Google, Chinese and South Asians, along with the Black community, form the three largest visible minorities in Canada. If we’re not properly represented in Canadian academia and literature—and I feel we aren’t—there’s something wrong with Canadian academia and literature.
Asian Heritage Month increases consciousness but can also be an excuse to ignore us for the other 11 months of the year.
Moreover, as I’ve learned of Asian-Canadian history through the novels of Wayson Choy, Paul Yee and William Ping, and the nonfiction of writers like Cheuk Kwan and Lily Cho, the more deeply I appreciate the courage and ingenuity of these earlier generations of Asian Canadians.
How can communities navigate celebration and appropriation during such heritage months?
If it’s led by an Asian group, then let them lead it. Wearing a culturally specific item of clothing can be appreciated in some contexts and then considered over-the-top or offensive in others. I could probably use the same Canadian politician as both a positive and negative example. When in doubt, you should consult with the event organizer.
Media Contact
Trending stories.
- Flag lowering: Logan Hall
- A hidden waterway comes alive through community art
- Powerful answers to energy questions may be blowing in ...
- Exceptional faculty members celebrated as 2024’s Researchers of the ...
- UBCO researchers hope to prevent catastrophes with next-generation sensors
About UBC Okanagan
UBC’s Okanagan campus is an innovative hub for research and learning founded in partnership with local Indigenous peoples, the Syilx Okanagan Nation, in whose traditional, ancestral and unceded territory the campus resides. The most established and influential global rankings all consistently place UBC in the top five per cent of universities in the world, and among the top three Canadian universities.
The Okanagan campus combines a globally recognized UBC education with a tight-knit and entrepreneurial community that welcomes students and faculty from around the world in British Columbia’s stunning Okanagan Valley. For more visit ok.ubc.ca .
Discover more about UBC Okanagan
Innovation Precinct Annexation 1 (IA1) 3505 Spectrum Court Kelowna, BC Canada V1V 2Z1
We respectfully acknowledge the Syilx Okanagan Nation and their peoples, in whose traditional, ancestral, unceded territory UBC Okanagan is situated.
Search all stories
Subscribe to receive news by email
Visit UBC's Vancouver news room
Global and Admin Messages
Okanagan Campus

The Creative Writing Breakfast Club Sunday 12th May 2024
Join writer Laurie Bolger for Creative Writing Breakfast Club, a chance to get scribbling from the comfort of your own space via Zoom.
Date and time
Refund policy, about this event.
The Creative Writing Breakfast Club as featured in Time Out is a Free Flow Creative Writing hour with writer Laurie Bolger.
This session is about letting your creativity lead the way, generating new and exciting writing in your own unique style.
During this 60 minute workshop Laurie will take you through fast paced writing exercises to boost mindfulness. All you need is a pen and paper and somewhere chilled to sit and let your imagination do it’s thing.
"My first workshop of Laurie's & definitely won’t be my last… ideas exploding all over the shop - thank you, loved it"
Writing: Water Participant 2023
“Laurie’s workshops are a safe & at the same time dangerous place for writing..."
Writing The Seven Deadly Sins Workshop Participant 2022
“If you ever want a cosy, creative, calming place to explore writing, Laurie's workshops are perfection…My heart is so full (I know what that means now)”
Breakfast Clubber 2023
"Probably the best, most productive w/s I've ever attended. Fantastic. Thank you!"
Writing The Body Participant 2023
Laurie Bolger is a London based writer and founder of The Creative Writing Breakfast Club. Her debut collection Box Rooms has featured at Glastonbury, TATE, RA & Sky Arts.
Laurie’s work has appeared in The Poetry Review, The London Magazine, Moth, Magma, Crannog, Stand, & Trinity College Icarus. Laurie’s writing has been shortlisted for The Bridport Prize, Moth Poetry Prize, Live Canon, Winchester & Sylvia Plath Prizes.
Her poem ‘Parkland Walk’ was awarded first place in The Moth Poetry Prize judged by Louise Glück & was highly commended in this years Forward Prize for Poetry.
Laurie has collaborated with organisations such Google, as Small Luxury Hotels of the World, Nationwide, Mind UK & Choose Love. Laurie's latest publication 'Makeover' is to be published by The Emma Press next year.
www.lauriebolger.com
Instagram @lauriebolger_
Twitter @lauriebolger
- Online Events
- Things To Do Online
- Online Classes
- Online Arts Classes
- #creativeworkshop
- #creativewriting
- #creativewritingbeginners
- #creative_class
- #creative_workshop
- #creative_writing_workshop
- #creativewritingworkshop
Organised by
About Cambridge Judge
- Overview of the Business School
- History and today
- External recognition
- Diversity and inclusion
- Virtual tours
- Jobs at Cambridge Judge
- Giving overview
- Fundraising priorities
- How to give
- Impact and recognition
- Recruiters and organisations overview
- Recruit from Cambridge Judge
- Student consultancy projects
- Develop your talent
- Corporate speaker opportunities
- Special interest groups and societies
- News overview
- Announcements
Programme news
- Student and alumni news
- Faculty news
Research centre news
- Fundraising news
- Media coverage
- News room (for journalists)
FT Responsible Business Education Awards: 2 wins for Cambridge Judge
Purpose of Finance course wins top Teaching award and a study on paedophile hunters wins Academic Research award, while Cambridge Judge is Highly Commended for School-wide activities in the Financial Times awards for business education responsibility and impact.
Degree programmes
- Masters degrees overview
- Executive MBA
- Executive Master of Accounting
- Master of Finance (MFin)
- MSt in Entrepreneurship
- MSt in Social Innovation
- MPhil in Management
- MPhil in Technology Policy
- PhD and research masters overview
- PhD pathways
- Business Doctorate
- Master of Research in Management
- MPhil in Finance
- MPhil in Innovation, Strategy and Organisation
- MPhil in Strategy, Marketing and Operations
- Management Studies (Tripos)
- Virtual tours of the Business School
- Cambridge life
- Entrepreneurship at Cambridge Judge
- Financial aid
- Admission events
Non-degree programmes
- Entrepreneurship programmes overview
- Accelerate Cambridge
- Enterprise Tuesday
- Venture Creation
- EnterpriseTECH
- EnterpriseWOMEN
- Social Venture Weekend
- First Certificate in Business overview
- For learners
- For organisations
- Executive Education overview
- Online ExecEd programmes
- Open programmes for individuals
- Custom programmes for organisations
Need help funding your degree programme studies at Cambridge Judge?
Explore our scholarship and loan opportunities.
Executive Education
- Open programmes for individuals overview
- Programme finder
- New programmes
- Online programmes
- Managing People
- Managing Organisations
- Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG)
- Strategy and Growth
- Innovation and Technology
- Professional Service Firms
- Custom programmes for organisations overview
- Open programmes for organisations
- Clients and case studies
- Psychometric services
- Professional service firms
- Certificate of Achievement
- B Corp certification
- Digital certificates
- Visa information
- Meet the team
Not sure which programme is for you?
Search our portfolio of over 40 well-crafted programmes that will expand your skills and understanding in service of your organisational, personal development and career objectives.
- Research and teaching staff
- Honorary appointments
- Subject groups overview
- Economics and Policy
- Operations and Technology Management
- Organisational Behaviour
- Organisational Theory and Information Systems
- Strategy and International Business
- Research centre finder
- Alternative Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Policy
- Business Research
- Chinese Management
- Circular Economy
- Digital Innovation
- Endowment Asset Management
- Energy Policy Research Group
- Entrepreneurship
- Experimental & Behavioural Economics Group
- Finance, Technology and Regulation
- Financial Reporting and Accountability
- Health Leadership and Enterprise
- India and Global Business
- International Human Resource Management
- Process Excellence and Innovation
- Psychometrics
- Regulatory Genome Project
- Risk Studies
- Social Innovation
- Wo+Men’s Leadership
- Impact and practitioner engagement overview
- Collaborate with our faculty
- Publications overview
- The Cadbury Archive
- Information and Library Services overview
- Research seminars
Faculty and research
- AI and technology
- Behavioural economics
- Career and personal development
- Entrepreneurship and innovation
- ESG and sustainability
- Equality, diversity and inclusion
- Finance and accounting
- Future of work
- Global strategy and international business
- Governance, economics, and policy
- Leadership and organisational behaviour
- Operations management
- Philanthropy
- Social impact

Exploring the rise of the global B Corp movement
The B Corp movement is helping to shift the focus of capitalism from shareholders to all stakeholders: find out how Cambridge fits in.
Find an expert
We have faculty, who can speak on many current UK and global issues, and are happy to be contacted by journalists.
- All insights
- Alumni council
- Regional Alumni groups
- Alumni Special Interest Groups (ASIGs)
- Alumni toolkit
- Alumni profiles
- Get involved
- CJBS network
- CJBS Connects: Worldwide
Leave your mark in LT1
The iconic Lecture Theatre 1 (LT1) is due for a refurbishment, and with it comes the opportunity for alumni, friends and other supporters of Cambridge Judge Business School to claim their seat in LT1.

What does it me…
What does it mean to be a scholar in an age of AI?
The article at a glance.
Academic publishing has long been based on the premise of elite scarcity. With generative AI promising to lower barriers for producing exceptional articles, Professor Matthew Grimes asks how this will change the scholarly profession.
Category: AI and technology Insight
The academic profession, including in business schools, is like an exclusive members club. Faculty members seek tenure, promotions and greater prestige among peers based on a well-understood set of elite rules. A scholar whose article is published in the most prestigious journal, with the highest standards for acceptance and rejection, will achieve rewards in a way publication in a less-lauded journal may not.
But this long-established code of the academic professor is based on a pivotal understanding: scarcity. The underlying premise is that there is a very limited number of truly exceptional journal articles competing for the career-advancing spots in the very best journals.
AI can speed up article creation and more
So what happens when generative artificial intelligence (AI) upends this understanding by allowing the creation – all within ethical academic bounds and peer-acknowledged excellence – of far more than a limited number of exceptional articles, perhaps even a virtually limitless supply of them?

That’s the focus of an editorial, ‘From scarcity to abundance’, in the Academy of Management Journal (AMJ) – one of the most elite journals in the field of business management, co-authored by Matthew Grimes, Professor of Entrepreneurship and Sustainable Futures at Cambridge Judge Business School.
Elite academic articles often take many years to reach publication stage, but the authors say “generative AI tools now increasingly offer capabilities aimed to increase those efficiencies and the pace at which those efficiencies are realised by scholars” – a very polite way of saying that AI may seriously disrupt the entire supply chain for academic articles, which currently assumes a molasses-like speed.
Then there’s another key question: can AI surface interesting research questions as well as the minds of human scholars? “The extent to which generative AI will augment or replace academics in the creative tasks associated with scholarship is a matter of debate (indeed, the authors of this editorial have internally expressed such debate), yet the potential should be taken seriously,” the editorial says.
What does it now mean to be a scholar or academic journal?
“We pose 2 questions, given the potential promise of generative AI to increase both the quantity and quality of scholarship,” says the editorial:
- What does it mean to be a scholar when the know-what’and know-how barriers to becoming one are minimised (anyone who wants to can participate in scholarship)?
- practical importance
- theoretical intrigue
- methodological rigor?
The editorial makes clear that the journal’s editors don’t have all the answers at this still-young point in the evolution of generative AI, but makes equally clear that these difficult questions need urgently to be asked.
Asking awkward questions and prompting deep thinking of academics
“The future of academic publishing in the age of AI poses very awkward questions for academics to be asking about ourselves, our colleagues and our profession,” says editorial co-author Professor Grimes. “We are all academics trained and working in an era where the scarcity of truly first-class research was the guiding principle, but we are looking at a rapidly advancing new era of generative AI in which the scarcity of knowledge production can no longer be assumed.
“The editorial doesn’t attempt to curb the use of generative AI in producing scholarship: there are clearly some hazards such as well-documented ‘AI hallucinations’ (relevant but false information) and ‘deep research fakes’ (data manipulation to deceive the academic community), but there is also truly great research potential in AI in areas ranging from the creation of academic articles, to bridging the gap between academic theory and practice, to the ability to improve the peer-review system of evaluating the merits of academic literature.
“Our purpose in writing this editorial is to prompt some deep thinking and soul searching amongst ourselves and our peers about what we want our profession to look like given the rapid advances in AI,” says Matthew.
The authors say they don’t seek to codify the academic profession’s response to AI, but rather to examine different uncertainties that will affect scholarship. “We are merely at the beginning of a conversation we expect to be having for many years to come,” they say.
Our purpose in writing this editorial is to prompt some deep thinking and soul searching amongst ourselves and our peers about what we want our profession to look like given the rapid advances in AI.
AI in academic journals: good faith should not be assumed
The editorial also looks at how journals currently deal with generative AI, noting that the Academy of Management will soon publish guidelines on AI use for its suite of journals and conference submissions.
“At the moment, however, many existing journal policies surrounding generative AI appear to be operating on the assumption that authors, reviewers, and editors will act in good faith,” the authors say. Given the risks such as “hallucinations” coupled with rapid advances in AI, “we believe such an assumption is inadequate” and that governance rules are needed such as specialised review protocols for papers that employ generative AI.
The editorial then returns to what generative AI means for the academic profession.
At the moment, however, many existing journal policies surrounding generative AI appear to be operating on the assumption that authors, reviewers, and editors will act in good faith … we believe such an assumption is inadequate.
Generative AI challenges the distinctive value of management scholarship
“Our investigation of the implications of generative AI for management scholarship and for our profession is not meant as a call to arms to defend the profession and its current boundaries,” the editorial concludes.
“Instead, in the short-term, we view this as a call to prepare ourselves, as well as our current and future PhD students, with the appropriate knowledge not only to use but, more critically, to evaluate algorithmic knowledge production.”
“In the long term, we view this editorial as a call to rethink the distinctive value of our profession in a world of abundant management scholarship. In other words, we suspect that a plausible generative AI-led shift from scarce academic knowledge production to abundant academic knowledge production will inevitably increase the urgency around answering a fundamental question: To what problems in society is management scholarship the (unique) solution?”
The editorial is co-authored by Professor Matthew Grimes of Cambridge Judge Business School, an editor of the AMJ, along with four of the journal’s other editors: Georg von Krogh of ETH Zurich, Stefan Feuerriegel LMU Munich, Floor Rink of the University of Groningen, and Marc Gruber of Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne.
In the long term, we view this editorial as a call to rethink the distinctive value of our profession in a world of abundant management scholarship.
Featured faculty
Matthew grimes.
Professor of Entrepreneurship and Sustainable Futures
View Matthew's profile
Featured research
Grimes, M., von Krogh, G., Feuerriegel, S., Rink, F. and Gruber, M. (2023) “From scarcity to abundance: scholars and scholarship in an age of generative artificial intelligence.” Academy of Management Journal , 66(6): 1617-1624 (DOI: 10.5465/amj.2023.4006)
Related articles

Creative writing prize breaks new ground with AI
The Cambridge Creative Writing Competition organised by the Psychometrics Centre at Cambridge Judge allowed AI (artificial intelligence) to be used for the first time.

The power of AI – and how it’s set to revolutionise the finance industry
With all eyes on AI following the release of ChatGPT early last year, we spoke to Alejandro Reynoso, External Lecturer in Algorithmic Trading and former Research Fellow at Cambridge Judge to get his take on the impact on the finance industry, and the key opportunities to look out for.

Staying on trend: AI, big data and blockchain on the Master of Finance
As AI, big data, blockchain and other areas continue to grow apace, how is the Cambridge Master of Finance keeping up? We spoke to 2 MFin alumni to find out how the programme helped in these areas, and what impact it’s had on their careers.
academia artificial intelligence (AI) Matthew Grimes technology

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Creative writing is an art form that transcends traditional literature boundaries. It includes professional, journalistic, academic, and technical writing. This type of writing emphasizes narrative craft, character development, and literary tropes. It also explores poetry and poetics traditions.
Creative writing can technically be considered any writing of original composition. In this sense, creative writing is a more contemporary and process-oriented name for what has been traditionally called literature , including the variety of its genres .
Types of Creative Writing. Examples of creative writing can be found pretty much everywhere. Some forms that you're probably familiar with and already enjoy include: • Fiction (of every genre, from sci-fi to historical dramas to romances) • Film and television scripts. • Songs. • Poetry.
5 Key Characteristics of Creative Writing. Creative writing is marked by several defining characteristics, each working to create a distinct form of expression: 1. Imagination and Creativity:Creative writing is all about harnessing your creativity and imagination to create an engaging and compelling piece of work.
Creative nonfiction is a broad genre that includes memoirs and biographies, personal essays, travel and food writing, and literary journalism. Ultimately, we each get to decide what is art and what is creative writing. Most of us will know creative writing when we experience it, either as a writer or as a reader.
A news article, for example, cannot be considered creative writing because its main goal is to present facts and not to express the feelings of the writer. While a news article can be entertaining ...
A lot falls under the term 'creative writing': poetry, short fiction, plays, novels, personal essays, and songs, to name just a few. By virtue of the creativity that characterizes it, creative writing is an extremely versatile art. So instead of defining what creative writing is, it may be easier to understand what it does by looking at ...
Start by writing a summary of your story in 1 paragraph. Use each sentence to explain the most important parts of your story. Then, take each sentence of your paragraph and expand it into greater detail. Keep working backward to add more detail to your story. This is known as the "snowflake method" of outlining.
What is Creative Writing and its Types? In addition to fiction writing, creative writing includes the genres of poetry, creative nonfiction (such as memoir, autobiography, or personal essay), screenwriting, plays, and/ or graphic novels. Blogs and other digital media could also be considered forms of creative writing.
In Cold Blood passes this test due to Capote's use of characterization, plot development, and world-building. It's considered today to be a pioneering example of the non-fiction novel, a paragon of the creative writing world. The original crime reports, local newspaper articles, and subsequent court documents detail the same events with the same participants.
What is creative writing? The answer can be simple, but breaking it down is far more useful. Learn more and gain some insightful tips for yourself, as well!
2. Poetry. Poetry can take many forms, but generally, it is a style of creative writing that is: (1) focused on the aesthetic and rhythmic qualities of language, (2) condensed into a tight form with no inessential words, and (3) striving to express an idea or evoke an emotion that is difficult to put into words.
Creative writing is the art of using your mind and imagination to come up with ideas and thoughts that are unique and can encompass many different forms. ... Similarly, scripts can be a type of creative writing that appeals to many. Technically, a script can be considered a work of fiction. Nevertheless, it depends on the script in question.
Creative writing spans multiple genres and art forms, including nonfiction. However, fiction is often the first and most popular area associated with creative writing. ... Speeches, for example, can be considered creative writing. Although a speech may include a discussion of certain facts, it is generally written in a creative way to capture ...
Type 2: Journals and Diaries. A journal is a written account of an author's experiences, activities, and feelings. A diary is an example of a journal, in which an author documents his/her life frequently. Journals and diaries can be considered creative writing, particularly if they offer more than just a log of events.
Creative writing is an art form that goes beyond traditional writing, allowing individuals to express their thoughts, emotions, and ideas through the power of words. In this blog post, brought to you by Oxford Summer Courses , we will delve into the essence of Creative Writing, exploring its definition, benefits, and how it can help unleash ...
How We Define Creative Writing. Creative writing is any form where writers can express their thoughts and feelings imaginatively. This type of writing allows authors to draw on their imagination when creating stories and characters and play with language and structure. While there are no boundaries in creative writing, most pieces will contain ...
Creative writing is any type of writing that requires imagination or invention to express an idea uniquely. Creative writing often focuses on the development of narrative, poetry or drama, but it can also include nonfiction writing in a professional setting. It is different from informational writing, which aims to convey an idea directly and ...
On its very baseline creative nonfiction is a literary genre. Some people call it the fourth genre, along with poetry, fiction and drama. And it's an umbrella term for the many different ways one can write what is called creative nonfiction. Memoir, for example, personal essay, biography, narrative history and long form narrative reportage ...
4. Go outside: Spending time in nature and wide-open spaces can expand your attention, enhance beneficial mind-wandering, and boost creativity. 5. Revisit your creative ideas: Aha moments can give you a high—but that rush might make you overestimate the merit of a creative idea.
"Creative writing is considered to be any writing, fiction or non-fiction that goes outside the bounds of normal professional, journalistic, academic, and technical forms of literature. Works which fall into this category include most novels and epics, as well as many short stories and poems. Writing for the screen and stage, screenwriting ...
Creative nonfiction is a genre of writing that uses elements of creative writing to present a factual, true story. Literary techniques that are usually reserved for writing fiction can be used in creative nonfiction, such as dialogue, scene-setting, and narrative arcs. However, a work can only be considered creative nonfiction if the author can ...
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects.
Grace Peserik. Grace Peserik, a writer for ASU Student Life and a communications aide for the School of Politics and Global Studies, spends her time outside of work writing fiction and playing tabletop roleplay games.. Now, as she prepares for graduation this spring, Peserik reflects on both her studies as an English literature major through The College of Liberal Arts and Sciences and her ...
The vast majority of authors don't use artificial intelligence as part of their creative process — or at least won't admit to it. Yet according to a recent poll from the writers' advocacy ...
A diverse and inclusive intellectual community is critical to an exceptional education, scholarly innovation, and human creativity. The Faculty of Arts and Sciences is committed to actions and investments that foster welcoming environments where everyone feels empowered to achieve their greatest potential for learning, teaching, researching, and creating.
In The Double Life of Benson Yu, author Kevin Chong's protagonist navigates a complicated future and a traumatic past by blurring the lines between fiction and reality as a graphic novelist.. As a creative writing professor in UBC Okanagan's Faculty of Creative and Critical Studies, Chong must remain realistic when it comes to discussions around identity and self-discovery, especially ...
this writing piece to be printed in a compilation booklet and distributed at the at the National Veterans Creative Arts Festival in April of 2023. VA Staff Checklist, be sure that each Veteran: • Meets the competition eligibility criteria • Is approved to enter the NVCA Competition as a representative of this VA facility
Writing The Seven Deadly Sins Workshop Participant 2022 "If you ever want a cosy, creative, calming place to explore writing, Laurie's workshops are perfection…My heart is so full (I know what that means now)" Breakfast Clubber 2023 "Probably the best, most productive w/s I've ever attended. Fantastic. Thank you!" Writing The Body ...
The Cambridge Creative Writing Competition organised by the Psychometrics Centre at Cambridge Judge allowed AI (artificial intelligence) to be used for the first time. Read more News The power of AI - and how it's set to revolutionise the finance industry. With all eyes on AI following the release of ChatGPT early last year, we spoke to ...