- Skip to content
We're Sorry! CAREERwise will be undergoing maintenance from 2/22 - 2/27 and you may experience periodic issues.
- MINNESOTA STATE
- CAMPUSES & PROGRAMS
- CAMPUS CAREER CENTERS

- Adult Learners
- Adult Basic Education
- Immigrants and Refugees
- People with a Criminal Conviction
- People with Disabilities
- Recently Unemployed
- CONTINUING EDUCATION & CUSTOMIZED TRAINING
- MN Programs of Study
- Online Learning Resource Center
- NEWS AND EVENTS
- ABOUT CAREERWISE


READY TO PLAN YOUR EDUCATION?
- Explore Careers
- Plan Your Education
- Higher Education
- Short-Term Training
- Online Learning
- Apprenticeship Programs
- Work-Based Learning
- Tips to Prepare for College
- Returning to School as an Adult
- Visit Schools
- Financial Aid 101
- Financial Aid Videos
- Calculate Costs
- Scholarship Websites
- Vouchers and Training Funds
- Applications
- Admissions Tests
- Transfer Credits
- Credit for Prior Learning
- Major Search
- Bachelor's Degree to Career Destination

- What is an Assessment?
- Take an Assessment
- ISEEK Skills Assessment
- CareerOneStop Skills Profiler
- MnCareers Interest Assessment
- ISEEK Career Cluster Interest Survey
- ISEEK Interest Assessment
- Set Career Goals
- Reality Check
- Career Planning for College Students
- Your Lifelong Journey
- Career Clusters and Pathways
- Growing Careers
- Minnesota Emerging Careers
- Unique Career Paths
- Employers Speak: MN Workforce Needs
- Career Videos
- Career Planning Resources
- Campus Career Centers
- Search Careers
- Search Industries
Search Majors
- Bachelor's Degree and Career Destination
- Education Search Tools
- Search K-12 Online Courses
- Salary Information
- Research Employers
- Occupations in Demand
- Regional Careers
- Minnesota Job Vacancies
- Industry Sites
- Cover Letters
- Showcase Your Work
- Career Planning Workbook
- How to Search for a Job
- Build Your Network
- Employment Agencies
- Job Applications
- Barriers to Employment
- How Employers Hire
- Worker Rights
- Types of Interviews
- Common Questions
- Interview Tips
- Interview Follow-Up
- Salary Negotiation
- Employee Benefits
- Consider the Job Offer
- Succeeding in the Workplace
- Dealing With Job Transition
- Job Search Services
- Search Jobs
- Search Businesses
- Search Salaries
Related Links
- Is Higher Education for You?
- How Higher Education Pays Off
- What is a Liberal Arts Education?
- Begin Your School Research
- Certificates, Diplomas, and Degrees
- Education Glossary
Certificates, Diplomas, and Degrees Explained
Learn about the most common types of certificates, diplomas, and degrees offered by post-secondary schools.
Consider types of Minnesota State schools and a liberal arts education to see how these awards might match your educational goals. Also check the requirements for each school . You might need a specific degree before being eligible for another.
Undergraduate Certificates, Diplomas, and Degrees
These awards usually take four years or less to complete. The actual completion time depends on how much time a student can commit to their studies. Part-time students, for example, may require more than four years for an undergraduate award.
- Certificate . These are academic programs of nine to 30 credits that are completed in a year or less by full-time students. Some programs provide specialized training for people who already have diplomas or degrees. Others are for those who want to quickly complete a program that leads to a specific job.
- Diploma . An academic program generally of 30 to 72 credits intended to provide students with skills leading directly to a specific job.
- Associate Degree . An award that normally requires at least two but less than four years of full-time college work. There are different types of associate degrees with varying transferability .
- Bachelor's Degree . An award that normally requires at least four but not more than six years of full-time college work. Also includes bachelor's degrees that are completed in three years.
Graduate Certificates and Degrees
Entering one of these programs generally requires prior completion of an undergraduate award.
- Post-Baccalaureate Certificate . An award that requires completion of an organized program of study requiring 18 credit hours beyond the bachelor's. Designed for those with a bachelor's degree who do not meet the academic requirements of a master's degree.
- Graduate Degree . A degree awarded for education at a level beyond the bachelor's degree. State universities offer graduate certificates, master's degrees, and specialist degrees in various professional and liberal arts fields.
- Master's Degree . An award that requires the completion of a program of study of at least one but not more than two of years of full-time academic work beyond the bachelor's degree.
- Post-Master's Certificate . An award that requires completion of an organized program of study of 24 credit hours beyond the master's degree, but does not meet the requirements of academic degrees at the doctor's level.
- Doctorate Degree . The highest award a student can earn for graduate study. The doctor's degree classification includes such degrees as Doctor of Education (Ed.D.), Doctor of Juridical Science (J.D.), Doctor of Public Health (D.P.H.), and the Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.).
- Chiropractic
- Osteopathic Medicine
- Veterinary Medicine
Continuing Education Units (CEU)
One CEU is normally defined as 10 contact hours of participation in an organized continuing education experience under responsible sponsorship, capable direction, and qualified instruction.
Source: Minnesota Office of Higher Education , Minnesota State Colleges and Universities , IPEDS Glossary
Search Programs
- Campuses and Programs
- Advanced Major Search
Search Courses
- Advanced Course Search
Search Certifications
- Certifications
Search Short-Term Training
Search apprenticeships.
- Apprenticeship Sponsors
Learn more about...
- Internal Resource Name
Other Resources on the Web
- External Resource Name
CAREERwise Newsletter Sign up to receive email updates from CAREERwise.

Why Choose an Online Diploma
Getting a quality education is the first step to a building a rewarding career, and Bryant & Stratton College diploma programs offer a reliable and accessible means of getting started on a solid, career-focused education. So what are the advantages of using an online diploma program – as compared to traditional on-campus education – for the average, career-minded individual?
Diploma-level programs can provide a relatively short path to the training, knowledge and credentials you need to get your foot in the door of your chosen field. Bryant & Stratton College diploma programs can generally be completed within a year. Online diploma programs can often be completed more quickly, since the virtual classroom offers more semesters of study each year than are offered in traditional, campus-based programs.
Getting qualified for work in your field more quickly via an online diploma program can help you get into a good, entry-level position sooner. If you are already in an entry-level position, and need that diploma for career advancement, sooner is certainly better. If earning a diploma is a stepping stone in a larger education or career-building plan, getting into the workforce quickly gets you started on gaining practical, hands-on experience in your field as you work towards earning an associate or bachelor degree. Completing a diploma program can also give you a head start on the next step of your education, as credits earned from diploma-level programs can be applied to Bryant & Stratton College associate and bachelor degree programs both in-class or online.
Flexibility is another important advantage of choosing an online diploma program over the traditional, on-campus learning environment. Students who attend the virtual classroom to earn their diplomas can schedule their studies around their daily lives, creating a more manageable college experience. Rather than reporting to on-campus classes at pre-set dates and times, online diploma students can access the classes, lectures, assignments and discussions 24 hours a day, 7 days per week. This gives them the freedom to complete coursework whenever it is most convenient, even if that is late at night or on weekends or holidays.
Those potential benefits of faster completion and superior flexibility and convenience come with another big advantage: A comprehensive suite of online education services that provide virtual students with the same level of support offered to on-campus learners. At Bryant & Stratton College, an online diploma is just as valuable as one earned in the classroom with the added conveniences of online learning and a wide choice of programs designed to match your needs or interests.
Request Information
Bryant & Stratton College: Available Online Diploma Programs
This online diploma program prepares students for positions in a variety of professional fields, since virtually all types of businesses, companies and industries have a need for skilled accounting work. Students who complete this program will be provided with a solid foundation of skills to perform an array of accounting tasks. They will be able to analyze and interpret financial reports, prepare accounting reports, interpret and apply accepted accounting principles, and analyze, record and report financial information via a range of accounting systems. These skills and abilities and others acquired in this 30-credit diploma program can open the door to accounting-related positions in accounting firms, manufacturing and retail, as well as many other industries. It can also be a stepping stone to more advanced career opportunities for individuals who plan to continue on to earn an associate or bachelor degree.
View major courses required and potential career options .
This online diploma program is designed to give students the foundation of knowledge, training and skills that they need to begin a career in the digital marketing field. Students learn skills that include search engine optimization, web data analytics, social media, brand monitoring and growth practices and much more. Upon graduation, students will know how to design and implement effective social media marketing campaigns, use digital marketing strategies to build website traffic and increase brand visibility and accessibility, create consumer loyalty via social media pathways, and analyze consumer digital behavior and the results of digital marketing campaigns. Earning this diploma prepares students to step into an entry-level position in marketing. It also provides them with the ability to continue on with their education to earn a Digital Marketing associate degree with Bryant & Stratton College, opening doors for career advancement in the digital marketing field.
View major courses required and potential career options.
Earning this diploma helps students become qualified and prepared for a variety of front-office roles in many professional fields. These include clerical, office support and administrative assistant positions, among other potential opportunities. Students will learn the skills necessary to adapt to the ever-changing technological aspects of the modern business setting. They will gain proficiency in the latest technology, learn office procedures, master document processing, and acquire or enhance communication skills. They will learn how to use today's technology to operate in the traditional office environment, as well as in the virtual workplace. Graduates will be able to employ key financial, managerial, relational, marketing, and ethical business principles in the office environment. They will gain the ability to use high-level organizational, technical and interpersonal skills to improve workplace efficiency, as well as business-related technologies and resources to enhance productivity. Students who plan to continue their education can apply courses and credits from this program towards Bryant & Stratton's associate degree in Office Information Technology.
Completing this diploma program prepares graduates to pursue a range of career opportunities in the field of business, including customer service, sales or front-office positions, among many others. Students will learn skills vital to functions in business, including improving processes and productivity, addressing customer concerns in a professional manner, and effectively communicating about products, services and other essential aspects of business. Students will also gain understanding of key business concepts and acquire or improve management, leadership, decision-making and mathematical skills. Graduates may apply courses and credits earned with the Business Assistant Diploma towards an associate degree in business.
Students who complete this program will be prepared to pursue many positions in the hospitality industry. This includes careers in workplace environments that include hotels, the food and beverage industry, travel and tourism companies and sports venues, among many others. Skills learned in this program can help students qualify for front-office positions, customer service roles and many other occupations within the hospitality field. Students will also be introduced to skills and concepts relevant to facilities management and other supervisory and managerial roles. Courses and credits earned with the Hospitality Assistant Diploma program can be applied towards an associate degree in Hospitality Management.
This course of study is designed to provide students with the credentials and skills they need to make their first steps in pursuing a career in the medical field. Earning the Medical Office Assistant Diploma qualifies graduates for a number of entry-level positions in healthcare environments that include hospitals, nursing homes, long-term care facilities, private medical practices and insurance providers, among many others. This program places an emphasis on the skills needed to succeed in front-office and administrative positions within the healthcare industry, preparing students to operate effectively within healthcare systems and processes, and perform various managerial functions. These skills help graduates qualify for positions that include medical secretary and office assistant roles, among others. Credits earned from this program can be applied to related degree programs, such as the Medical Administrative Assistant or Medical Reimbursement and Coding associate degree programs.
This is another diploma program that prepares students to begin a career in the healthcare field. Using a career-focused curriculum, this program works to help students become qualified for a variety of entry-level positions within the administrative side of the healthcare industry. Graduates will learn the skills needed to handle clerical functions and legal and financial systems. Courses and earned credits from this program can be applied towards the associate or bachelor’s degree in Health Services Administration at Bryant & Stratton College.
This 30-credit diploma program provides students with the foundation to embark on a career in criminal justice at the federal, state or local level. It prepares them for a wide variety of entry-level positions within the field, in employment environments that include law enforcement, juvenile justice systems, parole systems and probation programs, among many others. Courses and credits from this program can be applied towards earning an associate degree in Criminal Justice Studies.
This online diploma program prepares students to provide support to attorneys in law firms as well as business and corporate legal departments. Students learn to research and draft legal documents for civil and criminal cases, provide support in custody, separation and divorce cases, and work in case management, document and records maintenance and correspondence roles, among other key functions within the legal field. Graduates may apply courses and credits earned through this program towards an associate degree in Paralegal Studies at Bryant & Stratton College.
This program provides students with ethical and legal foundation and framework they need to effectively work with patients in the human and social services setting. A strong emphasis is placed on helping students develop a strong understanding of the changing needs of clients and an extensive skillset for effectively meeting those needs. Graduates of this program can apply courses and earned credits toward the associate degree in Human and Social Services.
This program is designed to prepare students to work in a variety of IT positions, including those related to computer networks, as well as other networking services and technology. Students gain a foundation of skills in computer technology, hardware, operating systems and information systems, qualifying them for entry-level positions within the IT field. Graduates are also prepared to take the CompTIA A+ certification exam, a credential that is highly sought by employers. Courses and earned credits can be applied towards the associate degree in Networking Technology or Security Technology
This program equips the graduate with the requisite skills and tools to properly apply thousands of codes used for diagnosis, injury and medical procedures. Based on application of varied numeric and alphanumeric codes, patients can be billed accordingly. The coding subsets focused on in the curriculum are the International Classification of Diseases, or ICD, codes, which correspond to a patient’s injury or sickness, and Current Procedure Terminology, or CPT, codes. Upon completion, graduates will be able translate medical procedures into code or translate codes into a financial report.
Shaping young minds is what this program is designed to prepare for. This online course envelops the student in theoretical knowledge and necessary skills to incorporate family participation. All graduates will earn a solid understanding of the developmental stages of early childhood. The 120-hour course develops the expertise necessary for working in child care centers, preschools, or other child development settings. Completion can be a definitive step towards a promising career in education for individuals who plan to continue and earn an associate or bachelor's degree.
- Online Experience
- Online Degrees
- Online Associate Degrees Online Bachelor Degrees Online Business Degrees Online Diplomas Online Education Degrees Online Healthcare Degrees Online Legal Services Degrees Online Technology Degrees
- Online Certificates
- Accounting Certificate Certified Coding Specialists Prep Course Healthcare Management Certificate Human Resources Certificate Information Technology Medical Billing Medical Billing and Coding Medical Coding Medical Office Technology Certificate Paralegal - Business Litigation Certificate Paralegal - Civil Litiagtion Certificate Paralegal - Criminal Litigation Certificate Paralegal - Domestic Law Certificate Paralegal Certificate
- Apply to Online College

America Needs a New Workforce Education System
Developing large-scale workforce education programs that enable workers to advance or change industries will not only reduce income inequality, but also support domestic innovation..
The American dream promised that if you worked hard, you could move up, with well-paying, working-class jobs providing a gateway to an ever-growing middle class. Today, however, the nation is seeing increasing inequality rather than economic convergence. Technological advances, combined with profound labor market shifts during the pandemic, are putting quality jobs out of reach for workers who lack the proper skills and training. One of the best ways to address this challenge is to improve workforce education.
Learning on the job has, of course, long been a feature of most occupations. But developing formal programs that allow most workers to advance from their current position or to even change industries has not been a priority for decades. Yet both research and practical experience have shown that such programs, designed to improve skills and education over the course of an employee’s work life, are precisely what is needed. Not just any jobs program will do. They must be carefully focused, flexible enough to meet emerging needs, and tailored to lifelong learning. Failure to meet these requirements could consign millions of workers to dead-end jobs during their most productive years.
The benefits of developing large-scale programs for workforce education will extend beyond the already considerable ones of addressing inequality. A more skilled workforce also contributes to innovation. Industrial policy in the United States has largely focused on two preproduction tasks aimed at earlier-stage innovation: support for agencies funding academic and lab research and development, and support for industry R&D through the federal R&D tax credit. But there hasn’t been a complementary workforce education thrust. Indeed, many economists view science and engineering at the college and graduate school levels as the principal educational key to future growth. Yet as innovation diffuses into production—be it robotic welding or new coating technologies—R&D has proven to be not the only educational need. A skilled technical workforce has an innovation role as well—in programming the robotic welders, for example, and in improving the coating technologies.
THE SOCIAL DISRUPTION IS REAL
Overall, job opportunities for high school graduates have shrunk significantly in recent years. For example, the share of men of prime working age with no college experience who are not working at all reached 18% in 2013. At the same time, median income for men who had not completed high school fell by 20% between 1990 and 2013 and by 13% for those with a high school diploma or some college. In a country that prides itself on its social mobility, this was a clear signal of a loss to middle-income ranks and of growing social inequality, as well as a harbinger of a postindustrial backlash.
A closer look at two sectors—manufacturing and retail—reveals the turmoil. Historically, manufacturing has been an important middle-class pathway for high school educated males—including African Americans and Hispanic Americans. From 2000 to 2010, however, manufacturing employment fell by 5.8 million jobs (or almost a third), from 17.3 million to 11.5 million. And by 2015, it had recovered to only about 12 million jobs, where it remains.
Retail, which often offers a first job or a job of refuge, is in trouble as well, as stores, malls, and entire chains have closed over the past decade. First, the extraordinary expansion in the second half of the 20th century crashed against the 2008 financial crunch. Then the disruptive growth of online ordering accelerated a decline in in-person retail even further. Warehousing positions offset some of this job loss, but they went to different people—female store clerks weren’t hired to do heavy lifting in warehouses. Fifteen million people were employed in retail trades at the beginning of 2020. Then the coronavirus hit.
The pandemic has been a shock not just to retail but to much of the system. The volume of jobs lost has been dramatic. Restaurants lost 5.5 million jobs in April 2020, then reopenings during the summer let the industry regain some jobs, only to lose them again with the spike in infections during the fall. Similarly, retail lost 2.3 million store jobs in April, rebounded by a million jobs by June, but by fall the job numbers were falling again. In travel and tourism, 35% of the jobs have been lost since February 2020. These aren’t the only hard-hit sectors, but they are big ones. Many jobs in retail, the restaurant industry, tourism, and travel won’t be coming back: bankruptcies are already climbing. Millions of workers in these sectors will be stranded.
This latest disruption will make American economic inequality even worse than it was before the pandemic. Workers from hard-hit sectors will need to shift to new sectors where there will be jobs. And to thrive, they must get not just any job but quality jobs. While lower-end services jobs had been growing as the middle class thinned out, new Labor Department data show the coronavirus has now hit that sector, so job openings will tend to require higher skills.
Opportunities exist. Health care, for example, is embracing suites of new technologies that will require skilled technologists at good pay. Manufacturing and utilities have aging workforces that will require millions of new workers in coming years, albeit for increasingly skilled jobs. The trick to minimizing further disruption will be to provide the skills and training needed to educate and shape the current worker pool.
WANTED: WORKER SKILLS AND HUMAN SKILLS
The United States was the first nation to develop mass higher education programs, and we used them as an engine for innovation as well as economic and social mobility. The high school degree was once the acceptable basic credential, but has since been displaced. A college degree is now the key differentiator for economic well-being.
Higher education is also a complex, established “legacy” sector, reluctant to change and adapt its operating modes to fit new needs. Although many of the necessary prerequisites are disconnected from actual job and life skills, college degrees have become a default credential for employers because there are no others that are as widely accepted and used.
Business requires new skills, particularly in information technology, so the workforce as a whole requires upskilling—current workers as well as incoming college graduates and those without college degrees. And yet universities have not embraced or contributed to these workforce developments.
Herein lies an opportunity for institutions of higher learning, particularly at a time when they themselves face increasing financial pressure: they can offer more career-related skills in addition to what they teach now. This approach may enable them to reach beyond their current declining demographic of 18- to 26-year-olds. Some critics have worried that this shift might erode liberal art traditions. We argue the opposite: in fact “human skills” such as critical thinking, creativity, writing, and communicating are in high demand, and can flourish in this new configuration.
Unlike many European nations, the United States never built a comprehensive workforce education system. So perhaps it comes as no surprise that current programs lack the proper focus, are small in scale, and siloed from each other. The Department of Labor’s training programs don’t reach the oncoming higher technical skills or help incumbent workers acquire them. In turn, the Department of Education’s programs tend to target college, not workforce education, and don’t mesh with the Labor programs. With the exception of a few states, such as Massachusetts, the vocational education system in high schools has largely been dismantled. And community colleges, which could provide advanced training in emerging fields, are largely underfunded—not to mention that their completion rates hover around a third.
Most colleges and universities don’t see workforce education as their bailiwick and so aren’t linked to the other participants in the system. Overall, the education system is disconnected from the workplace, and a system for lifelong learning is missing. In addition, the existing workforce education system operates at too small a scale to meet the growing demand. The system needs not only reforms but also the ability to reach many more people, more effectively. Online education is one tool that can help with the scale-up—if applied correctly. Addressing these problems should help to reduce economic inequality and deepen our capacity for innovation.
THE NEW COMMUNITY COLLEGE TRY
Community colleges could become the cornerstone of a robust, much-needed workplace education system. A number of these institutions, some highlighted below, have already begun to show the way. They will all need additional building blocks, however, to achieve the necessary scale and flexibility of offerings.
Asnuntuck Community College is in the middle of an aerospace industry corridor along the Connecticut River Valley. It has developed advanced manufacturing certificate programs, using a new state-supported, state-of-the-manufacturing-art equipment center. Enrollees include not only its own students, but also high school students as well as workers at area companies, small and large.
Valencia College in Florida set out to reach a large economic underclass stuck in low-end, low-paid, part-time service jobs. It tailored various short programs to help students quickly get on a career ladder leading to secure jobs with benefits that can support families. Each program lasted 10 to 22 weeks, five days per week for eight hours a day. Valencia offered industry-standard certificates in advanced manufacturing, construction, heavy equipment, logistics, and health care fields. Importantly, these certificates could be stacked for multiple, certified complementary skills and credits toward a Valencia associate degree.
Trident Technical College in Charleston, South Carolina, worked with area firms and the state’s Chamber of Commerce to develop a new youth apprenticeship program beginning in the junior year of high school. Students employed by participating companies go to high school classes in the morning, where they must take math and science, to the college at midday for technical courses, and to their sponsoring company for well-paying jobs in afternoons. This takes them out of a sometimes-disruptive high school culture into higher-expectation environments. By tearing down the wall between learning and work, the program places entry-level workers on a path to quality jobs and education.
Elsewhere, the US military has pioneered efforts to teach hands-on skills through virtual and augmented reality. The Navy’s Training Systems Division in Florida, for example, has developed programs that use online simulations run on touch screens and high-end gaming computers. The Navy is now shifting a substantial amount of its training for advanced equipment on ships, submarines, and at air bases into these online systems.
KEY FOUNDATIONS
Several elements are common to the most successful programs for workplace education. They include:
- Forming short programs . Programs focused on technical skills should typically run for 10 to 20 weeks. People who have been in the workforce won’t be able to take off time for two- or four-year degrees; they have families to support and obligations to meet.
- Embracing credentialing. Programs should provide certificates for specific groups of related skills, based on demonstrated competencies. These should be stacked toward college degrees and credits, which remain the most broadly recognized credentials.
- Supporting competency-based education . Programs should be organized around demonstrated skills broken down into particular competencies, unlike today’s education that is based on an agricultural calendar and standard completion times. If students show the skill competency, they get the certificate, regardless of how long they have spent in the program. This can cut time in school and student costs, and reward practical experience.
- Developing appropriate online education. Online modules will be critical if workforce education is going to scale up to meet postpandemic needs. And yet online education can’t replace effective instructors or hands-on work with actual equipment. Online education is best suited to conveying and assessing the foundational information behind the skills.
- Breaking down the work/learn barrier . Programs should be linked to industry, as today’s schools have become too disconnected from the workplace. Linkage programs in the form of apprenticeships, internships, and cooperative programs are needed to get students into the workplace, earning money while they build skills. At the same time, they can make a direct connection between the competencies they must learn for greater job opportunities.
- Improving completion rates . Completion rates at community colleges should be at least 70%, up from the 30% rate at many of them today. Frustration with required remedial prep courses leads many students to drop out. Successful programs have found one solution in integrating the supportive course work into students’ study program for career skills so they can clearly see how the remedial work is relevant to their career opportunities.
- Embedding industry-recognized credentials into educational programs . Many employers want the assurance of skill knowledge that a credential approved and accepted by industry provides. It creates an additional and parallel pathway to help students toward employment. It also ensures that academic programs are relevant to actual industry needs.
The latest research on workforce education is quite clear. Federal resources need to scale up. States, with backing from federal education funds, must implement the new strategies outlined above. Some states and employers, and the community colleges they work with, are starting to embrace these steps. The workforce disruption from the pandemic could be a driver that forces further action. A more equitable and innovative future is possible, provided we leave our previously scattershot approaches behind.
This story was originally published in Issues in Science and Technology on March 9, 2021.
Open Learning newsletter
Here to help you grow
Whether you're looking to build your business, develop your career, or pick up a new digital skill, we can help you get started.
What can we help you with?
And what would you like to do?
- Show me everything
- Prepare for a new job
- Develop communication skills
- Increase my productivity
- Learn about digital marketing
- Learn coding & development skills
- Get started with artificial intelligence
- Get started with cloud computing
- Stay safe online
- Learn design skills
- Improve my digital wellbeing
- Champion diversity
- Learn about sustainability
- Understand my audience
- Start selling online
- Expand internationally
- Keep my business safe online
Grow your career
Whether you're writing your first CV or deepening your technical knowledge, our library is full of ways to sharpen your digital skillset.

Google Career Certificates
Earn a Google Career Certificate to prepare for a job in a high-growth field like Data Analytics, UX Design, and more.

Introductory digital skills courses
Get started with a range of digital skills, with entry level courses in everything from online marketing to coding.

Cloud computing fundamentals
From intro to advanced-level learning, find out more about cloud computing principles and career paths.

Google product trainings
Learn how to get the most out of the Google products you use, like Google Ads or Analytics.
Grow your business
From bringing your business online for the first time to growing its reach internationally, our library of online learning and tools can help you take your business further.

Your Digital Essentials Guide
Get an introduction to the products, tools and tips that can help you build an online presence for your small business.

Flexible online training
Learn online, at your own pace, with a library of training made to help strengthen your business with digital skills.

Resources for startups
Google for Startups connects you to the right people, products and best practices to help your business thrive.
Helpful tools for small business owners

Google Business Profile
Manage how your business shows up on Google Search and Maps to help new customers find you more easily.

Market Finder
Identify new potential markets and start selling to customers at home and around the world.
Growth stories
Meet people all over Europe who are using technology to adapt and grow their business or career.
About Grow with Google
Grow with Google is a programme that helps people to grow their careers or businesses by learning new skills and making the most of digital tools. We partner with governments and local organisations to develop digital skills and tools where they are needed most.
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
.jpg?sfvrsn=de11c685_0)
- Student Login
- Staff Login
- e-Services & Forms
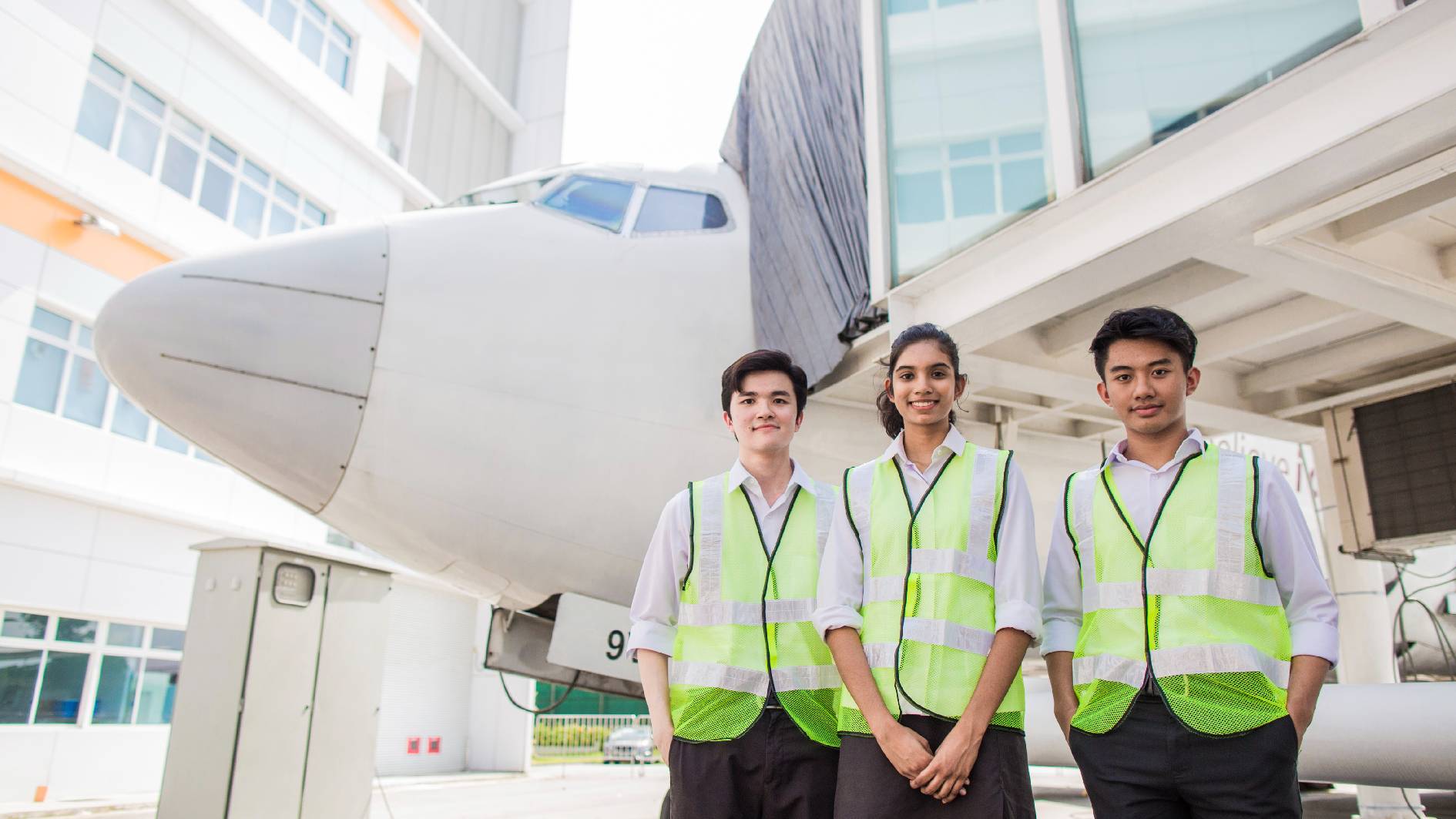

- Work-Study Diploma
Work, Learn and Earn at the same time!
Why choose the Work-Study Diploma?
You get a fully-sponsored and nationally-recognised Diploma
You have more opportunities for career advancement, skills upgrading and further education
You earn a monthly salary and enjoy employee benefits
In-service employees can also join the work and learn programme
You get a headstart by obtaining valuable work experience and on the job training from experts and practitioners
You get sign-on incentive of S$5,000*
* For Singapore Citizens who are fresh ITE full-time / traineeship graduates from relevant feeder courses and within three years of graduation or Operationally Ready Date.

Business & Services Sector

Engineering Sector

Infocomm & Media Sector

Work-Study Diploma – Full Course Listing

Starting Your Work-Study Journey

Download WSDip Information Booklet
Watch the videos to find out more:, for applicants.
For Employers
- Interview Questions
What is Diploma Course? : Types, Benefits, and Career Opportunities
Diploma courses have emerged as valuable pathways for individuals seeking specialized knowledge and skill enhancement. Whether you are a recent high school graduate exploring post-secondary options or a professional looking to upskill, understanding the types, benefits, and career opportunities associated with diploma courses is crucial. This blog aims to shed light on the significance of diploma courses in today’s educational world.
Table of Contents
What is a diploma course, eligibility criteria for a diploma course, types of diploma courses, benefits of pursuing a diploma course, career opportunities after a diploma course, how does the diploma course help you in interviews, diploma course vs. degree program, diploma course vs. certification program, diploma course vs. correspondence program.
A diploma course is a specialized and concise educational program designed to provide practical skills and knowledge in a specific field. Unlike traditional degree programs, diploma courses are shorter in duration, generally ranging from 6 months to 2 years. These courses cater to various industries and disciplines, including engineering, medical sciences, business, information technology, arts, and more.
The eligibility criteria for diploma courses often include a minimum educational qualification equivalent to high school completion. They are known for their hands-on approach, emphasizing real-world application of knowledge and skill development. This practical focus makes diploma holders well-prepared for immediate entry into the job market.
Diploma courses offer a cost-effective and time-efficient alternative to longer degree programs. They are particularly beneficial for individuals seeking specialized expertise and a quicker pathway to employment. Recognized by industries globally, diploma courses play an important role in bridging the gap between academic learning and the specific skill set demanded by various professions, making them a valuable option for those looking to kick-start their career.
Below, we have provided a simplified table that represents the general eligibility criteria for a diploma course:

In many areas, there are diploma programs that help students get ready for real-world job requirements by teaching them useful skills. However, these diplomas can vary in type depending on what they teach and the skills they focus on. Below, we have explained the three types of diplomas:
Vocational Diplomas
Vocational diplomas focus on practical skills and hands-on training in specific trades or professions. These courses are designed to prepare students for specific careers, such as automotive technology, cosmetology, or culinary arts. Emphasizing real-world applications, vocational diplomas enable individuals to enter the workforce with specialized expertise, making them valuable contributors in their chosen fields. Programs typically last 1 to 2 years and include apprenticeships or internships. Upon completion, students are qualified to work in entry-level positions in their chosen vocation.
Examples of Vocational Diplomas are:
- Diploma in Automobile Engineering
- Diploma in Culinary Arts
- Diploma in Welding
- Diploma in Graphic Design
Academic Diplomas
Academic diplomas are centered around traditional academic subjects, providing a comprehensive education in areas like science, humanities, or arts. These diplomas often serve as prerequisites for higher education, offering a well-rounded education in theoretical knowledge and critical thinking. Academic diplomas are commonly pursued in high schools and colleges, preparing students for diverse academic pursuits and careers requiring a strong academic background. Programs usually last 2 years, and credits may be transferable to a bachelor’s degree.
Examples of Academic Diplomas are:
- Diploma in Liberal Arts
- Diploma in Science
- Diploma in Mathematics
- Diploma in Humanities
Professional Diplomas
Professional diplomas are credentials awarded to individuals who have completed specialized training in a specific profession or field. These diplomas focus on practical skills and knowledge needed for a particular career, often bridging the gap between academic theory and practical application. In areas such as business, law, and healthcare, professional diplomas are recognized by industry bodies and may enhance employment prospects. They are well-suited for individuals seeking to advance their careers or transition into new professional roles, providing targeted expertise and credibility in the job market.
Examples of Professional Diplomas are:
- Diploma in Project Management
- Diploma in Accounting
- Diploma in Human Resource Management
- Diploma in Marketing
- Diploma in Business Administration
Get 100% Hike!
Master Most in Demand Skills Now !

Individuals who prefer not to commit to the time-intensive traditional paths of bachelor’s or master’s degrees can opt for diploma courses as an excellent alternative. Pursuing a diploma course offers various benefits, which we have mentioned below:
- Specialized Skills : Diploma programs are structured to provide individuals with hands-on training and specialized knowledge in a particular field. This focused approach ensures that graduates acquire specific skills relevant to their chosen industry, making them well-equipped for the tasks and responsibilities associated with their profession.
- Cost-Effective : Diploma programs often have a shorter duration compared to traditional degree courses, resulting in lower overall education costs. This affordability makes diplomas an attractive option for individuals seeking to acquire practical skills and enter the workforce more quickly without a substantial financial burden.
- Career Advancement : Completing a diploma signifies to employers that candidates have not only acquired theoretical knowledge but have also gained practical skills essential for the workplace. This can enhance their suitability for promotions and career advancements within their chosen field, showcasing a well-rounded skill set that aligns with industry needs.
- Practical Training : Many diploma courses prioritize practical training, allowing individuals to apply theoretical concepts in real-world scenarios. This hands-on experience is invaluable, as it not only deepens understanding but also prepares students to address challenges effectively in their professional roles.
- Transition to Employment : Diploma programs are structured to prepare candidates for specific roles within an industry. This targeted approach increases the likelihood of swift employment after completion, as employers recognize the practical skills and knowledge gained during the program as directly applicable to their workforce needs.

Completing a diploma opens up many job possibilities in various fields. The specialized skills acquired during these programs make graduates well-equipped for specific job roles. Here are some common career opportunities one can get after completing a diploma:
- Entry-Level Positions : Many diploma programs are designed to prepare students for specific entry-level positions in a particular industry. For example, a diploma in graphic design might lead to roles like graphic designer or junior artist.
- Technician Role : Diploma holders often find opportunities as technicians in fields such as engineering, electronics, and information technology. They play crucial roles in implementing, maintaining, and troubleshooting technical systems.
- Healthcare Professions : Medical diplomas lead to roles in healthcare, where graduates may work as medical laboratory technicians, radiology technicians, or dental assistants. These positions are integral to the functioning of healthcare facilities.
- Business and Management Positions : Diploma holders can pursue roles such as administrative assistants, office managers, or project coordinators. Their practical skills make them valuable assets in organizing and executing business operations.
- Creative Industries : Diploma courses in arts and design pave the way for careers in graphic design, fashion, interior decoration, and multimedia. Graduates may work in creative agencies, design studios, or even establish their own ventures.
- Automotive and Aviation Careers : Diplomas in automotive or aviation technology lead to roles as automotive technicians, aircraft mechanics, or aviation maintenance technicians. Graduates contribute to the maintenance and repair of vehicles or aircraft.

A diploma course not only equips candidates with practical skills but also enables them to effectively communicate, showcase their achievements, and demonstrate their suitability for specific job roles during interviews. Let’s see how a diploma course can significantly contribute to your success during job interviews:
- Skill Development and Showcase : The diploma program focuses on developing practical skills relevant to specific industries. During interviews, candidates can effectively showcase these hands-on abilities, providing tangible evidence of their competence.
- Real-World Application of Knowledge : Unlike purely theoretical learning, diploma courses emphasize the application of knowledge in real-world scenarios. This practical experience equips candidates with a deeper understanding of industry practices, making them more adaptable to workplace challenges.
- Enhanced Confidence : The hands-on experience gained in diploma courses often boosts candidates’ confidence. Having successfully applied skills in real-world problems, candidates feel more self-assured discussing their achievements and problem-solving capabilities in interviews.
- Portfolio Building : Completing a diploma course generally results in the creation of a portfolio showcasing the candidate’s work, projects, and achievements. This portfolio serves as a powerful visual aid during interviews, providing concrete examples of the candidate’s capabilities.
- Adaptability and Quick Learning : The practical nature of diploma courses cultivates adaptability and the ability to learn quickly. Interviewers appreciate candidates who can swiftly adapt to new environments and technologies, and diploma holders are often well-equipped in this regard.
Diploma courses and degree programs are two distinct educational pathways, each with its characteristics and purposes. Below, we have provided a table highlighting some key differences between a diploma course and a degree program:
Diploma courses and certification programs are both forms of specialized education, but they differ in terms of duration, depth, and focus of study. Below is a table that outlines some key differences between a diploma course and a certification program:
Both diploma courses and correspondence programs are alternative methods of education that cater to different needs and preferences. Below is a table comparing a diploma course and a correspondence program:
What is the duration of a diploma course?
Diploma courses usually range from 6 months to 2 years, depending on the field of study.
Is a diploma equivalent to completing class 12?
Yes, in India, a diploma is considered equivalent to completing class 12. However, it’s important to note that not all diplomas are considered equivalent to class 12 in certain cases.
Can I pursue a diploma course after completing a degree?
Yes, many individuals pursue diploma courses to gain specialized skills even after completing a degree program.
Are diploma courses internationally recognized?
The recognition of diploma courses varies, but many are recognized globally, especially if offered by reputable institutions.
Are diploma courses suitable for career changes?
Yes, diploma courses can be an excellent option for career changes, as they provide targeted training in a new field without the time commitment of a full-degree program.
Course Schedule

Course Preview
Expert-Led No.1

ADMISSION ENQUIRY
Complete your growth journey quickly without Quitting Your Job
UGC / MHRD / AICTE / NAAC / AIU APPROVED UNIVERSITY PART-TIME UG/PG DEGREE PROGRAMS FOR WORKING PROFESSIONALS (Up-skill yourself with part-time degree course and complete your growth journey quickly without Quitting Your Job)
Accelerate your future:, indian institute of industry interaction education and research has been the pioneer in professionally focused and industry-based education specially designed for working professionals. iiiier provides the platform by creating resurgence for working professionals and also providing the change by giving a new way of educational development in society., iiiier provides the cutting edge in the current industrial scenario by expanding your abilities within your current profession or to shift paths in the given sectors along with the skills acquired. iiiier put together provides the best in virtual education/work-integrated programs for working professionals with international quality standards relevant to your specialization along with opportunities to upgrade and to stay relevant without giving up on your profession., as you endeavour to shine in your career and taking it to next level or to pursue a career change by maintaining the existing position and income, iiiier offers a wide range of academic membership (degree course) program options with flexibility. all of the academic membership (degree) programs are presented to students by virtual education and asynchronous format., part-time / work integrated learning.
POLYTECHNIC DIPLOMA
Technician / diploma membership (2 or 3 years).
B.TECH / B.E
Graduateship / associate membership (3 or 4 years).
M.TECH / ME / MBA
Post graduateship / chartered membership (2 years), salient features:.
World class Innovative Virtual Education and Virtual Labs Environment at an Affordable fee (Learn Anywhere & Any Time).
Learn entire course from IIT’s & IIS’s professors in online.
Week end face to face classes will be delivered by highly qualified faculty.
Practical works and on job training will be carry out on campus and Industries.
Working professionals can earn UGC / MHRD / AICTE / NAAC / AIU approved University UG/PG Degree in Part-Time mode Without Quitting Your Job.
UGC / MHRD / AICTE / NAAC / AIU Approved University degree course are eligible to work in Government organization, Private Companies and International employment.
UGC / MHRD / AICTE / NAAC / AIU Approved University degree course eligible for higher education in government Universities, Private Universities and International Universities.
24X7 online support by professors.
IIIIER educational qualification is accepted by State & Central HRD and MEA for Attestation / Apostille / Endorsement.
IIIIER educational qualification is accepted for work in private sector and Government of India projects ( ie: NSDC, MOSDE, Skill India).
IIIIER educational qualification is accepted for higher education in Private Universities ( ie: BITS Pilani University - Institute of Eminence status granted by MHRD).
IIIIER reached a new milestone by the development of WORLD LONGEST HYBRID BIKE, which was recognized by India Book of Records and Asia Book of Records .
Convenient class Timings (Online&Offline)
Up skilling and Reskilling Opportunities
Networking Opportunities with Students & Alumni
Placement Opportunities
Flexible EMI payment & Education loan facility
RECOGNITION / APPROVAL:
- UGC / AICTE APPROVED COURSE: click here
- IIIIER COURSE: click here
HOW TO ACCESS THE PORTAL
ABOUT IIIIER
Indian institute of industry interaction education and research (iiiier) is an autonomous professional institution with the head office at chennai, tamilnadu. iiiier is the mentor organization promoted by a group of industrialists, entrepreneurs and academicians those who are contributing themselves in the field of education and skill development to bridging gap between academics and industries., iiiier conducts various industry oriented programs like seminars, workshop, internship, national and international level technical conferences in association with industries and national/international professional societies dedicated to the case of education and social development. the institution offers various memberships like donor, fellow, corporate, institutional, professional and student’s membership. for academic membership iiiier conduct examination like technician membership, graduateship/associate membership and post graduateship/chartered membership., iiiier is approved local chapter of swayam-nptel (init. by mhrd) and coordinated by iit madras to promote quality of technical education in virtual mode for working professionals. iiiier is also being a part of the government of india skill india mission under the pmkvy, naps and csr scheme. iiiier is committed to research in key areas across engineering and technology to provide plenty of opportunities for students to enhance their research skills during their academic/training period at the institution., why students choose us.
WHAT MEDIA SAYS ABOUT US

Subscribe to Get information
The Best way to help you reach your goals.Feel free and contact us
- Mobile: +91 93452 89082
- Landline: 044 25562143
- Toll Free: 1800-120-3034
- Mail: [email protected]
Popular Searches:
Follow us on
Follow us On
Processing!
Verify your email address.

Certificate I in Work Education
Gain basic workplace skills valued by all employers.
Prepare yourself for further education or entry-level employment with this hands-on course, designed for people with special learning needs. The Certificate I in Work Education will provide you with a broad range of practical experience and an understanding of basic workplace expectations. During the course you’ll learn how to work and communicate effectively in the workplace, participate in OHS processes, operate a personal computer, develop a vocational learning plan, apply basic mathematical concepts, develop personal management skills, and participate in job-seeking activities and practical placement with support.
Dedicated and experienced teachers will guide you through the program, which involves 300 hours of practical placement and 400 hours of vocational experience in a variety of fields from childcare, hospitality, building, IT, multimedia, retail,hairdressing and sport and recreation. This nationally recognised course can be completed part time over two years or full time over one year. Once complete, you can develop your skills further with Chisholm’s Certificate II in Work Education , a pre-apprenticeship or pre-vocational course.
Your current skills, knowledge and experience can help you get a qualification.
Find out about skills recognition and RPL for certificate to advanced diploma courses .
Find out about advanced standing for graduate certificate, graduate diploma and bachelor degree courses .
Applicants must be a minimum of 16 years of age at the time of course commencement and have a disability and/or special learning needs. Applicants are also required to complete an assessment for literacy and numeracy.
*Student tuition fees are correct at time of publishing and are subject to change given individual circumstances at enrolment. Please note: Fees will be subject to change if the course runs over two or more calendar years. Check to see if you are eligible for government-subsidised training . Training to eligible students is delivered with Victorian and Commonwealth funding. Students with a disability are encouraged to apply for this course using Skills First funding. **You are required to pay additional fees for materials and support services, not covered by your tuition fees. This may include things like learning resources, personal protective equipment/clothing, and vary depending on the course you study. Material fees are also subject to change given individual circumstances. Please note: You will also be required to pay the Student Services fee for each year of enrolment.
Payment plans
At Chisholm, you can spread your tuition costs over the year by making part payments via direct debit on a weekly, fortnightly or monthly basis. Payment plans are available for local students enrolling in certificate level courses only. Read more about payment plans .
Scholarships
Annual scholarships may be available to eligible students suffering financial hardship through the Caroline Chisholm Education Foundation. Find out more about the scholarships , which to date have supported more than 150 students with grants ranging from a few hundred dollars to a few thousand, depending on circumstance and the area of study.
Government-subsidised training
Check here to see if you are eligible for government-subsidised training . Training to eligible students is delivered with Victorian and Commonwealth funding. Students with a disability are encouraged to apply for this course using Skills First funding.
Please note: Students may be required to undertake an assessment of their literacy and numeracy as part of their application process.

Chisholm courses are subject to minimum and maximum group numbers. Courses may be cancelled or postponed if minimum numbers are not achieved by the start date of the course. Courses may close prior to the start date if the maximum numbers are reached. In that situation, eligible applicants will be offered a place in the next available intake.
- Add to shortlist
CALL 1300 244 746 TO SPEAK TO A COURSE ADVISOR
Or provide your details below and we’ll be in touch:
Best Global Universities for Engineering in Russia
These are the top universities in Russia for engineering, based on their reputation and research in the field. Read the methodology »
To unlock more data and access tools to help you get into your dream school, sign up for the U.S. News College Compass !
Here are the best global universities for engineering in Russia
Itmo university, tomsk state university, tomsk polytechnic university, lomonosov moscow state university, novosibirsk state university, saint petersburg state university, peter the great st. petersburg polytechnic university, moscow institute of physics & technology, national research nuclear university mephi (moscow engineering physics institute).
See the full rankings
- Clear Filters
- # 307 in Best Universities for Engineering (tie)
- # 696 in Best Global Universities (tie)
- # 364 in Best Universities for Engineering (tie)
- # 587 in Best Global Universities (tie)
- # 396 in Best Universities for Engineering (tie)
- # 879 in Best Global Universities (tie)
- # 632 in Best Universities for Engineering (tie)
- # 355 in Best Global Universities
- # 809 in Best Universities for Engineering (tie)
- # 579 in Best Global Universities (tie)
- # 847 in Best Universities for Engineering (tie)
- # 652 in Best Global Universities
- # 896 in Best Universities for Engineering (tie)
- # 679 in Best Global Universities (tie)
- # 902 in Best Universities for Engineering (tie)
- # 475 in Best Global Universities (tie)
- # 915 in Best Universities for Engineering (tie)
- # 483 in Best Global Universities (tie)
- Top Courses
- Online Degrees
- Find your New Career
- Join for Free
- Certificates >
- MasterTrack® Certificate >
Social Work: Practice, Policy and Research

In this 6-course program, you’ll build the skills and knowledge you’ll need to empower individuals, families, communities, and organizations to meet their needs and create positive change.
Enroll by April 29, 2024
Class starts the same day.
3-5 hours per week per class. Program duration alternates between 4 months and 6 months. See FAQs for more details.
In 4 installments of $500 or pay all at once to get 5% off the full tuition.
100% Online
+ Live session classes
No application necessary for the MasterTrack Certificate - enroll today.
#1 school for social work in the united states.
U.S. News & World Report’s top-ranked school of social work.
Accelerate your path to a master's degree from the University of Michigan
If you apply and are accepted into the University of Michigan Master of Social Work program and meet requirements, your MasterTrack® Certificate qualifies you to complete your degree in 45 credits instead of 60 credits.
Live sessions
Interact with School of Social Work instructors and peers to help build your professional network.

Program description
With this program you’ll gain a greater understanding of social work practice, the history and impact of policy on key social services, and the research that supports effective practice.
You’ll also have the chance to explore the social work profession from expert faculty. You’ll learn to apply key skills required to work with different stakeholders to promote positive changes and make a difference. Also, you’ll cover how to integrate social justice values into social change processes and actions as well as develop an understanding of the key knowledge bases and frameworks that social workers use to guide their work at the micro, mezzo, and macro levels of practice.
Watch the program trailer
Get inspired by this program trailer featuring faculty from the School of Social Work. Watch it today .

You can watch these videos to learn directly from University of Michigan faculty and admissions counselors about social work practice and program pathways .
Required background
No prerequisites are required. However, some human service experience is required if you are interested in pursuing a Master of Social Work degree at the University of Michigan.
Learn more about the MasterTrack curriculum from faculty and admissions counselors, discover the pathway to pursuing the full MSW program following the MasterTrack certificate, and gain insight into financial aid opportunities. Watch a past webinar recording!

Skills you will gain
- Social justice frameworks
- Role of social work in inter-professional practice
- Qualitative research methods
- Quantitative research methods
- Community organization
- Interpersonal, organizational, and community level practice methods
- National Association of Social Workers (NASW) Code of Ethics
6 courses in this 4-6 month program
Course 1 of 6
Social Work Practice: Advocating for Social Justice and Change
In this course, you will learn how social workers in the United States create change and support the resilience of individuals, families, and communities. You’ll have an opportunity to explore the social work profession, the different roles of social workers in a range of settings, the cross-cutting themes that guide social work practice, the history of social work, and current challenges.
Using a social justice lens, you’ll reflect on current challenges facing the lives of individuals, families, and communities, and examine ways to advocate for needed changes.
What you will learn
- Roles and skills of social workers
- How social workers engage in change efforts through core frameworks
- How different people, events, and policies have helped shape U.S. based social work over the past 100 years
- The connection between social work and social justice
- How to use a social justice lens
Course 2 of 6
Engaging Social Justice, Diversity, and Oppression in Social Work
In this course, you will develop a framework for engaging diversity and differences in social work practice, as well as advancing human rights and social and economic justice. Explore how societal power and diversity characterize and shape the human experience and are critical to the formation of social structures, cultural understandings, group and organizational processes, and identities.
Analyze how current experiences of privilege and oppression are shaped by historical forces, societal structures, social constructions, groups, interpersonal processes, and human understandings. You will also explore formulations of human rights, including positive rights and negative conditions that need to be eradicated.
- Intersectionality as a tool for analyzing complex social problems
- Social and cultural determinants of health
- How health disparities exist in communities
- Information related to housing inequality
- About crime and policing communities
- Current trends in policing
- Relevant environmental justice issues
- Information related to economic inequality
- Resources and activities for being an ally
- Information about implicit bias
Course 3 of 6
Essentials of Social Welfare Policy
In this course, you will explore current social welfare issues in the context of their history and the underlying rationale and values that support different approaches. Emphasis is placed on major fields of social work service such as income maintenance, health care, mental health, child welfare, corrections, and elderly services.
There are four main content areas for the course, beginning with the philosophic and practical basis for social welfare provisions. Your focus will then transition to the history of social work as a profession, as well as the emergence of specific policies and programs. Using this information, you will review critical analysis of current social welfare policies and programs in the U.S. and elsewhere. You will then focus on the understanding of theory, research, debates, and trends in social welfare.
- The importance of social welfare policy for social workers
- Fundamental components of policy: critical questions, themes, values and models
- Foundations of U.S social welfare policy and the role of non-governmental organizations and governments
- Financial influences on social policy
- How to identify potential solutions to poverty and growing inequality
- Social welfare policy applications in health and mental health
Course 4 of 6
Essentials of Interpersonal Practice
This course integrates content on multiculturalism, diversity, and social justice issues. You will examine social work values and ethics as well as issues of race, ethnicity, gender, sexual orientation, socio-economic status, age, religion, and ability as these relate to social work practice. You will build off of behavioral and social science theories to inform the practice concepts and skills presented.
During this module, you will learn about the transactional relationships between people and their social environments. You will learn social work practice methods to restore, maintain, and promote social functioning as it relates to individuals, families, and small groups.
- Context of social work practice with individuals, families, and small groups
- Social Work Code of Ethics and core mission
- Engagement skills and relationship building in interpersonal practice
- Social work core skills such as active listening, empathic responding, cultural humility
- Incorporating assessment tools into practice to better understand the issues and challenges of individuals and families
- Using evidence-informed practices and interventions to promote positive change
Interpersonal Practice Case Study
In this project you will approach cases requiring social work interpersonal practice and intervention.
By identifying issues, relationships, coping strategies, and resources you will learn how to spot the interrelated issues involved in social work case management, and you will be able to identify resources and strategies to apply to these situations.
Course 5 of 6
Essentials of Community and Organizational Practice
In this social science course, you will explore various methods, strategies, and skills within macro social work practice used to help identify and address needs on a larger scale. You will gain knowledge and skills in the areas of community organizing, management, and policy advocacy, and learn about the various roles social workers play within these areas.
This course will provide an appreciation of the historical and contemporary importance of these social work methods and the relevance of these methods for diverse populations and identities.
- Ethics, diversity, and inclusion in social work
- Recognizing when change is needed in communities and organizations
- The role of power in maintaining systems or changing them
- How to lead communities and organizations through ethical and responsible engagement
Course 6 of 6
Research Basics for Social Work Practice
In this course, you will begin to understand social work research through the critical examination of the methods and organization of the ever-expanding professional literature associated with social work practice.
This body of research is an essential source of knowledge to help you understand and solve complex social problems. However, utilizing this research effectively requires proper contextualization. In this course, you’ll learn to become an effective consumer of this professional literature by using the tools necessary to find and comprehend what the research does and, importantly, does not tell us.
- How to implementation of quantitative and qualitative research methods
- Search procedures to effectively find existing research
- The application of research to practice
Policy brief
Building upon all of the work throughout the course, you will create a policy brief about a topic of particular interest.
This project will teach you how to synthesize policy information into an informative and appealing brief used to argue for the effective use of policy recommendations.
Accelerate your path toward a master's degree from the University of Michigan
Enrolling in a MasterTrack® Certificate program means you can start learning job-relevant skills right away and give yourself a pathway to a full degree program.
MasterTrack® Certificate
Social Work: Practice, Policy and Research MasterTrack® Certificate accelerates your path towards:

Instructors
Frequently asked questions, what do social workers do .
Social workers help individuals, groups, and communities work together and solve problems. Social work is a rewarding and fulfilling career in a growing field. Social workers are in demand: Overall employment of social workers is projected to grow 12 percent from 2020 to 2030, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics.
How do I count my completion of this MasterTrack® towards the Master of Social Work program?
If you apply and are accepted into the full Master of Social Work program at the University of Michigan, your MasterTrack® Certificate reduces the credit hour requirement to complete your MSW from 60 to 45—the equivalent to a quarter of the program.
Prior to enrolling in the MasterTrack® Certificate, you are encouraged to complete the MasterTrack MSW Interest Form (including resume). Submission of the form will start the eligibility review process conducted by the School of Social Work's Office of Student Services. Submission of the form does not guarantee admission to the Master of Social Work program. If you have questions about the review process, or the program contact the School of Social Work via email at [email protected]. .
Students can potentially receive an MSW Program admissions decision prior to beginning the MasterTrack Certificate, if they prefer.
Please note, participation in the Online MSW has no impact on U.S. visa eligibility and cannot be used to satisfy U.S. visa requirements. Please review the University of Michigan's Distance Education Disclosures page for more information.
How can I get started?
The deadline to enroll in the next cohort can be found at the top of this page. Enroll before then and you will gain access to the onboarding course and any available materials right away.
You can also get started with this course and apply your progress toward the MasterTrack® Certificate: Social Work Practice: Advocating Social Justice and Change
Can I enroll in this MasterTrack Certificate Program if I live in a country outside the United States?
Learners located outside the United States are welcome to enroll in the MasterTrack Certificate program. However, some learners may be unable to enroll due to international restrictions set by United States Export Control Regulations. For more information, please visit the International Restriction Help Article .
Eligibility for the Online Master of Social Work (MSW) associated with this MasterTrack may be limited for learners located outside of the United States. Please contact the University of Michigan School of Social Work at [email protected] .
Please note, participation in the MasterTrack Certificate has no impact on U.S. visa eligibility and cannot be used to satisfy U.S. visa requirements.
How long does this program take to complete?
Program duration alternates between 4 months and 6 months to complete, allowing students to complete the courses in time to start in the Master of Social Work program at the University of Michigan.
During a 4 month program length, learners are required to complete 3 classes at a time.
During a 6 month program length, learners are required to complete 2 classes at a time.
What jobs can I get with skills in the field of social work?
Social work frameworks and methods are useful in a variety of careers. Building your social work skills can help you work toward advancing a career in many different fields, including:
- Community Organizing
- Criminal Justice Advocation
- Development
- Family Counseling
- Grant Writing
- Health Education
- Hospice Work
- Human Rights
- Mental Health Therapy
- Nonprofit Executive Roles
- Policy Analysis
- Program Evaluation
- Program Management
- School Social Work
- Substance Abuse Therapy
What percentage of the Master of Social Work is covered by this MasterTrack® program?
Completers of this MasterTrack® Certificate will be eligible to pursue an accelerated Master of Social Work program, which reduces the credit hour requirement for the MSW from 60 to 45, equivalent to completing a quarter of the program.
When will I have access to the lectures and assignments?
You will have access to your onboarding course and all available self-paced content for this MasterTrack® Certificate immediately after you enroll and pay. Once the first course officially begins, you’ll be able to ask questions from the course facilitators, get feedback on your projects, and work with other peers on group assignments.
What will I get if I pay for this program?
You will get access to all MasterTrack® Certificate courses. You will have access to content and live interactions developed by leading experts in the social work field. You'll be working with an elite network of peers towards your goals.
Can I take this program for free?
No. The MasterTrack® Certificate is available only to learners who have paid for the program.
What is the refund policy?
You will have 2 weeks after the start of the first course session to refund your payment.
Is financial aid available?
Financial assistance is not available at this time for MasterTrack® Certificates.
Is social work right for me?
Social work might be a good fit for you if you are empathetic, a problem solver, thrive on challenges, care deeply about social justice, relate well with others, see the big picture, and want to make a difference in the world. Read more about whether or not social work is right for you on the University of Michigan School of Social Work website .
Can I discuss more flexible options for the MasterTrack® enrollment?
Please reach out to the School of Social Work via email at [email protected] or visit the website for more information.
More questions? Visit the Learner Help Center.
Coursera does not grant academic credit; the decision to grant, accept, or recognize academic credit, and the process for awarding such credit, is at the sole discretion of the academic institutions offering the MasterTrack® Certificate program and/or other institutions that have determined that completion of the program may be worthy of academic credit. Completion of a MasterTrack® Certificate program does not guarantee admission into the full Master’s program referenced herein, or any other degree program.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
10 facts about today’s college graduates

Having a bachelor’s degree remains an important advantage in many sectors of the U.S. labor market. College graduates generally out-earn those who have not attended college, and they are more likely to be employed in the first place. At the same time, many Americans say they cannot afford to get a four-year degree – or that they just don’t want to.
Here are key facts about American college graduates.
This Pew Research Center analysis about U.S. college graduates relies on data from sources including the Census Bureau, the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the National Center for Education Statistics, the National Student Clearinghouse and the Federal Reserve Bank, as well as surveys conducted by the Center.
Everyone who took the Pew Research Center surveys cited is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Nearly four-in-ten Americans ages 25 and older have a bachelor’s degree, a share that has grown over the last decade. As of 2021, 37.9% of adults in this age group held a bachelor’s degree, including 14.3% who also obtained a graduate or professional degree, according to data from the Census Bureau’s Current Population Survey. That share is up 7.5 percentage points from 30.4% in 2011.
An additional 10.5% had an associate degree in 2021. About four-in-ten Americans ages 25 and older had a high school diploma with no further education (25.3%) or completed some college but didn’t have a degree (14.9%).
In a reversal, women are now more likely than men to graduate from college, according to the Current Population Survey . In 2021, 39% of women ages 25 and older had a bachelor’s degree or more education, compared with 37% of men in the same age range. The gap in college completion is even wider among adults ages 25 to 34: 46% of women in this age group have at least a bachelor’s degree, compared with 36% of men.
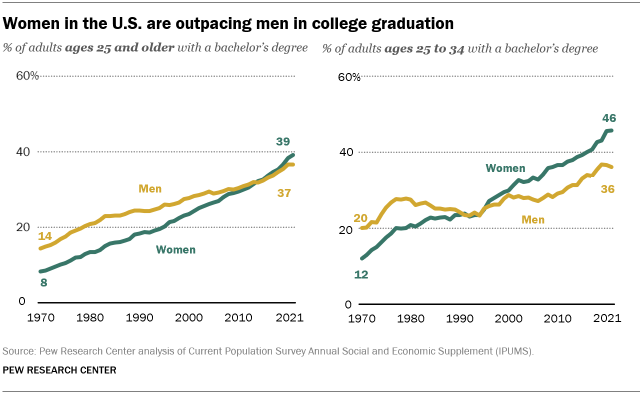
In an October 2021 Pew Research Center survey of Americans without a degree, 34% of men said a major reason why they have not received a four-year college degree is that they just didn’t want to. Only one-in-four women said the same. Men were also more likely to say a major reason they didn’t have a four-year degree is that they didn’t need more education for the job or career they wanted (26% of men said this vs. 20% of women).
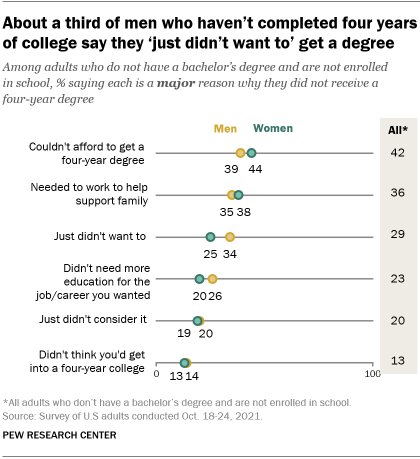
Women (44%) were more likely than men (39%) to say not being able to afford college was a major reason they don’t have a bachelor’s degree. Men and women were about equally likely to say a major impediment was needing to work to help support their family.
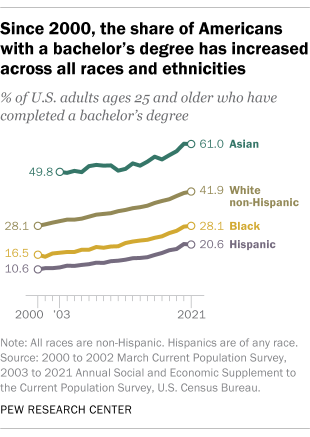
There are racial and ethnic differences in college graduation patterns, as well as in the reasons for not completing a degree. Among adults ages 25 and older, 61% of Asian Americans have a bachelor’s degree or more education, along with 42% of White adults, 28% of Black adults and 21% of Hispanic adults, according to 2021 Current Population Survey data. The share of bachelor’s degree holders in each group has increased since 2010. That year, 52% of Asian Americans had a four-year degree or more, compared with a third of White adults, 20% of Black adults and 14% of Hispanic adults.
The October 2021 Center survey found that among adults without a bachelor’s degree, Hispanic adults (52%) were more likely than those who are White (39%) or Black (41%) to say a major reason they didn’t graduate from a four-year college is that they couldn’t afford it. Hispanic and Black adults were more likely than their White counterparts to say needing to work to support their family was a major reason.
While a third of White adults said not wanting to go to school was a major reason they didn’t complete a four-year degree, smaller shares of Black (22%) and Hispanic (23%) adults said the same. White adults were also more likely to cite not needing more education for the job or career they wanted. (There weren’t enough Asian adults without a bachelor’s degree in the sample to analyze separately.)
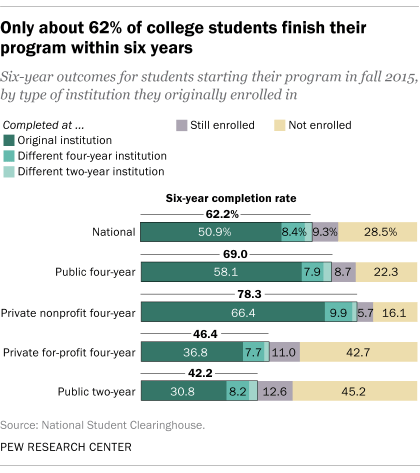
Only 62% of students who start a degree or certificate program finish their program within six years, according to the most recent data from the National Student Clearinghouse , a nonprofit verification and research organization that tracked first-time college students who enrolled in fall 2015 with the intent of pursuing a degree or certificate. The degree completion rate for this group was highest among students who started at four-year, private, nonprofit schools (78.3%), and lowest among those who started at two-year public institutions (42.2%).
Business is the most commonly held bachelor’s degree, followed by health professions. According to the National Center for Education Statistics , about a fifth (19%) of the roughly 2 million bachelor’s degrees conferred in 2019-20 were in business. Health professions and related programs were the second most-popular field, making up 12.6% of degrees conferred that year. Business has been the single most common major since 1980-81; before that, education led the way.
The least common bachelor’s degrees in 2019-20 were in military technologies and applied sciences (1,156 degrees conferred in 2019-20), library science (118), and precision production (39).
There is a growing earnings gap between young college graduates and their counterparts without degrees. In 2021, full-time workers ages 22 to 27 who held a bachelor’s degree, but no further education, made a median annual wage of $52,000, compared with $30,000 for full-time workers of the same age with a high school diploma and no degree, according to data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics. This gap has widened over time. Young bachelor’s degree holders earned a median annual wage of $48,481 in 1990, compared with $35,257 for full-time workers ages 22 to 27 with a high school diploma.
The unemployment rate is lower for college graduates than for workers without a bachelor’s degree, and that gap widened as a result of the coronavirus pandemic. In February 2020, just before the COVID-19 outbreak began in the U.S., only 1.9% of college graduates ages 25 and older were unemployed, compared with 3.1% of workers who completed some college but not a four-year degree, and 3.7% of workers with only a high school diploma. By June 2020, after the pandemic hit, 6.8% of college grads, 10.8% of workers with some college, and 12.2% of high school grads were unemployed.
By March 2022, the unemployment rate had nearly returned to pre-pandemic levels for college graduates (2%) while dropping to 3% among those with some college education but no four-year degree, and 4% among those with only a high school diploma.
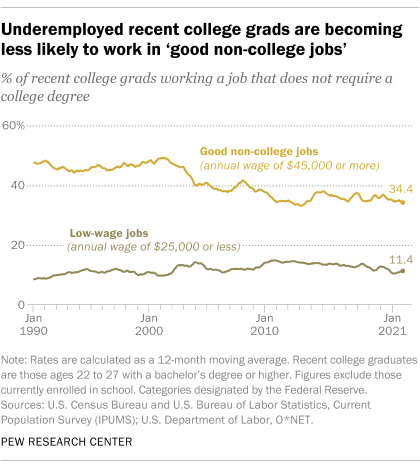
Recent college graduates are more likely than graduates overall to be underemployed – that is, working in jobs that typically do not require a college degree, according to an analysis of Census Bureau and BLS data by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York . As of December 2021, 41% of college graduates ages 22 to 27 were underemployed, compared with 34% among all college graduates. The underemployment rates for recent college grads rose in 2020 as the COVID-19 outbreak strained the job market, but have since returned to pre-pandemic levels.
As of the end of 2021, only 34% of underemployed graduates ages 22 to 27 worked what the Fed defines as “good non-college jobs” – those paying at least $45,000 a year – down from around half in the 1990s. The share of underemployed graduates ages 22 to 27 in low-wage jobs – those earning less than $25,000 annually – rose from about 9% in 1990 to 11% last year.
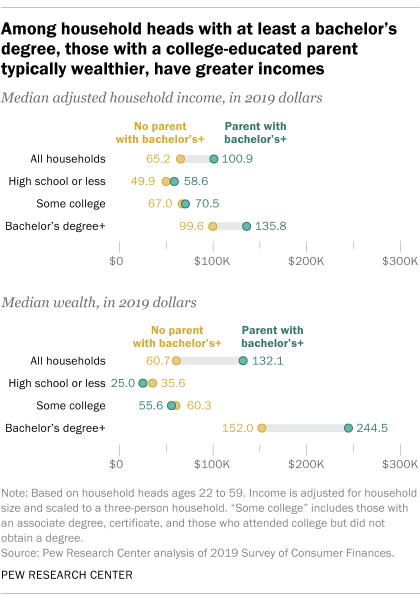
When it comes to income and wealth accumulation, first-generation college graduates lag substantially behind those with college-educated parents, according to a May 2021 Pew Research Center analysis . Households headed by a first-generation college graduate – that is, someone who has completed at least a bachelor’s degree but does not have a parent with a college degree – had a median annual income of $99,600 in 2019, compared with $135,800 for households headed by those with at least one parent who graduated from college. The median wealth of households headed by first-generation college graduates ($152,000) also trailed that of households headed by someone with a parent who graduated from college ($244,500). The higher household income of the latter facilitates saving and wealth accumulation.
The gap also reflects differences in how individuals finance their education. Second-generation college graduates tend to come from more affluent families , while first-generation college graduates are more likely to incur education debt than those with a college-educated parent.
Most Americans with college degrees see value in their experience. In the Center’s October 2021 survey , majorities of graduates said their college education was extremely or very useful when it came to helping them grow personally and intellectually (79%), opening doors to job opportunities (70%) and developing specific skills and knowledge that could be used in the workplace (65%).
Younger college graduates were less likely than older ones to see value in their college education. For example, only a third of college graduates younger than 50 said their college experience was extremely useful in helping them develop skills and knowledge that could be used in the workplace. Among college graduates ages 50 and older, 45% said this.
- Higher Education

About 1 in 4 U.S. teachers say their school went into a gun-related lockdown in the last school year
About half of americans say public k-12 education is going in the wrong direction, what public k-12 teachers want americans to know about teaching, what’s it like to be a teacher in america today, race and lgbtq issues in k-12 schools, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
100 Best universities for Mechanical Engineering in Russia
Updated: February 29, 2024
- Art & Design
- Computer Science
- Engineering
- Environmental Science
- Liberal Arts & Social Sciences
- Mathematics
Below is a list of best universities in Russia ranked based on their research performance in Mechanical Engineering. A graph of 714K citations received by 136K academic papers made by 158 universities in Russia was used to calculate publications' ratings, which then were adjusted for release dates and added to final scores.
We don't distinguish between undergraduate and graduate programs nor do we adjust for current majors offered. You can find information about granted degrees on a university page but always double-check with the university website.
1. Moscow State University
For Mechanical Engineering

2. Tomsk State University

3. St. Petersburg State University

4. Bauman Moscow State Technical University

5. Ufa State Aviation Technical University


6. Peter the Great St.Petersburg Polytechnic University

7. Tomsk Polytechnic University

8. Ural Federal University

9. South Ural State University

10. National Research University Higher School of Economics

11. Moscow Aviation Institute

12. Novosibirsk State University

13. ITMO University

14. N.R.U. Moscow Power Engineering Institute

15. National Research Nuclear University MEPI

16. Kazan Federal University

17. National University of Science and Technology "MISIS"

18. Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology

19. Samara National Research University

20. Moscow State Technological University "Stankin"

21. Novosibirsk State Technical University

22. RUDN University

23. Southern Federal University

24. Saratov State University

25. Ufa State Petroleum Technological University

26. Samara State Technical University

27. Siberian Federal University

28. Kazan National Research Technical University named after A.N. Tupolev - KAI

29. Perm State Technical University

30. Omsk State Technical University

31. Saint Petersburg State Electrotechnical University

32. Moscow Polytech

33. Saint-Petersburg Mining University

34. Magnitogorsk State Technical University

35. Saratov State Technical University

36. Moscow State University of Railway Engineering

37. Lobachevsky State University of Nizhni Novgorod

38. Nizhny Novgorod State Technical University

39. Tula State University

40. Belgorod State Technological University

41. Far Eastern Federal University

42. Novgorod State University
43. belgorod state university.

44. Finance Academy under the Government of the Russian Federation

45. Moscow Medical Academy

46. Kazan State Technological University

47. Russian State University of Oil and Gas
48. siberian state aerospace university.

49. Tambov State Technical University

50. Voronezh State University

51. Siberian State Industrial University

52. Saint Petersburg State Institute of Technology

53. Kalashnikov Izhevsk State Technical University

54. St. Petersburg State University of Architecture and Civil Engineering

55. Mendeleev University of Chemical Technology of Russia

56. Murmansk State Technical University

57. South-Western State University

58. Ogarev Mordovia State University

59. Tomsk State University of Control Systems and Radioelectronics
60. south-russian state university of economics and service.

61. Perm State University

62. Kuzbass State Technical University

63. Russian National Research Medical University

64. Plekhanov Russian University of Economics

65. Ulyanovsk State Technical University

66. Ulyanovsk State University

67. Penza State University

68. Kuban State University of Technology

69. Polzunov Altai State Technical University

70. Chelyabinsk State University

71. Yaroslavl State University

72. University of Tyumen
73. National Research University of Electronic Technology

74. Leningrad State University

75. Moscow State Pedagogical University

76. Udmurt State University

77. Irkutsk State University

78. North-Eastern Federal University

79. Bashkir State University

80. Russian Presidential Academy of National Economy and Public Administration

81. Kuban State University

82. Kuban State Agricultural University

83. St. Petersburg State University of Aerospace Instrumentation

84. Kemerovo State University

85. Immanuel Kant Baltic Federal University

86. Orenburg State University
87. Baltic State Technical University "Voenmeh"

88. Tomsk State University of Architecture and Building

89. Chuvash State University
90. ivanovo state power university.

91. Irkutsk National Research Technical University

92. Orel State University

93. State University of Management

94. Tomsk State Pedagogical University

95. Volgograd State University

96. Petrozavodsk State University

97. Tver State University

98. Northern Arctic Federal University

99. Omsk State Transport University

100. Kaliningrad State Technical University

The best cities to study Mechanical Engineering in Russia based on the number of universities and their ranks are Moscow , Tomsk , Saint Petersburg , and Ufa .
Engineering subfields in Russia

Cincinnati Business Courier: UC, CPS partner on College Innovation Pathway
Launch uc makes college course credits available for cincinnati public school students.

The University of Cincinnati has partnered with Cincinnati Public Schools (CPS) to broaden access to higher education for CPS students by creating the College Innovation Pathway. This College Credit Plus program will enable students to earn an associate degree at the same time as their high school diploma, saving money and earning credits toward their future academic goals.
“This program creates brighter futures for CPS students,” explains Jack Miner, vice provost for enrollment management at University of Cincinnati. “Not only does it lay a foundation for a student to pursue a 4-year degree saving as much as $60,000 in tuition and expenses, but it also provides an alternative for students who do not want to attend college immediately after graduation. Earning an associate degree in conjunction with their high school diploma gives these students more job options, and higher earning potential.”
The College Innovation Pathway was recently featured in the Cincinnati Business Courier .
The initiative, available to students at Shroder High School, will allow participants the opportunity to seamlessly transition into college-level courses, enrolling through the University of Cincinnati, while still in high school. Through the program, students will have free access to a comprehensive curriculum and diverse choices to tailor their experience to their future interests. Launch UC, an innovative early enrollment program charged with developing accessible and equitable pathways for high school students to UC, is helping move this initiative forward.
“The College Innovation Pathway highlights our efforts to transform high school options by expanding access to early college programming and career pathways,” CPS Superintendent and CEO Iranetta Rayborn Wright said. “By offering a seamless transition from high school to higher education, we are empowering our students to unlock their potential while also having affordable access to a degree. This initiative underscores our partnership with UC and our continued vision to create equitable opportunities for our students.”
The program, beginning for students in ninth grade, features a first-year experience course taught by a UC faculty member and CPS teacher, equipping students with study skills, access to resources, time management, collegiate-level writing and communication. Students in the cohort will work alongside their classmates to learn how to be a successful college student. Through the pathway, students will also have the opportunity to take classes at all three of UC’s campuses.
Incoming freshmen at Shroder High School will be eligible to apply to the program, launching in the 2024- 25 school year. Upon completion of the program, students will earn an associate degree and can further their education with a bachelor’s degree at UC, graduating in half the time.
Read the full Cincinnati Business Courier story online .
Learn more about Launch UC online .
Featured top student image taken by Andrew Higley/UC Marketing + Communications.
- College bound
- In The News
- Innovation Agenda
- Student Experience
Related Stories
April 22, 2024
The University of Cincinnati has partnered with Cincinnati Public Schools (CPS) to broaden access to higher education for CPS students by creating the College Innovation Pathway. It allows high school students to earn credits for an associate degree while completing their high school diploma. Launch UC is helping move this initiative forward.
The Cincinnati Enquirer: UC’s Early IT program helping to curb talent shortage
September 14, 2021
The University of Cincinnati's Early Information Technology program is preparing students for in-demand jobs and helping them save money by graduating early, the Cincinnati Enquirer reported.
Yahoo: Future University of Cincinnati Bearcats get surprised at school and at home
January 28, 2022
News media highlight UC's Decision Day records as students get surprised with admission and scholarships.
- International
- Today’s Paper
- Premium Stories
- Express Shorts
- Health & Wellness
- Board Exam Results
Earth Day 2024: Here’s a list of ‘green skills’ courses you can pursue to do your bit for the environment
From an mtech in sustainable engineering offered by iit hyderabad to wwf’s pg diploma in environmental law, there are several courses on offer that enable people to understand and work for green causes.
As Earth Day 2024 is observed on Monday, April 22, it becomes pertinent to note that the need for green or sustainable learning has only grown over the years. LinkedIn’s Global Green Skills Report 2023 shows that the demand for people with ‘green skills’ has also seen a rapid increase.
If you are someone who wants to do your bit for environmental causes while earning well, below are some of the courses you can apply for:

Master’s in Climate Finance and Sustainability, IIT Kanpur
Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur has introduced an online Master’s course on Climate Finance and Sustainability. A GATE score is not required to apply for the course. The selection of the candidate will be based on academic and professional background followed by a test and an interview.
The course is designed to provide training and exposure on carbon management, ESG (environmental, social, and governance) aspects, and green finance in a one-year, fully online programme which includes a flexible curriculum, self-paced learning opportunities, live and interactive sessions, and practical learning. Students will get an opportunity to complete the programme over a period of one to three years. They can also get a waiver of up to 60 credits for higher education from the institute.
MTech in Sustainable Engineering/Energy Science and Tech, IIT Hyderabad

Indian Institute of Technology Hyderabad is offering three distinct inter-disciplinary two-year MTech programmes in sustainable engineering, energy science and technology, and e-waste resource engineering and management. The course is under IIT’s Greenko School of Sustainability.
The sustainable engineering course will include various topics including infrastructure, energy systems, and industrial processes. A GATE score is mandatory for the course. Candidates will be selected through the online COAP (Common Offer Acceptance Portal) process. Selected applicants will be informed via email.
Pollution Monitoring, Environment Ministry
The course on Pollution Monitoring under the Green Skill Development Programme of the Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change will help students gain a comprehensive understanding of all aspects of air, water, and soil pollution, its management and control, while imparting basic skills. It will also cover the science of the atmosphere, including its physics and chemistry, which is important to understand air pollution and its dispersal.
Environmental Engineering, IIT Kanpur
Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur is offering a course on environmental engineering. Students interested should have a bachelor’s degree in civil, environmental, mechanical, chemical, and agricultural engineering or a related branch.
The subject includes knowledge of various topics, water and waste treatment, aerosol properties, regional climate change, and modeling and simulation of environmental systems, among others. Applicants with civil, chemical, and environmental engineering background can get direct admission based on GATE scores, while for others GATE scores are mandatory along with a written test and interview.
PG Diploma in Environmental Law and Policy, WWF
World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) India, is offering a PG Diploma course in environmental law and policy in partnership with National Law University, Delhi (NLUD). The one-year course will cover green law issues worldwide, particularly in the Indian context.
The course is available for law graduates and professionals working in the field of environment to enrich their understanding of the issues, institutions, and initiatives in the field of environmental law and policy. Students will also get hands-on practical training.
Besides the above courses, magazines like ‘Towards Responsible Use of Plastics’ of the Centre for Environment Education aim to inculcate behavioural changes among students towards the responsible use of plastics.
- IIT Hyderabad

The BSEAP is set to announce the AP SSC results 2024 today at 11 M. Over 6.3 lakh students appeared for the exam this year, which was conducted from March 8 to 30. Students can check their scorecards on the official websites or through the direct link provided. Last year, the overall passing percentage was 72.26%.
- Donald Trump Trial Live Updates: Former US president returns to court for opening statements in hush money case 14 mins ago
- RR vs MI Live Score, IPL 2024: MI 20/3 (3.1 overs); Rohit Sharma, Ishan Kishan, Suryakumar Yadav fall early 17 mins ago
- JEE Mains 2024 Live Updates: Session 2 result expected by tomorrow, says NTA, latest news 2 hours ago
- TS Inter Results 2024 Live Updates: TSBIE intermediate 1st, 2nd year results date and time out 2 hours ago

Best of Express

Buzzing Now

Apr 22: Latest News
- 01 Iveco chief Marx quits to become CEO at CNH Industrial
- 02 PBKS vs GT, what caught our eye: Prabhsimran fills in at the start, Harpreet never gets going; Punjab flounder as Ashutosh-Shashank can’t rescue one more time
- 03 SI returning from kin’s funeral dies after his car rams road divider
- 04 Ecuadorians head to polls to toughen fight against gangs behind wave of violence
- 05 Chess Candidates 2024 Live Updates: Gukesh makes history by becoming youngest-ever World Championship contender
- Elections 2024
- Political Pulse
- Entertainment
- Movie Review
- Newsletters
- Gold Rate Today
- Silver Rate Today
- Petrol Rate Today
- Diesel Rate Today
- Web Stories

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Affordable online diplomas & career training programs. Ashworth College online diplomas can help you stand out from the crowd, gain employer-demanded skills, and make tangible progress toward your professional goals. Follow your calling and take your first steps into online career training today!
Professional Certificates on Coursera help you get job-ready for an in-demand career field in less than a year. Earn a career credential, apply your knowledge to hands-on projects that showcase your skills for employers, and get access to job search resources. Many programs also provide a pathway to an industry-recognized certification.
Diploma. An academic program generally of 30 to 72 credits intended to provide students with skills leading directly to a specific job. Associate Degree. An award that normally requires at least two but less than four years of full-time college work. There are different types of associate degrees with varying transferability. Bachelor's Degree ...
Call 1-800-275-4410 (10AM - 6:30PM ET) Request Info Enroll Now. *Start for $20 offer applies to select programs. From online degree programs and professional certification courses to our high school diploma program, start your education here.
Alison offers hundreds of free online diploma programs in categories such as Health, IT, Business and more. Start your free online diploma today. ... Explore Free Online Courses With Diplomas . Alisons free online diploma programs provide comprehensive training across a variety of industries, fields and careers. ...
Why Choose an Online Diploma Getting a quality education is the first step to a building a rewarding career, and Bryant & Stratton College diploma programs offer a reliable and accessible means of getting started on a solid, career-focused education. ... Getting qualified for work in your field more quickly via an online diploma program can ...
Benefit from master's degree learning that can count as credit With MasterTrack Certificates, portions of Master's programs have been split into online modules, so you can earn a high quality university-issued career credential at a breakthrough price in a flexible, interactive format. Benefit from a deeply engaging learning experience with real-world projects and feedback from expert ...
Here are the types of online certificate programs you'll find on edX: Professional Certificates: curated series of self-paced courses that can provide a pathway to your next milestone. Build comprehensive, career-relevant skills in high-demand fields in 2-18 months. Executive Education: instructor-led, cohort-based courses that hone ...
Take the next step toward your personal and professional goals with Coursera. Join now to receive personalized recommendations from the full Coursera catalog. Learn new job skills in online courses from industry leaders like Google, IBM, & Meta. Advance your career with top degrees from Michigan, Penn, Imperial & more.
This story was originally published in Issues in Science and Technology on March 9, 2021. Developing large-scale workforce education programs that enable workers to advance or change industries will not only reduce income inequality, but also support domestic innovation. The American dream promised that if you worked hard, you could move up ...
The Google Career Certificate program is an online training program that offers professional certificates in fast-growing, high-demand technology fields. The program is designed by Google and taught by experts in the areas of IT, user experience design, project management, and more, and combines skills training with hands-on practice.
Academic Progression Pathways for Work-Study Diploma (WSDip) Graduates. Upon fulfilling specific admission requirements, WSDip graduates are eligible to apply for: Full-time or Part-time Degree programmes at Nanyang Technological University (NTU), National University of Singapore (NUS), Singapore Institute of Technology (SIT), Singapore ...
Explore how online social work courses can help you achieve your personal and professional goals and begin your learning journey today with edX. We've added 500+ learning opportunities to create one of the world's most comprehensive free-to-degree online learning platforms. Explore social work courses and more.
Prepare for advanced study and move up in your industry with graduate education offered through Stanford Online. These rigorous credit-bearing, graduate-level courses are broadcast from the Stanford classroom, offering a flexible format for working professionals. You can take graduate courses, enroll in a graduate certificate program, or earn ...
Academic diplomas are commonly pursued in high schools and colleges, preparing students for diverse academic pursuits and careers requiring a strong academic background. Programs usually last 2 years, and credits may be transferable to a bachelor's degree. Examples of Academic Diplomas are: Diploma in Liberal Arts.
Time requirements. One of the biggest differences between a certificate, degree and diploma is the time it takes to complete each. A certificate typically takes between a few months to a few years to complete and is often done while working toward a degree. Sometimes, a certificate can also be a standalone option that's faster to complete than ...
World class Innovative Virtual Education and Virtual Labs Environment at an Affordable fee (Learn Anywhere & Any Time). Learn entire course from IIT's & IIS's professors in online. Week end face to face classes will be delivered by highly qualified faculty. Practical works and on job training will be carry out on campus and Industries.
The Certificate I in Work Education will provide you with a broad range of practical experience and an understanding of basic workplace expectations. During the course you'll learn how to work and communicate effectively in the workplace, participate in OHS processes, operate a personal computer, develop a vocational learning plan, apply ...
The skills you'll develop in this online BSW. In this program, you'll take courses sequentially, allowing you to build a foundation in social work concepts and apply them in practice. The curriculum is designed to build your abilities as a social work generalist. Key areas of learning include advocacy, consultation and education, as well as ...
Germany. India. Italy. Japan. Netherlands. See the US News rankings for Engineering among the top universities in Russia. Compare the academic programs at the world's best universities.
This MasterTrack® Certificate reduces the credit hour requirement for the Master of Social Work from 60 to 45 - the equivalent to completing a quarter of the program. Upon successful completion of your MasterTrack® program, you will receive an official University of Michigan certificate, regardless of whether you elect to enroll in the full ...
47.7% have completed secondary education (the full 11-year course); 26.5% have completed middle school (9 years) and 8.1% have elementary education (at least 4 years). The highest rates of tertiary education (24.7%) are recorded among women aged 35 to 39 years (compared to 19.5% for men of the same age bracket).
An additional 10.5% had an associate degree in 2021. About four-in-ten Americans ages 25 and older had a high school diploma with no further education (25.3%) or completed some college but didn't have a degree (14.9%). In a reversal, women are now more likely than men to graduate from college, according to the Current Population Survey. In ...
Below is a list of best universities in Russia ranked based on their research performance in Mechanical Engineering. A graph of 714K citations received by 136K academic papers made by 158 universities in Russia was used to calculate publications' ratings, which then were adjusted for release dates and added to final scores.
The University of Cincinnati has partnered with Cincinnati Public Schools (CPS) to broaden access to higher education for CPS students by creating the College Innovation Pathway. It allows high school students to earn credits for an associate degree while completing their high school diploma. Launch UC is helping move this initiative forward.
1 Mechanical Engineering Bachelor's in Russia. Spacecraft Engineering. Moscow Aviation Institute. This page shows a selection of the available Bachelors programmes in Russia. If you're interested in studying a Mechanical Engineering degree in Russia you can view all 1 Bachelors programmes.
The course is designed to provide training and exposure on carbon management, ESG (environmental, social, and governance) aspects, and green finance in a one-year, fully online programme which includes a flexible curriculum, self-paced learning opportunities, live and interactive sessions, and practical learning.